 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1706586
飛機用LRU的全球市場:2025年~2035年Global Aircraft LRU Market 2025-2035 |
||||||
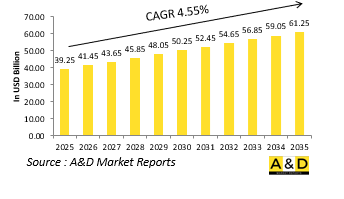
2025 年全球飛機 LRU 市場規模估計為 392.5 億美元,預計到 2035 年將增長到 612.5 億美元,在 2025-2035 年預測期內的複合年增長率 (CAGR) 為 4.55%。
飛機 LRU 市場簡介:
LRU(線路可更換單元)是模組化組件,可在操作層面快速更換,以保持飛機可用性並減少停機時間。在軍事航空中,LRU 是可維護性和準備性的關鍵,允許機組人員和維護團隊更換故障的子系統 - 從雷達模組和航空電子設備箱到液壓執行器和通訊設備 - 而無需進行大規模拆卸或倉庫級支援。 LRU 對於軍用飛機的作戰效率至關重要,因為軍用飛機必須在通常惡劣且不可預測的環境中保持戰鬥準備。 LRU 的使用使組織單位能夠在現場進行快速維修或更換,支援 "兩階段維護:組織和倉庫" 的概念。這種能力顯著提高了出動率並最大限度地減少了任務中斷。隨著軍用飛機平台變得越來越先進和系統集成,對基於 LRU 的設計的依賴也越來越強。 LRU 不僅簡化了維護物流,而且還使多種飛機類型的組件標準化,從而使軍方能夠減少庫存開銷、簡化培訓並促進更快的升級。在現代戰鬥機、運輸機、直升機和無人系統中,LRU是永續性、生命週期成本管理和戰備的隱藏推動因素。
科技對飛機 LRU 市場的影響:
技術的進步正在極大地改變飛機 LRU 的形式、功能和性能。現代 LRU 不再是簡單可替換的“黑盒子”,在航空電子、數位化和模組化系統架構趨勢的推動下,它變得更加聰明、更輕巧、更加整合。小型化和增強的處理能力使得更多的功能能夠被裝入更小的空間。這對於現代軍用飛機來說至關重要,因為空間和重量都非常寶貴。現今的 LRU 通常包含先進的微處理器、容錯電路和整合診斷系統,使它們能夠監控自身的健康狀況並在故障發生之前預測故障。
模組化開放系統架構(MOSA)也產生了重大影響。許多軍隊,特別是美國國防部,正在推行航空電子設備和電子產品的開放標準。這種轉變意味著 LRU 在設計時考慮了互通性和未來的可升級性。 VITA 標準和 OpenVPX 等標準化介面可實現跨多個平台和供應商的即插即用,從而顯著降低系統生命週期成本並簡化物流鏈。網路安全已成為另一個主要關注點。由於 LRU 通常處理關鍵的飛行、目標和通訊數據,因此確保其免受網路威脅的安全至關重要。這就是為什麼 LRU 韌體和硬體包括內建加密、安全啟動機制和身份驗證協定。可信任平台模組 (TPM) 和入侵偵測感測器等技術正在成為任務關鍵型 LRU 的標準。
此外,數位孿生和擴增實境 (AR) 工具開始與 LRU 結合使用。這些技術透過為技術人員提供虛擬覆蓋來模擬虛擬環境中的 LRU 操作,從而增強了培訓和操作規劃。此外,與物流系統和數位維護記錄的整合可以實現無縫資產追蹤和配置管理。
飛機 LRU 市場的關鍵推動因素:
全球飛機 LRU 市場的成長和發展受到營運、物流和戰略因素的共同推動。主要推動因素之一是軍用飛機系統日益複雜。第五代戰鬥機、隱形轟炸機和多用途運輸機現在依賴數千個相互連接的電子和機械部件。如果沒有模組化 LRU,維護這樣的平台將會非常耗時、低效率且成本高昂。對作戰準備的要求也是一個強大的驅動力。世界各國的軍隊都優先考慮飛機的高可用性和任務能力。 LRU 可實現任務之間的快速週轉時間,減少前沿部署或高節奏作戰期間的飛機停機時間。這對於遠徵軍和艦載航空聯隊來說尤其重要。此外,對飛機生命週期成本管理的日益重視也推動了 LRU 使用量的增加。軍方面臨著越來越嚴格的預算審查,必須延長老化平台的使用壽命,同時整合新技術。 LRU 有助於實現增量升級,而無需更換整個系統。例如,偵察機的傳統雷達處理器可以用更新、功能更強大的裝置替換,同時仍與原始的雷達陣列介接。
