 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1851187
硫肥:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢、統計數據和成長預測(2025-2030 年)Sulfur Fertilizer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
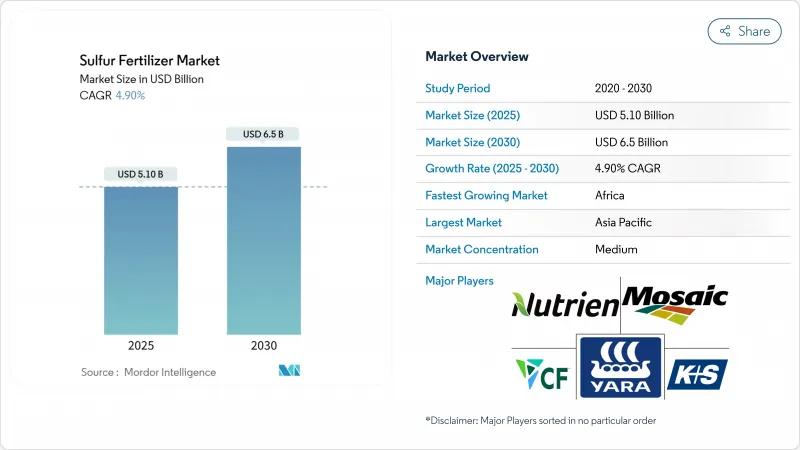
預計硫肥市場規模將在 2025 年達到 51 億美元,在 2030 年達到 65 億美元,預測期內複合年成長率為 4.9%。
這是由於自1990年代以來大氣硫沉降量下降了70%以上,導致土壤硫含量下降,作物對硫肥的反應日益增強。亞太地區是化肥消費的主導地區,這主要得益於中國每年4,890萬噸的化肥用量以及印度不斷擴大的精準施肥計畫。非洲是成長最快的地區,基礎設施的改善和糧食安全措施加速了均衡營養的普及。煉油廠脫硫排放也進一步推動了產業發展,目前煉油廠脫硫排放提供的元素硫佔化肥生產所需元素硫總量的60%以上,但隨著煉油廠利潤率的下降,供應可能會趨緊。
全球硫肥市場趨勢及洞察
土壤硫缺乏
土壤測試表明,由於空氣品質法規禁止硫酸鹽氣溶膠排放,過去30年間土壤硫含量下降了30%至50%,硫成為繼氮、磷、鉀之後第四大限制產量的營養元素。每公頃施用30至45公斤硫肥的作物,小麥產量增加了15%至25%,籽粒蛋白質含量也增加。有機質含量低的集約化耕作區最容易受到影響,而針對特定地點的檢測套組包使農民能夠在作物生長季開始前識別出養分缺乏問題。這項技術已成為硫肥市場的主要驅動力,將潛在的養分缺乏轉化為可衡量的需求。目前,商業玉米農場的產量監測數據顯示,當葉片硫含量低於0.2%時,產量損失高達18%,這清楚顯示了大規模種植的經濟風險。隨著氣候模式的改變,降雨分佈發生變化,淋溶損失進一步降低了土壤中殘留的硫含量,使得每年補充硫肥成為現實的必要措施。
增加油料作物種植面積及產量
油菜籽和大豆等油料作物每單位氮所需的硫量是穀物的兩到三倍,隨著全球種植面積的擴大,化肥需求也隨之增加。密蘇里大學的田間試驗表明,施用100磅硫酸銨可使大豆每英畝增產8.1蒲式耳,扣除投入成本後,每英畝利潤增加80美元。這種經濟效益促使成熟市場繼續採用硫酸銨,從而增強了硫肥生產的穩定拉動動作用。預計到2030年,全球油菜籽種植面積將增加180萬公頃,這將推動加拿大和澳洲對高硫混合物的需求。高蛋白質多樣性品種也具有更高的硫吸收率,這使得種子遺傳與施肥策略直接相關。
與多種營養成分的特殊肥料的競爭
農民越來越傾向於使用能夠解決多種營養缺乏問題的單一途徑施用複合肥,這可能會降低對純硫的需求。供應商正透過將硫添加到更廣泛的營養組合中來應對這一趨勢,但價格競爭和配方複雜性對小型生產商構成了障礙。大型經銷商正在銷售價格更低的含硫微量元素複合肥,減少了純硫的銷售量。為了保持競爭力,硫肥供應商正在尋求共同行銷夥伴關係,以提供承包作物營養方案。這種轉變可能會降低純硫的淨利率,並推動小型公司之間的整合。
細分市場分析
2024年,硫酸鹽肥料(包括硫酸銨、硫酸鉀和過磷酸鈣肥料)將佔全球銷售額的51%。元素硫雖然規模較小,但由於其含量高、運輸成本低,且氧化過程可控,使其能夠應用於精準施肥方案,因此正以6.7%的複合年成長率快速成長。微粉化和糊化技術縮短了氧化時間,使其適用於生長週期短的作物。分次施用策略,即硫酸鹽用於早期生長,元素硫用於緩釋性,清楚地表明硫肥市場的需求是互補的,而非零和博弈。
元素硫的需求趨勢將促使變數施用器和遙感探測地圖得到廣泛應用,而這些技術需要更高的養分密度來限制田間作業。隨著硫包膜尿素和硫膨潤土成為主流混合肥料,能夠確保顆粒大小均勻和氧化過程可預測的種植者將獲得更大的市場佔有率。
到2024年,固態硫磺產品將保持70%的市場佔有率,這得益於其高效的儲存方式以及與傳統噴霧器在大面積作業中的兼容性。顆粒狀和球狀硫磺產品將在生產效率和儲存便利性至關重要的合作式混合種植系統中佔據主導地位。然而,液態硫磺將以7.2%的複合年成長率成長,這主要得益於其在高價值園藝灌溉和葉面噴布計畫的優勢。
硫代硫酸銨(12-0-0-26S)是一種領先的液態硫肥,可與氮肥溶液和農藥混合使用,實現單一途徑高效施肥。種植者讚賞其在微灌中的均勻性以及在關鍵生殖期植物的快速吸收。供應商正在建造區域性終端,以縮短運輸時間,縮小與固態肥料的交付成本差距,並擴大硫肥市場的潛在覆蓋範圍。
區域分析
