 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1516954
全球洲際彈道飛彈(ICBM)市場(2024-2034)Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market 2024-2034 |
||||||
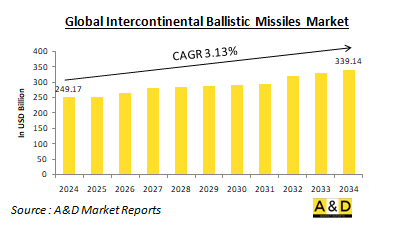
2024年全球洲際彈道飛彈(ICBM)市場規模預估為2,491.7億美元,預估在預測期內(2024-2034年)複合年增長率(CAGR)為3.13%。億美元。

洲際彈道飛彈市場概況
洲際彈道飛彈(ICBM)是一種遠程戰略飛彈,旨在跨大陸發射核彈頭。它能夠攻擊5500公里以上的目標,是國家戰略威懾力量的重要組成部分。洲際彈道飛彈通常遵循彈道軌跡,包括由火箭發動機推動的□□發射階段、太空中的中間軌道階段以及彈頭下降到目標的再入階段。洲際彈道飛彈的出現標誌著軍事力量的重大升級,使各國能夠遠距離投射力量,從而改變了世界的戰略動態。
科技對全球洲際彈道飛彈市場的影響
技術進步對洲際彈道飛彈(ICBM)的開發和部署產生了重大影響。從早期彈道飛彈到現代洲際彈道飛彈的進步涉及推進系統、導引技術、彈頭能力和再入技術的重大改進。火箭推進技術的進步對於擴大洲際彈道飛彈的射程和提高可靠性至關重要。早期的洲際彈道飛彈使用液體燃料火箭,這種火箭結構複雜,在發射前需要加油。相較之下,現代洲際彈道飛彈主要使用固體燃料火箭。固體燃料技術提供更高的可靠性、縮短髮射準備時間並提高儲存穩定性。固體燃料火箭也促進了獨立定向再入火箭(MIRV)的發展,這種火箭攜帶多個彈頭,可以有效攻擊不同的目標。
導引技術的進步大大提高了洲際彈道飛彈的精度。早期的導引系統依賴慣性導航,這限制了其準確性。然而,現代洲際彈道飛彈採用了先進的導引系統,包括 GPS 和先進的慣性導航,大大提高了瞄準精度。終端導引系統的整合進一步提高了精度,最大限度地減少了潛在的附帶損害並提高了飛彈的整體效能。先進彈頭的發展增加了洲際彈道飛彈的破壞力。儘管早期的彈頭主要是核彈頭,但現代洲際彈道飛彈可以攜帶各種類型的彈頭,包括熱核彈頭、氫彈頭和其他可提高產量和效率的先進設計。此外,現代核彈頭採用對抗技術和誘餌來提高其針對飛彈防禦系統的生存能力,並確保其到達目標後的有效性。再入技術的創新解決了重返地球大氣層的課題。現代洲際彈道飛彈利用先進的隔熱罩和再入飛行器設計來保護其彈頭免受再入大氣層期間所經歷的高溫和壓力的影響。這些進步使得彈頭能夠以最小程度的退化有效地到達目標,並保持飛彈的預期破壞能力。
洲際彈道飛彈市場的主要驅動因素
洲際彈道飛彈 (ICBM) 的開發和部署受到多種因素的推動,包括戰略、技術和地緣政治考量。
戰略威懾是洲際彈道飛彈發展的主要動力。各國遵循相互確保毀滅(MAD)原則投資洲際彈道飛彈,以阻止潛在對手發動核攻擊。以毀滅性武力進行報復的能力具有強大的威懾力,有助於維護穩定、防止衝突。透過確保潛在侵略者面臨壓倒性的報復,各國可以減少核衝突的可能性。地緣政治緊張局勢和區域衝突也在鼓勵洲際彈道飛彈能力發展方面發揮重要作用。各國可能會尋求加強其威懾態勢,以應對感知到的威脅或對抗敵對國家的能力。洲際彈道飛彈的開發和部署與全球權力動態和安全考量密切相關,各國都在尋求維護其戰略影響力並應對區域安全課題。
技術進步也是推動洲際彈道飛彈發展的重要因素。飛彈技術的不斷創新,包括推進系統、導引技術和彈頭設計的改進,使各國得以開發出更先進、更有效的飛彈系統。洲際彈道飛彈的技術優勢提供了戰略優勢,影響全球力量平衡,增強國家力量投射能力和威懾力。軍事現代化建設將進一步帶動洲際彈道飛彈武器的發展與更新。作為更廣泛的現代化舉措的一部分,各國正在投資維持其洲際彈道飛彈系統的戰備狀態和技術充足性。這包括對現有飛彈系統進行現代化改造、開發新型飛彈以及加強支援基礎設施以確保可靠性和有效性。這些投資對於維持可靠和強大的戰略威懾至關重要。軍備管制協議和條約也影響洲際彈道飛彈的開發和部署。 《削減戰略武器條約》(START)等協議對洲際彈道飛彈和核彈頭的數量設定了限制,並鼓勵各國調整戰略並投資於合規措施。軍控談判動態影響戰略格局,影響洲際彈道飛彈發展方向,塑造國際軍控總體框架。
洲際彈道飛彈市場的區域趨勢