另一個關鍵推動因素是互通性和聯合力量。隨著多國軍事聯盟變得越來越普遍,擁有標準化、易於互換的零件有助於保持聯軍之間的兼容性。共享 LRU 平台和開放式架構使盟友能夠在聯合任務和維和行動期間相互支援。此外,供應鏈彈性和本地製造目標正在鼓勵各國投資國內 LRU 製造能力。這減少了對海外供應商的依賴,實現了快速定制,並使國防承包商能夠靈活地適應不斷變化的任務需求。許多國家正在將遠程武器系統發展納入其更廣泛的國防工業戰略,以實現自力更生和自主創新。
飛機LRU市場的區域趨勢:
飛機 LRU 市場的地理趨勢反映了每個地區的戰略立場、採購理念和國內工業基礎。在北美,尤其是美國,飛機LRU市場高度成熟且由技術驅動。 F-35 Lightning II、B-21 Raider 和下一代空中優勢 (NGAD) 等項目都嚴重依賴以 LRU 為中心的設計,以促進快速零件更換和系統升級。美國軍方推動模組化開放系統和數位化工程,為全球樹立了標準,LRU 的設計旨在實現長壽命和快速整合人工智慧、電子戰和量子通訊等下一代功能。
在歐洲,聯合平台開發和 LRU 標準化受到大力推動,尤其是在法國、德國和西班牙參與的 FCAS(未來作戰航空系統)等項目中。歐洲國家擴大採用模組化方法來製造飛機系統,以促進共同開發並維持對美國供應商的獨立性。空中巴士公司、萊昂納多公司和泰雷茲公司正在領導開發基於開放標準、專為北約互通性而設計的 LRU 系統。在亞太地區,地緣政治緊張局勢加劇以及對自主防禦的推動正在刺激遠程武器系統的發展。中國、印度、韓國和日本等國家正在透過進口和國產平台擴大其軍事航空能力。中國的殲-20和印度的光輝戰鬥機採用LRU框架,可實現可擴展的升級和維護。該地區也出現了能夠生產導航、火控和任務管理系統的本土 LRU 供應商的崛起。
主要飛機 LRU 計畫
印度空軍總部(Vayu Bhawan)工程 B 局(技術)代表印度國防部,邀請知名印度公司表達意向(EoI),為印度空軍的 KIRAN MK-I/IA 機隊採購四 (4) 個線路可更換單元 (LRU)。符合條件的公司必須位於印度,並擁有該專案所需的技術專長、財務能力、基礎設施和相關經驗。工作範圍包括在適用的情況下獲得適航認證,並確保在規定的期限內交付。
本報告提供全球飛機用LRU市場相關調查,彙整10年的各分類市場預測,技術趨勢,機會分析,企業簡介,各國資料等資訊。
目錄
飛機用LRU市場報告定義
飛機用LRU市場區隔
各平台
各地區
各類型
未來 10 年飛機 LRU 市場分析
本章透過十年的飛機 LRU 市場分析,詳細概述了飛機 LRU 市場的成長、變化趨勢、技術採用概述和整體市場吸引力。
飛機 LRU 市場的市場技術
本部分涵蓋預計將影響該市場的十大技術以及這些技術可能對整個市場產生的影響。
全球飛機 LRU 市場預測
針對上述細分市場,詳細介紹了該市場 10 年的飛機 LRU 市場預測。
飛機 LRU 市場趨勢及各地區預測
本部分涵蓋區域飛機 LRU 市場趨勢、推動因素、阻礙因素、課題以及政治、經濟、社會和技術方面。它還提供了詳細的區域市場預測和情境分析。區域分析的最後階段包括主要公司概況、供應商格局和公司基準測試。目前市場規模是根據正常業務情境估算的。
北美
促進因素,阻礙因素,課題
PEST
市場預測與情勢分析
主要企業
供應商階層的形勢
企業基準
歐洲
中東
亞太地區
南美
飛機LRU市場國家分析
本章重點介紹該市場的主要防禦計劃,並介紹該市場的最新新聞和專利。它還提供國家級的 10 年市場預測和情境分析。
美國
防衛計劃
最新消息
專利
這個市場上目前技術成熟度
市場預測與情勢分析
加拿大
義大利
法國
德國
荷蘭
比利時
西班牙
瑞典
希臘
澳洲
南非
印度
中國
俄羅斯
韓國
日本
馬來西亞
新加坡
巴西
飛機用LRU市場機會矩陣
飛機用LRU市場報告相關專家的意見
結論
關於航空·國防市場報告
The Global Aircraft LRU market is estimated at USD 39.25 billion in 2025, projected to grow to USD 61.25 billion by 2035 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.55% over the forecast period 2025-2035.