至2024年,亞太地區將以37%的市佔率引領硫肥市場。中國的化肥使用強度仍高於全球標準,為控制氮肥過量施用,中國正在推行平衡的氮磷鉀肥(NPK-S)施用方案,以在減少損失的同時保持產量。在印度,精準噴施技術的普及和政府對土壤健康卡的補貼,正推動硫肥成為常規施肥手段。東南亞國家透過棕櫚油和雙季稻種植提升硫肥需求,而日本等已開發國家則在探索高價值農產品的超低氯化物方案。到2030年,亞太地區硫肥市場將以5.6%的複合年成長率成長,這得益於與氣候智慧型農業目標一致的政策。
非洲是成長最快的地區,年均複合成長率達6.4%。土壤調查顯示,撒哈拉以南許多地區缺硫,各國政府目前正將化肥補貼與推廣服務結合,以促進均衡營養。衣索比亞計劃在復興大壩建成後建造國產複合肥廠,以減少對進口的依賴。南非的商業農場已經開始使用元素硫混合物來改良鹼性土壤。儘管分銷仍面臨挑戰,但捐助方支持的走廊計劃和旨在改善「最後一公里」分銷的私人配製中心正在為硫肥市場帶來積極前景。
北美地區硫磺市場維持4.1%的穩定複合年成長率,美國每年從煉油廠回收820萬噸硫磺,用於生產磷酸鹽和硫酸銨。加拿大近期對硫磺徵收的關稅將在短期內導致供應緊張,但加拿大豐富的天然氣和煉油網路將支撐供應。精準農業、覆蓋作物的推廣以及永續性認證將推動需求成長。歐洲地區的硫磺市場複合年成長率為3.2%,嚴格的水質法規與維持作物蛋白質含量的需求相平衡,使得控制釋放硫磺更具吸引力。
其他福利:
- Excel格式的市場預測(ME)表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場情勢
- 市場概覽
- 市場促進因素
- 土壤中硫元素缺乏
- 增加油籽種植面積及產量
- 政府對永續農業的獎勵
- 採用控制釋放硫包覆尿素
- 提高脫硫裝置中回收硫的可用性
- 以人工智慧為基礎的精準營養應用平台
- 市場限制
- 與多種營養成分的特殊肥料的競爭
- 元素硫原料價格波動
- 硫酸鹽滲入地下水造成的環境風險
- 新興市場顆粒狀元素硫的分銷瓶頸
- 監管環境
- 技術展望
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買方的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章 市場規模與成長預測
- 按類型
- 硫酸肥料
- 硫酸銨
- 硫酸鉀
- 硫酸鈣(石膏)
- 單過磷酸鈣
- 單質硫
- 細粉狀硫
- 顆粒狀/膏狀硫磺
- 微量營養素硫酸鹽
- 硫酸鋅
- 硫酸鎂
- 其他
- 其他(硫包覆尿素、硫磺膨潤土)
- 硫酸肥料
- 按形式
- 固體的
- 液體
- 透過使用
- 土壤施用
- 施肥灌溉
- 葉面噴布
- 緩釋/包衣顆粒
- 按作物類型
- 穀物和穀類
- 油籽和豆類
- 水果和蔬菜
- 草坪和觀賞植物
- 其他
- 透過分銷管道
- 農場直銷
- 零售商
- 合作社
- 線上平台
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 英國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 西班牙
- 其他歐洲地區
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 亞太其他地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 其他南美洲
- 中東
- 沙烏地阿拉伯
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 其他中東地區
- 非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 其他非洲地區
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭情勢
- 市場集中度
- 策略趨勢
- 市佔率分析
- 公司簡介
- Nutrien Ltd.
- Yara International ASA
- The Mosaic Company
- K+S AG
- Israel Chemicals Ltd.
- Haifa Chemicals Ltd.
- Nufarm Limited
- Koch Industries Inc.
- CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- OCP SA
- BASF SE
- Sinochem Holdings Corp. Ltd.
- Saudi Arabian Fertilizer Company(SAFCO)(Saudi Basic Industries Corporation(SABIC))
- Tiger-Sul Products LLC(Tessenderlo Group)