在北美,美國擁有先進的洲際彈道飛彈庫,作為其核三邊體系的關鍵組成部分。美國空軍使用民兵 III 洲際彈道飛彈,一項現代化計劃正在進行中,以延長其使用壽命並增強其能力。在這些努力的同時,美國正在與俄羅斯進行軍備管制談判,並致力於控制和減少洲際彈道飛彈。儘管加拿大不是核國家,但它參與了導彈防禦和軍備控制方面的戰略夥伴關係和協議,為更廣泛的區域安全框架做出了貢獻。
在歐洲,洲際彈道飛彈的發展不如北美明顯,歐洲國家主要依賴北約的集體威懾。法國和英國等國擁有自己的戰略核武力量,包括潛射彈道飛彈(SLBM)和空射系統,這與其整體戰略態勢相輔相成。歐洲的洲際彈道飛彈能力已融入北約更廣泛的核子戰略和威懾框架,反映了戰略威懾的集體方法。
在亞太地區,特別是中國和印度等國家對洲際彈道飛彈開發的興趣日益濃厚。作為其更廣泛的軍事現代化努力和戰略願望的一部分,中國開發了多種洲際彈道飛彈,包括東風5和東風41。印度也憑藉烈火五號飛彈在洲際彈道飛彈發展方面取得了飛躍,增強了其戰略能力和地區威懾力。亞太地區對洲際彈道飛彈的關注是由區域安全動態和權力競爭所驅動的,反映了該地區不斷變化的戰略格局。俄羅斯擁有重要的洲際彈道飛彈作為其戰略核武力量的核心要素。俄羅斯的洲際彈道飛彈庫存包括 RS-24 Yars 和 RS-28 Sarmat 等先進系統,展示了持續的現代化努力和技術進步。俄羅斯洲際彈道飛彈的研發和部署與其戰略態勢和與美國的軍控協議密切相關。此外,獨立國家聯合體(獨聯體)國家,特別是與俄羅斯有歷史聯繫的國家,可以參與聯合戰略舉措和現代化計劃。在中東和非洲,洲際彈道飛彈的發展比其他地區更為有限。這些地區的大多數國家更關注傳統軍事力量和區域安全問題,而不是追求洲際彈道飛彈計畫。然而,導彈技術的擴散和區域衝突可能會影響這些地區的未來發展和戰略考量。
主要洲際彈道飛彈計畫
Lockeed Martin公司是政府和工業界在維護和現代化洲際彈道飛彈(ICBM)方面的重要合作夥伴,該飛彈是國家核三位一體的一部分,為軍隊提供可靠的陸基飛彈,並提供戰略威懾。在超過 65 年的合作夥伴關係中,Lockeed Martin與美國空軍密切合作,開發 Mk21A 再入系統以供未來使用。 Mk21A 綜合再入飛行器 (RV) 旨在為美國空軍即將推出的哨兵洲際彈道飛彈部署 W87-1 彈頭,並基於原始 Mk21 設計。Lockeed Martin公司利用先進的數位工程工具(包括先進的建模和模擬)來成熟 Mk21A 設計。此外,洛克希德·馬丁公司還負責 "哨兵" 的武器系統整合和RV集成,同時為現役洲際彈道飛彈提供保障支援。
民兵III已經服役了50年,是一種彈頭能夠在戰時攜帶核彈的飛彈。美國國防部週三宣佈,Boeing公司已獲得一份價值 16 億美元的合同,為美國民兵 III 洲際彈道飛彈提供導引子系統支援。根據國防部聲明,這項工作將在猶他州希爾空軍基地進行,預計將於 2039 年 2 月 1 日完成。
目錄
洲際彈道飛彈市場:報告定義
洲際彈道飛彈市場細分
- 按地區
- 按推進方式
- 依續航距離
洲際彈道飛彈市場分析(未來10年)
洲際彈道飛彈市場的市場技術
世界洲際彈道飛彈市場預測
洲際彈道飛彈市場:區域趨勢與預測
- 北美
- 促進/抑制因素和課題
- PEST分析
- 市場預測與情境分析
- 主要公司
- 供應商層級狀況
- 企業基準比較
- 歐洲
- 中東
- 亞太地區
- 南美洲
洲際彈道飛彈市場:國家分析
- 美國
- 防禦規劃
- 最新趨勢
- 專利
- 該市場目前的技術成熟度水平
- 市場預測與情境分析
- 加拿大
- 義大利
- 法國
- 德國
- 荷蘭
- 比利時
- 西班牙
- 瑞典
- 希臘
- 澳大利亞
- 南非
- 印度
- 中國
- 俄羅斯
- 韓國
- 日本
- 馬來西亞
- 新加坡
- 巴西
洲際炸彈公路飛彈市場:市場機會矩陣
洲際彈道飛彈市場:專家的研究觀點
結論
關於航空和國防市場報告
The global Intercontinental Ballistic Missile market is estimated at USD 249.17 billion in 2024, projected to grow to USD 339.14 billion by 2034 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3.13% over the forecast period 2024-2034.