Introduction to Aircraft LRU Market:
Line Replaceable Units (LRUs) are modular components that can be quickly replaced at the operational level to maintain aircraft availability and reduce downtime. In military aviation, LRUs are a cornerstone of maintainability and readiness, allowing flight crews and maintenance teams to swap out faulty subsystems-ranging from radar modules and avionics boxes to hydraulic actuators and communication devices-without requiring extensive disassembly or depot-level support. LRUs are essential to the operational efficiency of military aircraft, which must remain combat-ready in often austere and unpredictable environments. Their use supports the "two-level maintenance" concept-organizational and depot level-by allowing organizational units to perform rapid repairs and replacements on-site. This capability significantly increases sortie generation rates and minimizes mission interruptions. As military aircraft platforms become more advanced and system-integrated, the reliance on LRU-based design has grown. Not only do they simplify maintenance logistics, but LRUs also standardize components across multiple aircraft types, helping militaries reduce inventory overhead, streamline training, and facilitate faster upgrades. In modern fighter jets, transport aircraft, helicopters, and unmanned systems, LRUs are the hidden enablers of sustainability, lifecycle cost management, and combat readiness.
Technology Impact in Aircraft LRU Market:
Advancements in technology are dramatically reshaping the form, function, and performance of military aircraft LRUs. Modern LRUs are no longer just replaceable "black boxes"; they are becoming smarter, lighter, and more integrated, aligning with trends in avionics, digitalization, and modular system architecture. Miniaturization and increased processing power allow more functionality to be packed into a smaller footprint. This is crucial for modern military aircraft, where space and weight are at a premium. Today's LRUs often contain advanced microprocessors, fault-tolerant circuitry, and integrated diagnostics systems, allowing them to monitor their own health and predict failures before they occur-an essential element of predictive maintenance.
Modular Open Systems Architecture (MOSA) is having a significant impact as well. Many militaries, particularly the U.S. Department of Defense, are pushing for open standards in avionics and electronics. This shift means LRUs are being designed with interoperability and future upgradeability in mind. Standardized interfaces, like VITA standards or OpenVPX, allow for plug-and-play capabilities across multiple platforms and vendors, drastically reducing system lifecycle costs and simplifying logistics chains. Cybersecurity has become another major area of focus. Since LRUs often handle critical flight, targeting, or communication data, ensuring that they are secure from cyber threats is paramount. This has led to the integration of embedded encryption, secure boot mechanisms, and authentication protocols within LRU firmware and hardware. Technologies like Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) and intrusion detection sensors are increasingly becoming standard in mission-critical LRUs.
Further, digital twin and augmented reality (AR) tools are beginning to be used alongside LRUs. These technologies provide technicians with virtual overlays for guided maintenance and simulate LRU behaviors in virtual environments, enhancing training and operational planning. Integration with logistics systems and digital maintenance records also allows for seamless asset tracking and configuration control.
Key Drivers in Aircraft LRU Market:
The growth and evolution of the global military aircraft LRU market are driven by a combination of operational, logistical, and strategic factors. One of the primary drivers is the increased complexity of military aircraft systems. Fifth-generation fighter jets, stealth bombers, and multi-role transport aircraft now rely on thousands of interconnected electronic and mechanical components. Without modular LRUs, maintaining such platforms would be slow, inefficient, and prohibitively expensive. Operational readiness requirements are another powerful driver. Military forces worldwide prioritize high availability and mission-capable rates for their aircraft fleets. LRUs enable quick turnaround times between missions, reducing aircraft downtime during forward deployments or high-tempo operations. For expeditionary forces or carrier-based air wings, this is especially vital. The emphasis on fleet lifecycle cost management is also promoting greater use of LRUs. Militaries are under increasing budgetary scrutiny and must extend the operational life of aging platforms while integrating new technologies. LRUs facilitate incremental upgrades without needing to replace entire systems. For instance, a legacy radar processor in a reconnaissance aircraft can be replaced with a newer, more capable unit while maintaining the original radar array and interface.
Another key driver is interoperability and joint force integration. As multinational military coalitions become more common, having standardized, easily replaceable components helps maintain compatibility across allied forces. Shared LRU platforms and open architectures enable allied nations to support each other logistically during joint missions or peacekeeping operations. In addition, supply chain resilience and local manufacturing goals are encouraging countries to invest in domestic LRU production capabilities. This reduces reliance on foreign suppliers, enables rapid customization, and allows defense contractors to respond more flexibly to changing mission needs. Many nations are incorporating LRU development into broader defense industrial strategies to build self-reliance and indigenous innovation.
