 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1689777
區域供熱:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)District Heating - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
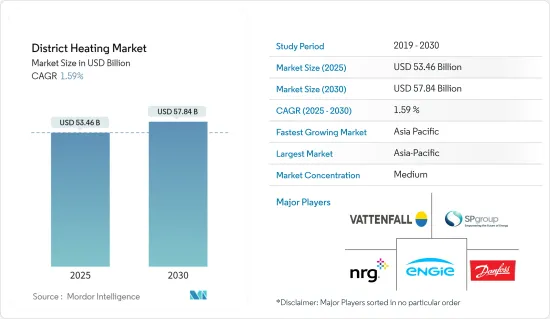
區域供熱市場規模預計在 2025 年為 534.6 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 578.4 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 1.59%。
受全球經濟體設定的積極氣候目標的推動,區域能源是全球快速成長的產業。初步評估發現,這些區域供熱和冷凍公司透過替代持有結構具有更大的機會實現驚人的成長和價值潛力。在區域供熱供應中加入電熱泵可以使更高水準的可再生能源用於供熱目的,從而實現能源系統之間的整合和平衡。隨著全球風力發電機容量的快速增加,大型熱泵將在2050年維持綠色能源發展和擺脫石化燃料發揮關鍵作用。
主要亮點
- 區域供熱是一種透過高度絕緣的管道分配網以熱水的形式向建築物(住宅或商業)提供熱能的方法。將工業製程轉化為區域供熱的可能性有限,因為熱負荷因工業和製程的類型而異,因此擴大工業區域供熱使用的潛力有限。
- 然而,轉向區域供熱可減少 11% 的電力使用和 40% 的石化燃料使用,將整個產業的最終能源使用量降低 6%。
- 轉變工業流程每年可減少全球二氧化碳排放112,000噸。然而,預計住宅和商業市場將佔據相當大的佔有率。
- 約有 6,000 萬歐盟公民使用區域供熱,另有 1.4 億歐盟公民居住在至少擁有一個區域供熱系統的城市。根據歐盟和國際能源總署的報告,區域供熱透過 6,000 個區域供熱和製冷網路滿足了歐盟約 11-12% 的熱量需求。
- 其想法是利用機器學習從客戶和營運資料中預測熱負荷,並將其與天氣預報、節日和工作日等資料相結合,以最佳化和規劃熱量生產,減少熱量損失並滿足尖峰負載。這種潛力擴展到故障檢測中的智慧演算法,以識別由於漏水、加熱系統效率低下或與單一組件相關的故障而導致的錯誤。
- 2024 年 6 月,瑞典 SMR計劃開發商 Kahnfl Next 與芬蘭 Steady Energy 建立策略合作夥伴關係,在瑞典引進 SMR 用於區域供熱。此次合作旨在利用 Karnfur 獨特的資金籌措結構和供應模式,將 Steady Energy 著名的區域供熱核子反應爐引入瑞典市場。
區域供熱市場趨勢
住宅推動成長
- 區域供熱在世界各國已開發國家普遍採用。區域供熱相對於單一建築系統有幾個優點,包括提高安全性和可靠性、降低排放氣體和提高燃料靈活性(特別是在使用生質能或廢物等替代燃料時)。
- 區域供熱廣泛應用於單戶住宅、多用戶住宅、高層建築和特大城鎮。需要區域供熱的主要住宅用途是空間供熱和熱水供熱。區域供熱市場在氣候寒冷的國家已經很成熟,例如丹麥、冰島、德國、美國、其他歐盟國家和加拿大。
- 然而,由再生能源來源動力來源動力的區域供熱網路可以顯著減少排放,並幫助政府實現排放目標。各國政府正在製定法律承諾和獎勵,如補貼、津貼和能源稅,以增加可再生能源在火力發電中的佔有率。
- 此外,區域供熱以前主要來自發電廠、垃圾焚化發電設施和工業活動。但瑞典現在正在擁抱更多的可再生能源。競爭幫助這家社區電力公司成為全國領先的家庭供暖公司。
- 據 BDH 稱,2023 年,德國售出了約 79 萬套燃氣暖氣系統。其中約94,000台機組採用傳統低溫技術,超過6,96,500台機組選擇了冷凝鍋爐技術。
亞太地區佔區域供熱市場的大部分佔有率
- 推動中國市場成長的主要因素是可支配收入的增加、對二氧化碳排放的日益關注以及供暖和製冷系統的高利用率。此外,經合組織預測,到2060年,印度和中國的人均GDP將成長7倍。
- 亞太地區各國政府也正與當地企業合作開發住宅市場。例如,北京區域熱力集團是中國一家大型供熱公司。本公司為北京中央政府及軍隊、中國駐外使領館、重要企事業單位、一般市民提供暖氣解決方案。我們在其他省份也有許多計劃。
- 現代區域供熱系統對東南亞國家尤其重要,因為這些國家的空氣污染造成了長期的經濟成本並導致數十萬人過早死亡。 《東南亞製冷的未來》研究了到 2040 年能源消耗、尖峰電力需求和二氧化碳排放的預期成長。
- 印度和澳洲是該地區最大的兩個市場。區域供熱和製冷解決方案的投資不斷增加,以及政府為推廣這些解決方案而開展的活動活性化,推動了這個區域市場的發展。
- 為了應對能源危機和氣候變化,韓國政府制定了推廣零能耗建築的國家計劃,並且最近還推出了多項針對新建和現有建築的節能政策來實現這些計劃。
區域供熱產業概況
區域供熱市場競爭較為溫和,有許多全球性和地區性公司。這些公司正在努力擴大其全球消費者群體。該公司還優先考慮研發支出,用於開發創新解決方案、策略聯盟以及其他有機和無機成長策略,以在預測期內獲得競爭優勢。
2023年5月,Vattenfall AB和可口可樂在瑞典宣布合作,制定了雄心勃勃的氣候變遷目標,到2040年實現整個價值鏈的淨零排放。兩家公司已經啟動了先導計畫,其中設立了三個充電站,以滿足電動交通的電力需求。
2023 年 3 月,NRG Energy 將完成對 Vivint Smart Home 的收購,加速 NRG 以消費者為中心的成長策略,為消費者提供簡單、互聯的體驗,以智慧方式為其家庭供電、保護和管理。 NRG 處於能源和家庭服務的交匯處,提供以卓越的客戶體驗為基礎的獨特的端到端智慧家庭生態系統。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 研究範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場洞察
- 市場概況
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
- 產業價值鏈分析
- COVID-19 市場影響
- 政府針對區域供熱轉型的措施和計劃
- 區域供熱的主要趨勢和創新
第5章 市場動態
- 市場促進因素
- 對節能、經濟的暖氣系統的需求不斷增加
- 都市化和工業化進程
- 市場限制
- 基礎設施成本高
第6章 市場細分
- 按植物類型
- 鍋爐
- 熱電聯產 (CHP)
- 按熱源分類
- 煤炭
- 天然氣
- 可再生能源
- 石油和石油產品
- 按應用
- 住宅
- 商業和工業
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞洲
- 澳洲和紐西蘭
- 拉丁美洲
- 中東和非洲
第7章 競爭格局
- 公司簡介
- Vattenfall AB
- SP Group
- Danfoss Group
- Engie
- NRG Energy Inc.
- Statkraft AS
- Logstor AS