- TogliattiAzot PJSC(Uralchem Group)
第7章 市場機會與未來展望
The sulfur fertilizers market reached USD 5.1 billion in 2025 and is projected to climb to USD 6.5 billion by 2030, advancing at a 4.9% CAGR during the forecast period.

Gains stem from the sharp decline in atmospheric sulfur deposition, which has fallen more than 70% since the 1990s, leaving soils depleted and crops increasingly responsive to applied sulfur. The Asia-Pacific region leads consumption on the back of China's 48.9 million metric tons annual fertilizer use and India's expanding precision fertilization programs. Africa represents the fastest-growing regional opportunity as infrastructure upgrades and food-security initiatives accelerate balanced nutrient adoption. Industry momentum is further supported by refinery desulfurization streams that now provide more than 60% of all elemental sulfur used in fertilizer manufacturing, although supply can tighten whenever refining margins compress.
Global Sulfur Fertilizer Market Trends and Insights
Sulfur Deficiency in Soil
Soil tests indicate sulfur levels have fallen 30-50% during the past three decades as air-quality rules removed sulfate aerosols, making sulfur the fourth most yield-limiting nutrient after nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Crops that receive 30-45 kilograms of sulfur per hectare show wheat yield gains of 15-25% together with higher grain protein. Intensively cropped regions with low organic matter are the most vulnerable, and site-specific test kits now allow farmers to map deficiencies before the season begins. This capability is a primary engine for the sulfur fertilizers market because it converts latent nutrient shortages into measurable demand. Yield monitors on commercial corn farms now record site yield drops of up to 18% when leaf sulfur falls below 0.2%, underscoring the economic stakes for large operations. As climate patterns shift rainfall distribution, leaching losses further lower residual sulfur, making annual supplementation a practical necessity.
