 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1440176
海運:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2024-2029)Sea Freight Forwarding - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
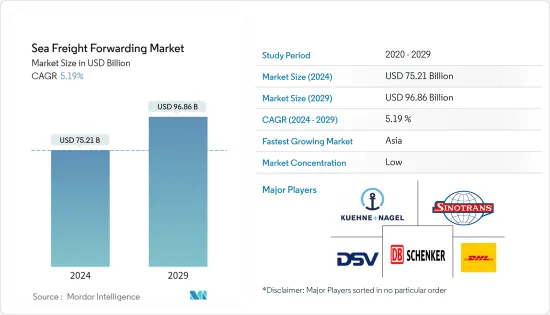
預計2024年海運市場規模為752.1億美元,預計2029年將達到968.6億美元,預測期內(2024-2029年)年複合成長率為5.19%。
主要亮點
- 由於網路普及不斷提高、購買力平價不斷上升以及專為電子商務行業設計的基礎設施和服務的發展,全球海運市場正在蓬勃發展。冠狀病毒的感染疾病對航運業產生了負面影響,為了安全和防止 COVID-19 的傳播,航運業員工已關閉。
- 海運已成為多個最終用戶產業的首選模式,多個策略合作夥伴關係也可能在預測期內推動海運的成長。不斷成長的全球跨境電子商務市場正在推動拼箱貨量的成長,對海運市場的成長產生正面影響。
- 數千年來,海上運輸一直是運輸貨物、產品和人員的重要手段。如今,船舶運輸煤炭、石油和天然氣等重要商品,支撐全球經濟。光是2021年,就出貨了約150萬噸煤炭和110萬噸石油。
- 更重要的是,大約85%的貨物透過海上運輸,主要是透過貨櫃船。與其他運輸工具相比,船舶具有巨大的運力,使其更加經濟,適合運輸大型、重型和體積大的物品,同時排放相對較低。
- 船東和分析師表示,預計今年剩餘時間和 2023 年運費將進一步下降。隨著未來兩年大量新船投入使用,2023年至2024年船隊規模淨成長率預計將超過9%。相比之下,Bremer 表示,2024 年貨櫃吞吐量可能會略有負成長。
海運市場趨勢
跨經紀商電子商務的興起推動市場
2021年全球零售電子商務銷售額達到約52,110億美元,預計未來幾年電子零售收益將進一步以更快的速度成長。此外,網路購物是全球最受歡迎的線上活動之一,推動了中國、印度和印尼等新興市場的國內和跨境電子商務。這包括直接面對消費者的銷售以及電子產品、藥品和消費品的出貨。
隨著新興經濟體逐漸從製造業驅動的成長轉向由不斷擴大的中階驅動的更高消費水平,電子商務的成長與該地區的消費成長密切相關。
跨境電商已佔中國進出口貿易總額的25%。與中國相比,其他地區的電子商務相關業務規模要小得多,但也在快速成長。海運是電商貨運最受歡迎的方式之一,受到許多企業青睞,預計2021年海運量將增加至200億噸。
海上貿易運輸量增加
海上貿易的成長透過降低運輸成本使世界各地的客戶受益。由於航運作為一種運輸方式的效率不斷提高以及經濟進一步自由化,該行業持續成長的前景仍然樂觀。
儘管目前情況嚴峻,但該行業的長期前景仍然非常樂觀。世界人口持續成長,開發中國家將繼續需要更多的貨物和原料透過海上安全有效地運輸。近期,透過海上進行的國際貿易量再次開始穩定成長。航運是最環保、最具成本效益的商業運輸方式,這一事實最終將導致海上運輸在世界貿易中所佔的佔有率不斷增加。
超過5萬艘商船在海外營運,運輸各類貨物。全球船隊由超過 100 萬名幾乎各國籍的海員組成,在 150 多個國家註冊。
根據聯合國貿易和發展會議 (UNCTAD) 的數據,商船運輸為全球經濟帶來了價值約 3,800 億美元的貨運成本,約佔貿易總額的 5%。
工業化程度的提高和國民經濟自由化促進了自由貿易和消費品需求的成長。技術的進步也提高了運輸作為運輸手段的效率和速度。
1990年至2020年間,海運貿易量增加了一倍多,達到106.5億噸。 2020年,貨櫃船承運國際海上貿易量18.5億噸。截至 2021 年 1 月,巴拿馬持有世界上最大的商船隊,營運商席位達 3.436 億載重噸。過去30年,海運貿易流量成長了近兩倍,2021年達到1,500億噸,導致海運業務量穩定成長。
海運行業概況
海運市場競爭激烈且高度分散,參與者眾多。海運是充當中間人的個人或公司,透過普通海洋運輸運輸貨物並代表客戶安排所有運輸事宜。
海運處理所有必要的物流並執行與出貨相關的活動。從 2012 年到 2022 年,海運量增加了兩倍,近年來市場上出現了許多新進業者。
市場上現有的主要企業包括Kuehne+Nagel、DHL Supply Chain & Global Forwarding、DB Schenker、DSV Panalpina、中國外運送、Expeditors、日本通運、CEVA Logistics、CH Robinson、嘉里物流等。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月分析師支持
目錄
第1章 簡介
- 研究成果
- 調查先決條件
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
- 分析調查方法
- 調查階段
第3章執行摘要
第4章市場洞察
- 目前的市場狀況
- 價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 科技趨勢
- 投資場景
- 政府法規和舉措
- 焦點 - 海運成本/運費
- 電商產業洞察
- COVID-19疾病對海運市場的影響
第5章市場動態
- 市場促進因素
- 市場限制因素
- 市場機會
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭公司之間敵對的強度
第6章市場區隔
- 按類型
- FCL
- LCL
- 其他
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 歐洲
- 德國
- 法國
- 荷蘭
- 英國
- 義大利
- 其他歐洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 中國
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 印度
- 新加坡
- 馬來西亞
- 印尼
- 韓國
- 其他亞太地區
- 中東和非洲
- 南非
- 埃及
- 海灣合作理事會國家
- 其他中東和非洲
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 智利
- 南美洲其他地區
- 北美洲
第7章 競爭形勢
- 市場集中度概況
- 公司簡介
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Sinotrans
- DHL
- DB Schenker
- DSV Panalpina
- Expeditors
- CH Robinson
- Ceva Logistics
- Kerry Logistics
- Nippon Express
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Geodis
- Fr. Meyer's Sohn
- Yusen Logistics
- Bollore Logistics
第8章市場的未來
第9章 免責聲明