Introduction to Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) are long-range strategic missiles designed to deliver nuclear warheads across continents. They represent a key component of a nation's strategic deterrence capabilities, given their ability to strike targets at distances exceeding 5,500 kilometers. ICBMs typically follow a ballistic trajectory, involving a launch phase where the missile is propelled by rocket engines, a midcourse phase in space, and a reentry phase where the warhead descends to the target. The advent of ICBMs marked a significant escalation in the capability of military forces, transforming global strategic dynamics by enabling countries to project power over vast distances.
Technology Impact in Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market:
Technological advancements have profoundly impacted the development and deployment of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs). The progression from early ballistic missiles to modern ICBMs has involved significant improvements in propulsion systems, guidance technology, warhead capabilities, and reentry technology. The evolution of rocket propulsion technology has been crucial in extending the range and enhancing the reliability of ICBMs. Early ICBMs utilized liquid-fueled rockets, which were complex and required refueling before launch. In contrast, modern ICBMs predominantly use solid-fueled rockets. Solid-fuel technology offers greater reliability, reduced launch preparation times, and enhanced storage stability. It has also facilitated the development of Multiple Independently targetable Reentry Vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry multiple warheads and strike different targets effectively.
Advances in guidance technology have significantly improved the accuracy of ICBMs. Early guidance systems relied on inertial navigation, which provided limited accuracy. Contemporary ICBMs, however, incorporate sophisticated guidance systems, including GPS and advanced inertial navigation, which significantly enhance targeting precision. The integration of terminal guidance systems has further refined accuracy, minimizing the potential for collateral damage and increasing the overall effectiveness of the missile. The development of advanced warheads has augmented the destructive power of ICBMs. While early warheads were primarily nuclear, modern ICBMs can carry various types of warheads, including thermonuclear, hydrogen, and other advanced designs that improve yield and efficiency. Additionally, modern warheads employ countermeasure technologies and decoys to enhance their survivability against missile defense systems, ensuring their effectiveness upon reaching their targets. Innovations in reentry technology have addressed the challenges of re-entering the Earth's atmosphere. Modern ICBMs utilize advanced heat shielding and reentry vehicle designs to protect warheads from the intense heat and pressure experienced during atmospheric reentry. These advancements ensure that warheads can effectively reach their targets with minimal degradation, maintaining the missile's intended destructive capability.
Key Drivers in Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market:
Several factors drive the development and deployment of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs), reflecting a mix of strategic, technological, and geopolitical considerations.
Strategic deterrence is a primary driver behind ICBM development. Nations invest in ICBMs to deter potential adversaries from launching a nuclear attack, adhering to the principle of mutually assured destruction (MAD). The capability to retaliate with devastating force serves as a powerful deterrent, helping to maintain stability and prevent conflicts. By ensuring that any potential aggressor faces overwhelming retaliation, countries can reduce the likelihood of nuclear conflict. Geopolitical tensions and regional conflicts also play a significant role in driving the enhancement of ICBM capabilities. Countries may seek to bolster their deterrent posture in response to perceived threats or to counterbalance the capabilities of rival states. The development and deployment of ICBMs are closely linked to global power dynamics and security considerations, with nations investing in these systems to assert their strategic influence and address regional security challenges.