Rising Oilseed Acreage and Yields
Oilseed crops such as canola and soybean require two to three times more sulfur per unit of nitrogen than cereals, which intensifies fertilizer demand as the global planted area expands. University field trials in Missouri report 8.1 bushel-per-acre soybean gains from 100 pounds of ammonium sulfate, yielding a USD 80 per-acre profit lift after input costs. The economics encourage continued adoption even in mature markets, reinforcing a stable pull-through on sulfur volumes. Global canola acreage is projected to expand by 1.8 million hectares by 2030, amplifying demand for high-sulfur blends in Canada and Australia. Biotech cultivars with higher protein ceilings also pull more sulfur, linking seed genetics directly to fertilizer strategy.
Competition from Multi-Nutrient Specialty Fertilizers
Farmers increasingly favor single-pass blends that address multiple deficiencies, which can dilute standalone demand for sulfur. Suppliers are responding by embedding sulfur into broader nutrient packages, but pricing competition and formulation complexity raise barriers for smaller producers. Large distributors bundle mix and match micronutrient packs that include sulfur at lower incremental cost, eroding standalone sales. To stay relevant, sulfur fertilizer suppliers are exploring co-marketing alliances that offer turnkey crop nutrition programs. Such shifts could compress standalone sulfur margins and push consolidation among smaller players.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Incentives for Sustainable Agriculture
- Adoption of Controlled-Release Sulfur-Coated Urea
- Volatility in Elemental Sulfur Prices
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2024, sulfate fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and single superphosphate delivered 51% of global revenue, reflecting their immediate plant availability and ease of blending. Elemental sulfur, though smaller, is growing faster at a 6.7% CAGR as its higher analysis lowers freight costs and its controlled oxidation fits precision programs. Micronized and pastilled innovations shorten oxidation lag, extending applicability to short-season crops. Split-application strategies combine sulfate for early growth and elemental sulfur for sustained release, underscoring complementary rather than zero-sum demand within the sulfur fertilizers market.
The elemental trend plays into the wider adoption of variable-rate applicators and remote-sensing maps, which rely on higher nutrient density to limit field passes. As sulfur-coated urea and sulfur-bentonite enter mainstream blends, producers that can guarantee uniform particle size and predictable oxidation stand to gain share.
Solid products retained a 70% share in 2024, backed by efficient storage and compatibility with conventional spreaders across broad acres. Granulated and prilled formats dominate cooperative blending plants where throughput and shelf life matter. Yet liquid sulfur is advancing at a 7.2% CAGR on the strength of fertigation and foliar programs in high-value horticulture.
Ammonium thiosulfate (12-0-0-26S) typifies liquid momentum, allowing tank mixing with nitrogen solutions and pesticides for single-pass efficiency. Growers appreciate the uniformity in micro-irrigation as well as quicker plant uptake during critical reproductive stages. Vendors are building regional terminals to shorten hauls, which should reduce delivered cost gaps versus solids and widen addressable acreage across the sulfur fertilizers market.
The Sulfur Fertilizers Market Report is Segmented by Type (Sulfate Fertilizer, Elemental Sulfur, and More), Form (Solid and Liquid), Mode of Application (Soil Application, Fertigation, and More), Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, Oilseeds and Pulses, and More), Distribution Channel (Direct-To-Farm, Retail, and More) and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific led the sulfur fertilizers market with a 37% share in 2024. China's fertilizer intensity remains above global norms, and efforts to curb excess nitrogen spur the adop-tion of balanced NPK-S regimens that sustain yields while reducing losses. India's shift toward precision spreaders and state subsidies for soil health cards pushes sulfur deeper into standard practice. Southeast Asian nations are raising demand through palm oil estates and double-cropped rice, whereas developed economies such as Japan seek ultra-low chloride options for high-value produce. Regional growth of 5.6% CAGR through 2030 is anchored by policy alignment with climate-smart agriculture goals.