The Sea Freight Forwarding Market size is estimated at USD 75.21 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 96.86 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.19% during the forecast period (2024-2029).

Key Highlights
- The global sea freight forwarding market is booming, owing to the growing internet penetration, increasing Purchasing Power Parity, and developments in infrastructure and services designed particularly for the e-commerce industry. The epidemic negatively impacted the shipping industry as workforces in these sectors were shut down for safety and to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
- Sea freight forwarding has emerged as a preferred mode among several end-user industries and several strategic partnerships are also likely to promote the growth of sea freight forwarding during the forecast period. The growing global cross-border e-commerce market is driving the LCL volume and is positively impacting the sea freight forwarding market growth.
- Sea freight has been an important means of transporting goods, products, and people for thousands of years. Today, ships transport vital commodities such as coal, oil and gas, supporting the global economy. In 2021 alone, about 1.5 million tonnes of coal and about 1.10 million tonnes of oil were shipped.
- More importantly, about 85% of all goods are transported by sea, mainly by container ships. Compared to other means of transport, vessels have vast capacities suitable for transporting large, heavy, and bulky items that are more economical while producing relatively small amounts of emissions.
- Shipping rates are expected to drop further for the rest of the year and into 2023, according to shipowners and analysts. With a number of new vessels entering service over the next two years, net growth in the fleet size is expected to be over 9% through 2023 to 2024. By contrast, container volume growth in 2024 could be slightly negative according to Braemer.
Sea Freight Forwarding Market Trends
Rising Cross Broder E-Commerce is driving the Market
In 2021, retail e-commerce sales worldwide amounted to around USD 5,211 Billion and e-retail revenues are projected to grow even further at a quicker pace in the coming few years. Further, as online shopping is one of the most popular online activities worldwide is driving both the domestic and cross-border e-commerce in developing markets such as China, India, and Indonesia. This encompasses not just direct-to-consumer retail, but also shipments of electronics, pharmaceuticals, and consumer packaged goods.
Growth in e-commerce is tied very closely to the consumption growth in the region as developing economies make the gradual shift from growth by manufacturing for export to higher levels of consumption by expanding middle classes.
In China, cross-border e-commerce transactions already accounted for up to 25 percent of total import and export trading volumes. Compared to China, in other regions, the size of e-commerce related businessess is much smaller, but the growth is also rapid. One of the most preferred modese for e-commerce freight forwarding is through sea and many business are favoring that as evidenced by the growing of ocean freight volumes to 20 billion tons in 2021.