- Shinryo Corporation
- Vital Energi Ltd
- Gteborg Energi
- Alfa Laval AB
- Ramboll Group AS
- Keppel Corporation Limited
- FVB Energy
第8章投資分析
第9章:未來機會
The District Heating Market size is estimated at USD 53.46 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 57.84 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 1.59% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

District energy is a quick-growing industry globally, supported by the aggressive climate objectives set by the global economies. Based on initial assessments, these district heating and cooling companies have been recognized as operations that could produce more extraordinary growth and value potential with an alternative holding structure. By including electrically powered heat pumps in the district heating supply, higher renewable energy levels can be used for thermal purposes, generating integration and balance between energy systems. With a burgeoning global wind turbine capacity, big heat pumps will play a meaningful role in the sustained global green energy development and phasing out fossil fuels by 2050.
Key Highlights
- District heating provides a method of delivering thermal energy to buildings (homes and commercial space) in the form of hot water through a distribution network of highly insulated pipelines. The potential for increased use of industrial district heating is limited because conversions of industrial processes to district heating involve varying heat loads amongst types of industries and processes.
- However, the conversion to district heating serves an 11% reduction in the use of electricity and a 40% reduction in the use of fossil fuels, with a total energy end-use saving of 6% among industries.
- Converting the industrial processes has led to a potential reduction of global carbon dioxide emissions by 112,000 tons per year. However, the residential and commercial markets are expected to hold a significant share.
- Approximately 60 million EU citizens are served by district heating, and an additional 140 million people live in cities with at least one district heating system. According to reports by the EU and the IEA, DH meets around 11-12% of the EU's heat demand via 6,000 district heating and cooling networks.
- With machine learning, the idea is to predict heat loads from customer data and operational data, along with weather forecasts, national holidays, weekdays, etc., to optimize and plan heat production, thereby lowering heat loss and handling peak loads. The potential is extended to intelligent algorithms in fault detection to identify leakages, inefficient heating systems, or errors from failure related to single components.
- In June 2024, Swedish SMR project developer Karnfull Next has strategically partnered with Finnish counterpart Steady Energy to introduce SMRs for district heating in Sweden. The collaboration aims to capitalize on Karnfull's unique financing structures and delivery models to introduce Steady Energy's renowned district heating reactors to the Swedish market.