Regional Trends in Aircraft LRU Market:
Regional trends in the military aircraft LRU market reflect each region's strategic posture, procurement philosophy, and domestic industrial base. In North America, particularly the United States, the military LRU market is highly mature and technology-driven. Programs such as the F-35 Lightning II, B-21 Raider, and Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) all heavily rely on LRU-centric design to facilitate rapid component replacement and system upgrades. The U.S. military's push toward modular open systems and digital engineering is setting the global standard, with LRUs designed for longevity and rapid integration of next-gen capabilities like AI, EW, and quantum communications.
Europe is experiencing a strong push toward joint platform development and LRU standardization, especially under programs like the Future Combat Air System (FCAS) involving France, Germany, and Spain. European nations are increasingly adopting a modular approach to aircraft systems to foster collaboration and maintain independence from U.S. suppliers. Airbus, Leonardo, and Thales are leading efforts to develop LRU systems aligned with open standards and tailored for NATO interoperability. In the Asia-Pacific region, rising geopolitical tensions and a push for indigenous defense production are fueling LRU development. Countries like China, India, South Korea, and Japan are expanding their military aviation capabilities with both imported and domestic platforms. China's J-20 and India's Tejas fighters use LRU frameworks that enable scalable upgrades and maintenance. The region is also witnessing the emergence of local LRU suppliers capable of producing navigation, fire control, and mission management systems.
Key Aircraft LRU Program:
The Directorate of Engineering B (Technical), Air Headquarters (Vayu Bhawan), on behalf of the Ministry of Defence, Government of India, invites Expressions of Interest (EoI) from reputable Indian firms for the procurement of four categories of Line Replaceable Units (LRUs) for the KIRAN MK-I/IA fleet of the Indian Air Force. Eligible firms must be based in India and possess the necessary technical expertise, financial capability, infrastructure, and relevant experience to undertake the project. The scope of work includes obtaining airworthiness certification where applicable and ensuring delivery within defined timelines.
Table of Contents
Aircraft LRU Market Report Definition
Aircraft LRU Market Segmentation
By Platform
By Region
By Type
Aircraft LRU Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year aircraft LRU market analysis would give a detailed overview of aircraft LRU market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Aircraft LRU Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Aircraft LRU Market Forecast
The 10-year aircraft LRU market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Aircraft LRU Market Trends & Forecast
The regional aircraft LRU market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Aircraft LRU Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Aircraft LRU Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Aircraft LRU Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2025-2035
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Type, 2025-2035
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2025-2035
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Type, 2025-2035
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Aircraft LRU Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 2: Global Aircraft LRU Market Forecast, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 3: Global Aircraft LRU Market Forecast, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 4: Global Aircraft LRU Market Forecast, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 5: North America, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 6: Europe, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 7: Middle East, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 8: APAC, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 9: South America, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 10: United States, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 11: United States, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 12: Canada, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 13: Canada, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 14: Italy, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 15: Italy, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 16: France, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 17: France, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 18: Germany, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 19: Germany, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 22: Belgium, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 23: Belgium, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 24: Spain, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 25: Spain, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 26: Sweden, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 27: Sweden, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 28: Brazil, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 29: Brazil, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 30: Australia, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 31: Australia, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 32: India, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 33: India, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 34: China, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 35: China, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 38: South Korea, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 39: South Korea, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 40: Japan, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 41: Japan, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 44: Singapore, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 45: Singapore, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Aircraft LRU Market, Technology Maturation, 2025-2035
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Aircraft LRU Market, Market Forecast, 2025-2035
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Aircraft LRU Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Aircraft LRU Market, By Region (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Aircraft LRU Market, By Platform (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Aircraft LRU Market, By Platform (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Aircraft LRU Market, By Type (Cumulative Market), 2025-2035
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Aircraft LRU Market, By Type (CAGR), 2025-2035
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Aircraft LRU Market, Cumulative Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Aircraft LRU Market, Global Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Aircraft LRU Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Aircraft LRU Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Aircraft LRU Market, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Aircraft LRU Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Aircraft LRU Market, Total Market, 2025-2035
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Aircraft LRU Market, By Region, 2025-2035
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Aircraft LRU Market, By Platform, 2025-2035
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Aircraft LRU Market, By Type, 2025-2035
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Aircraft LRU Market, 2025-2035