Rise In Seaborne Trade Transport Volume
The growth of seaborne trade benefits customers all around the world by lowering the cost of shipping. The prospects for the industry's continued growth remain favorable due to the increasing efficiency of shipping as a mode of transportation and further economic liberalization.
Despite the current circumstances, the industry's long-term prospects are still highly favorable. The world's population is still growing, and developing nations will keep needing more of the goods and raw materials that shipping transfers so securely and effectively. The volume of international trade conducted by sea has recently started to rise steadily once more. The fact that shipping is the most environmentally benign and cost-effective method of commercial transportation should eventually lead to an increase in the percentage of world trade that is transported by sea.
Over 50,000 merchant ships operate abroad and carry all different kinds of goods. More than a million seafarers of essentially every nationality make up the world fleet, which is registered in more than 150 countries.
According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the operation of commercial ships generates freight rates worth roughly USD 380 billion for the global economy or about 5% of all trade.
The expansion of free trade and the demand for consumer goods has been fueled by rising industrialization and the liberalization of national economies. Technology advancements have also increased the effectiveness and speed of the shipping as a mode of transportation.
Between 1990 and 2020, seaborne trade volumes more than doubled to reach 10.65 billion tons. In 2020, 1.85 billion tons of international seaborne trade was carried by container ships. As of January 2021, Panama had the world's largest merchant fleet with 343.6 million DWT operator seats. The business volume of ocean freight forwarders has been steadily increasing because in the last three decades, the seaborne trade transport volume roughly tripled, reaching 150 billion metric tons in 2021.
Sea Freight Forwarding Industry Overview
The Sea Freight Forwarding Market is highly competitive and is highly fragmented with the presence of many players. A Sea Freight forwarder is an individual or company that acts as an intermediary and dispatches the shipments via common sea carriers and makes all arrangements for those shipments on behalf of its clients.
Sea Freight forwarders handle all the logistics needed and perform activities pertaining to shipments. With the Ocean freight volumes tripling from 2012 to 2022, the market has seen many new players entering in the last few years.
Some of the existing major players in the market include Kuehne + Nagel, DHL Supply Chain & Global Forwarding, DB Schenker, DSV Panalpina, Sinotrans, Expeditors, Nippon Express, CEVA Logistics, C.H. Robinson, and Kerry Logistics.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.3 Technological Trends
- 4.4 Investment Scenarios
- 4.5 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.6 Spotlight - Sea Freight Transportation Costs/Freight Rates
- 4.7 Insights on the E-commerce Industry
- 4.8 Impact of COVID-19 on the Sea Freight Forwarding Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.3 Market Opportunities
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 5.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Type
- 6.1.1 Full Container Load (FCL)
- 6.1.2 Less-than Container Load (LCL)
- 6.1.3 Others
- 6.2 By Geography
- 6.2.1 North America
- 6.2.1.1 United States
- 6.2.1.2 Canada
- 6.2.1.3 Mexico
- 6.2.2 Europe
- 6.2.2.1 Germany
- 6.2.2.2 France
- 6.2.2.3 Netherlands
- 6.2.2.4 United Kingdom
- 6.2.2.5 Italy
- 6.2.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 6.2.3 Asia-Pacific
- 6.2.3.1 China
- 6.2.3.2 Japan
- 6.2.3.3 Australia
- 6.2.3.4 India
- 6.2.3.5 Singapore
- 6.2.3.6 Malaysia
- 6.2.3.7 Indonesia
- 6.2.3.8 South Korea
- 6.2.3.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 6.2.4 Middle East & Africa
- 6.2.4.1 South Africa
- 6.2.4.2 Egypt
- 6.2.4.3 GCC Countries
- 6.2.4.4 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 6.2.5 South America
- 6.2.5.1 Brazil
- 6.2.5.2 Chile
- 6.2.5.3 Rest of South America
- 6.2.1 North America
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 Kuehne + Nagel
- 7.2.2 Sinotrans
- 7.2.3 DHL
- 7.2.4 DB Schenker
- 7.2.5 DSV Panalpina
- 7.2.6 Expeditors
- 7.2.7 C.H Robinson
- 7.2.8 Ceva Logistics
- 7.2.9 Kerry Logistics
- 7.2.10 Nippon Express
- 7.2.11 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 7.2.12 Geodis
- 7.2.13 Fr. Meyer's Sohn
- 7.2.14 Yusen Logistics
- 7.2.15 Bollore Logistics