Technological advancements are another crucial factor fueling the development of ICBMs. Continuous innovation in missile technology, including improvements in propulsion systems, guidance technology, and warhead designs, allows nations to develop more sophisticated and effective missile systems. Technological superiority in ICBMs can provide strategic advantages, influencing global power balances and enhancing a nation's ability to project power and deterrence capabilities. Military modernization efforts further drive the development and upgrading of ICBM arsenals. As part of broader modernization initiatives, countries invest in maintaining operational readiness and technological relevance of their ICBM systems. This includes modernizing existing missile systems, developing new variants, and enhancing support infrastructure to ensure reliability and effectiveness. Such investments are essential for maintaining a credible and capable strategic deterrent. Arms control agreements and treaties also impact the development and deployment of ICBMs. Agreements such as the Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START) set limits on the number of ICBMs and warheads, prompting countries to adapt their strategies and invest in compliance measures. The dynamics of arms control negotiations affect the strategic landscape, influencing the direction of ICBM development and shaping the overall framework of international arms control.
Regional Trends in Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market:
Regional trends in Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) development reflect the diverse strategic priorities and geopolitical contexts of different areas.
In North America, the United States maintains a sophisticated ICBM arsenal as a key component of its nuclear triad. The U.S. Air Force operates the Minuteman III ICBM, which is subject to ongoing modernization programs aimed at extending its service life and enhancing its capabilities. Alongside these efforts, the U.S. engages in arms control negotiations with Russia to manage and reduce ICBM arsenals. Canada, while not a nuclear-armed state, participates in strategic partnerships and agreements related to missile defense and arms control, contributing to the broader regional security framework.
In Europe, ICBM development is less pronounced compared to North America, with European countries primarily relying on NATO's collective deterrence capabilities. Nations such as France and the United Kingdom possess their own strategic nuclear forces, including submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) and air-launched systems, which complement their overall strategic posture. European ICBM capabilities are integrated into NATO's broader nuclear strategy and deterrent framework, reflecting a collective approach to strategic deterrence.
The Asia-Pacific region has seen increasing interest in ICBM development, particularly among countries like China and India. China has developed a range of ICBMs, including the DF-5 and DF-41, as part of its broader military modernization efforts and strategic aspirations. India has also made strides in ICBM development with the Agni-V missile, enhancing its strategic capabilities and regional deterrence. The focus on ICBMs in the Asia-Pacific region is driven by regional security dynamics and power competition, reflecting the evolving strategic landscape of the area.Russia maintains a significant ICBM arsenal as a core element of its strategic nuclear forces. The Russian ICBM inventory includes advanced systems such as the RS-24 Yars and the RS-28 Sarmat, which showcase ongoing modernization efforts and technological advancements. The development and deployment of ICBMs in Russia are closely linked to its strategic posture and arms control agreements with the United States. Additionally, Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries, particularly those with historical ties to Russia, may participate in joint strategic initiatives and modernization programs. In the Middle East and Africa, ICBM development is limited compared to other regions. Most countries in these areas focus on conventional military capabilities and regional security issues rather than pursuing ICBM programs. However, the proliferation of missile technology and regional conflicts may influence future developments and strategic considerations in these regions.
Key Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Program:
Lockheed Martin is a crucial partner for both the government and industry in sustaining and modernizing the intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) component of the nation's nuclear triad, providing a credible, land-based strategic deterrent for the military. With a partnership spanning over 65 years, Lockheed Martin collaborates closely with the U.S. Air Force and is developing the Mk21A reentry system for future use. The Mk21A, an integrated reentry vehicle (RV), is designed to deploy the W87-1 warhead for the U.S. Air Force's upcoming Sentinel ICBM, adapting the original Mk21 design. Lockheed Martin leverages advanced Digital Engineering tools, including sophisticated modeling and simulation, to mature the Mk21A design. Additionally, the company handles weapon system integration and RV integration for the Sentinel, while providing sustainment support for in-service ICBMs.
The Minuteman III, in service for 50 years, is a warhead-equipped missile capable of carrying a nuclear bomb during wartime. Boeing has been awarded a $1.6 billion contract to provide guidance subsystem support for the US Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missiles, the Pentagon announced on Wednesday. The work will be conducted at Hill Air Force Base in Utah and is expected to be completed by February 1, 2039, according to a Department of Defense statement.
Table of Contents
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Report Definition
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Segmentation
By Region
By Propulsion
By Range
Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Analysis for next 10 Years
The 10-year Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market analysis would give a detailed overview of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market growth, changing dynamics, technology adoption overviews and the overall market attractiveness is covered in this chapter.
Market Technologies of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market
This segment covers the top 10 technologies that is expected to impact this market and the possible implications these technologies would have on the overall market.
Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Forecast
The 10-year Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market forecast of this market is covered in detailed across the segments which are mentioned above.
Regional Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Trends & Forecast
The regional Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market trends, drivers, restraints and Challenges of this market, the Political, Economic, Social and Technology aspects are covered in this segment. The market forecast and scenario analysis across regions are also covered in detailed in this segment. The last part of the regional analysis includes profiling of the key companies, supplier landscape and company benchmarking. The current market size is estimated based on the normal scenario.
North America
Drivers, Restraints and Challenges
PEST
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Key Companies
Supplier Tier Landscape
Company Benchmarking
Europe
Middle East
APAC
South America
Country Analysis of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market
This chapter deals with the key defense programs in this market, it also covers the latest news and patents which have been filed in this market. Country level 10 year market forecast and scenario analysis are also covered in this chapter.
US
Defense Programs
Latest News
Patents
Current levels of technology maturation in this market
Market Forecast & Scenario Analysis
Canada
Italy
France
Germany
Netherlands
Belgium
Spain
Sweden
Greece
Australia
South Africa
India
China
Russia
South Korea
Japan
Malaysia
Singapore
Brazil
Opportunity Matrix for Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market
The opportunity matrix helps the readers understand the high opportunity segments in this market.
Expert Opinions on Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Market Report
Hear from our experts their opinion of the possible analysis for this market.
Conclusions
About Aviation and Defense Market Reports
List of Tables
- Table 1: 10 Year Market Outlook, 2024-2034
- Table 2: Drivers, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 3: Restraints, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 4: Challenges, Impact Analysis, North America
- Table 5: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 6: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 7: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Europe
- Table 8: Drivers, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 9: Restraints, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 10: Challenges, Impact Analysis, Middle East
- Table 11: Drivers, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 12: Restraints, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 13: Challenges, Impact Analysis, APAC
- Table 14: Drivers, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 15: Restraints, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 16: Challenges, Impact Analysis, South America
- Table 17: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Region, 2024-2034
- Table 18: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Propulsion, 2024-2034
- Table 19: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 1, By Range, 2024-2034
- Table 20: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Region, 2024-2034
- Table 21: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Propulsion, 2024-2034
- Table 22: Scenario Analysis, Scenario 2, By Range, 2024-2034
List of Figures
- Figure 1: Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 2: Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market Forecast, By Region, 2024-2034
- Figure 3: Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market Forecast, By Propulsion, 2024-2034
- Figure 4: Global Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market Forecast, By Range, 2024-2034
- Figure 5: North America, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 6: Europe, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 7: Middle East, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 8: APAC, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 9: South America, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 10: United States, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 11: United States, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 12: Canada, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 13: Canada, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 14: Italy, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 15: Italy, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 16: France, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 17: France, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 18: Germany, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 19: Germany, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 20: Netherlands, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 21: Netherlands, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 22: Belgium, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 23: Belgium, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 24: Spain, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 25: Spain, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 26: Sweden, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 27: Sweden, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 28: Brazil, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 29: Brazil, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 30: Australia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 31: Australia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 32: India, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 33: India, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 34: China, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 35: China, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 36: Saudi Arabia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 37: Saudi Arabia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 38: South Korea, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 39: South Korea, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 40: Japan, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 41: Japan, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 42: Malaysia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 43: Malaysia, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 44: Singapore, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 45: Singapore, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 46: United Kingdom, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Technology Maturation, 2024-2034
- Figure 47: United Kingdom, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Market Forecast, 2024-2034
- Figure 48: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Region (Cumulative Market), 2024-2034
- Figure 49: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Region (CAGR), 2024-2034
- Figure 50: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Propulsion (Cumulative Market), 2024-2034
- Figure 51: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Propulsion (CAGR), 2024-2034
- Figure 52: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Range (Cumulative Market), 2024-2034
- Figure 53: Opportunity Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Range (CAGR), 2024-2034
- Figure 54: Scenario Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Cumulative Market, 2024-2034
- Figure 55: Scenario Analysis, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Global Market, 2024-2034
- Figure 56: Scenario 1, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Total Market, 2024-2034
- Figure 57: Scenario 1, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Region, 2024-2034
- Figure 58: Scenario 1, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Propulsion, 2024-2034
- Figure 59: Scenario 1, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Range, 2024-2034
- Figure 60: Scenario 2, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, Total Market, 2024-2034
- Figure 61: Scenario 2, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Region, 2024-2034
- Figure 62: Scenario 2, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Propulsion, 2024-2034
- Figure 63: Scenario 2, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, By Range, 2024-2034
- Figure 64: Company Benchmark, Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Market, 2024-2034