District Heating Market Trends
Residential to Witness the Growth
- District heating is commonly used in industrialized nations worldwide. It has several advantages over individual building equipment, including improved safety and dependability, lower emissions, and greater fuel flexibility, particularly when utilizing alternative fuels such as biomass or garbage.
- District heating is widely utilized in single-family houses, multi-family dwellings, high-rise buildings, and mega townships. The primary home uses that require district heating are space and water heating. District heating markets are well-established in several cold-climate nations, such as Denmark, Iceland, Germany, the United States, other EU countries, and Canada.
- However, the District heating networks powered by renewable energy sources may significantly reduce emissions and help governments meet their emission reduction objectives. Various governments have established statutory responsibilities and incentives, such as grants, subsidies, and energy taxes, to boost the percentage of renewables in heat generation.
- Moreover, District heating was previously primarily powered by byproducts of power plants, waste-to-energy facilities, and industrial activities. However, Sweden is now incorporating more renewable energy sources into the mix. Due to competition, this localized kind of electricity has risen to the national top home-heating industry.
- According to BDH, in 2023, Germany saw sales of approximately 790,500 gas heating systems. Among these, approximatly 94,000 employed traditional low-temperature technology, with the majority, over 696,500, opting for condensing boiler technology.
Asia-Pacific Holds a Significant Share in the District Heating Market
- The primary reasons driving the market's growth in China are rising disposable income, increased worries about CO2 emissions, and high usage of heating and cooling systems. Moreover, OECD states that projections for India and China's per capita GDP might climb sevenfold by 2060.
- Governments in the Asia-Pacific region are also collaborating with local businesses to develop the home market. For example, the Beijing District Heating Group is a major heating firm in China. The firm provided heating solutions to the central Beijing government and army, Chinese embassies, significant corporations and organizations, and the general people. It also has a large number of projects in other provinces.
- Modern district heating systems are especially important for Southeast Asian countries, where air pollution causes long-term economic expenses and hundreds of thousands of premature fatalities. The Future of Cooling in Southeast Asia investigates the anticipated growth in energy consumption, peak power demand, and CO2 emissions by 2040.
- India and Australia are two of the region's biggest marketplaces. The regional market is rising due to increased investment in district heating and cooling solutions and increased government activities to promote these solutions.
- To respond to energy crises and climate change, the South Korean government established a national plan to promote zero energy buildings, and several energy efficiency policies for new and existing buildings in recent years have been developed to achieve these plans.
District Heating Industry Overview
The district heating market is moderately competitive and has many global and regional players. These companies are working hard to broaden their consumer base globally. To gain a competitive advantage during the predicted term, they also prioritize R&D expenditure in developing innovative solutions, strategic collaborations, and other organic and inorganic growth tactics.
In May 2023, Vattenfall AB and Coca-Cola announced the collaboration in Sweden and have set ambitious climate targets for net zero emissions across their entire value chains by 2040. The companies have initiated a pilot project with three charging stations to meet the need for powering electric transport.
In March 2023, NRG Energy Inc completed its acquisition of Vivint Smart Home, Inc. by accelerating NRG's consumer-focused growth strategy and offering consumers simple, connected experiences to power, protect, and manage their homes intelligently. NRG is at the intersection of energy and home services, with a unique end-to-end smart home ecosystem underpinned by our exceptional customer experience.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.2.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.2.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.2.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.2.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.2.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.3 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
- 4.5 Government Initiatives and Programs on District Heating Transition
- 4.6 Key Trends and Innovations in District Heating
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Augmented Demand for Energy-efficient and Cost-effective Heating Systems
- 5.1.2 Rising Urbanization and Industrialization
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 High Infrastructure Cost
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Plant Type
- 6.1.1 Boiler
- 6.1.2 Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
- 6.2 By Heat Source
- 6.2.1 Coal
- 6.2.2 Natural Gas
- 6.2.3 Renewables
- 6.2.4 Oil and Petroleum Products
- 6.3 By Application
- 6.3.1 Residential
- 6.3.2 Commercial and Industrial
- 6.4 By Geography
- 6.4.1 North America
- 6.4.2 Europe
- 6.4.3 Asia
- 6.4.4 Australia and New Zealand
- 6.4.5 Latin America
- 6.4.6 Middle East and Africa
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Company Profiles
- 7.1.1 Vattenfall AB
- 7.1.2 SP Group
- 7.1.3 Danfoss Group
- 7.1.4 Engie
- 7.1.5 NRG Energy Inc.
- 7.1.6 Statkraft AS
- 7.1.7 Logstor AS
- 7.1.8 Shinryo Corporation
- 7.1.9 Vital Energi Ltd
- 7.1.10 Gteborg Energi
- 7.1.11 Alfa Laval AB
- 7.1.12 Ramboll Group AS
- 7.1.13 Keppel Corporation Limited
- 7.1.14 FVB Energy