Africa is the fastest-growing region at 6.4% CAGR. Soil surveys indicate sulfur scarcity in many sub-Saharan zones, and governments now couple fertilizer subsidies with extension services that promote balanced nutrition. Ethiopia's domestic complex under construction post-GERD will cut import reliance, while South Africa's commercial farms already leverage elemental sulfur blends to manage alkaline soils. Distribution challenges persist, yet donor-backed corridor projects and private blending hubs aim to improve last-mile reach, brightening prospects for the sulfur fertilizers market.
North America posts a steady 4.1% CAGR as the United States channels 8.2 million metric tons of recovered sulfur each year from refineries into phosphate and ammonium sulfate production. Recent tariffs on Canadian sulfur inject short-term tightness, but abundant domestic gas and refinery networks anchor supply. Precision agronomy, cover-crop adoption, and sustainability certifications fuel incremental demand. Europe, at 3.2% CAGR, balances stringent water-quality directives with the need to uphold crop protein levels, making controlled-release sulfur variants attractive.
- Nutrien Ltd.
- Yara International ASA
- The Mosaic Company
- K+S AG
- Israel Chemicals Ltd.
- Haifa Chemicals Ltd.
- Nufarm Limited
- Koch Industries Inc.
- CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- OCP S.A.
- BASF SE
- Sinochem Holdings Corp. Ltd.
- Saudi Arabian Fertilizer Company (SAFCO) (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC))
- Tiger-Sul Products LLC (Tessenderlo Group)
- TogliattiAzot PJSC (Uralchem Group)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Sulfur deficiency in soil
- 4.2.2 Rising oilseed acreage and yields
- 4.2.3 Government incentives for sustainable agriculture
- 4.2.4 Adoption of controlled-release sulfur-coated urea
- 4.2.5 Increasing availability of recovered sulfur from desulfurization units
- 4.2.6 AI-based precision nutrient application platforms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Competition from multi-nutrient specialty fertilizers
- 4.3.2 Volatility in elemental sulfur feedstock prices
- 4.3.3 Environmental risk of sulfate leaching into groundwater
- 4.3.4 Distribution bottlenecks for prilled elemental sulfur in emerging markets
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Sulfate Fertilizers
- 5.1.1.1 Ammonium Sulfate
- 5.1.1.2 Potassium Sulfate
- 5.1.1.3 Calcium Sulfate (Gypsum)
- 5.1.1.4 Single Superphosphate
- 5.1.2 Elemental Sulfur
- 5.1.2.1 Micronized Sulfur
- 5.1.2.2 Prilled/Pastilled Sulfur
- 5.1.3 Sulfate of Micronutrients
- 5.1.3.1 Zinc Sulfate
- 5.1.3.2 Magnesium Sulfate
- 5.1.3.3 Others
- 5.1.4 Others (Sulfur-coated Urea, Sulfur Bentonite)
- 5.1.1 Sulfate Fertilizers
- 5.2 By Form
- 5.2.1 Solid
- 5.2.2 Liquid
- 5.3 By Mode of Application
- 5.3.1 Soil Application
- 5.3.2 Fertigation
- 5.3.3 Foliar Spray
- 5.3.4 Controlled-Release/Coated Granules
- 5.4 By Crop Type
- 5.4.1 Cereals and Grains
- 5.4.2 Oilseeds and Pulses
- 5.4.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.4.4 Turf and Ornamentals
- 5.4.5 Others
- 5.5 By Distribution Channel
- 5.5.1 Direct-to-Farm
- 5.5.2 Retail Dealers
- 5.5.3 Cooperatives
- 5.5.4 Online Platforms
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Russia
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Egypt
- 5.6.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Nutrien Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Yara International ASA
- 6.4.3 The Mosaic Company
- 6.4.4 K+S AG
- 6.4.5 Israel Chemicals Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Haifa Chemicals Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Nufarm Limited
- 6.4.8 Koch Industries Inc.
- 6.4.9 CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.10 OCP S.A.
- 6.4.11 BASF SE
- 6.4.12 Sinochem Holdings Corp. Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Saudi Arabian Fertilizer Company (SAFCO) (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC))
- 6.4.14 Tiger-Sul Products LLC (Tessenderlo Group)
- 6.4.15 TogliattiAzot PJSC (Uralchem Group)













