 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1636191
印度的 EPCM(工程、採購和施工管理):市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢和統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
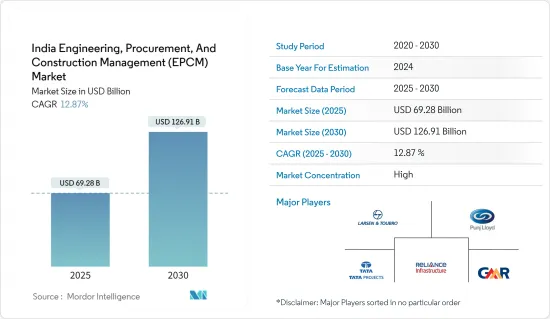
印度EPCM(工程、採購和施工管理)市場規模預計到2025年為692.8億美元,預測期內(2025-2030年)複合年成長率為12.87%,到2030年將達到1269.1億美元。
主要亮點
- 印度的工程、採購和施工(EPC)市場在該國基礎設施發展中發揮著至關重要的作用。這個市場呈現出不同產業的趨勢、挑戰和機會。在雄心勃勃的基礎設施藍圖和工業進步的推動下,印度的 EPC 市場正在穩步成長。在政府支持和私人投資的支持下,市場的複合年成長率預計將保持勢頭。大量投資正投入道路建設、鐵路網現代化和智慧城市使命等巴拉特馬拉計劃等措施。此外,太陽能、風能等可再生能源計劃也迅速增加。
- 此外,火力發電廠、水電廠、核能發電廠的開發和擴建以及輸電加固也在取得進展。智慧城市使命、AMRUT 和 Bharatmala 等關鍵舉措凸顯了印度對基礎設施發展的承諾。此外,快速的工業化和都市化也增加了對基礎設施發展的需求。最後,外商直接投資政策的自由化正在吸引國際EPC參與者,他們也正在採用尖端的施工技術和計劃管理工具。
印度EPCM(工程、採購和施工管理)市場趨勢
基礎建設發展帶動EPC服務需求
印度政府已著手實施雄心勃勃的基礎設施項目,包括智慧城市使命、Bharatmala Pariyojana 高速公路項目和 Sagarmala計劃等。智慧城市使命旨在透過加強核心基礎設施、提高生活品質、創造清潔和永續的環境以及引入「智慧」解決方案來改善城市。該任務以永續和包容性成長為重點,重點關注緊湊地區,旨在創建可複製的模式來指南其他城市。這項舉措不僅改變了各個城市,也促進了全國各地邁向智慧城市中心的運動。
這些舉措凸顯了印度對基礎建設發展的承諾,也為 EPCM 服務帶來了巨大機會。隨著都市化的加快,從地鐵到機場和智慧城市計劃等城市基礎設施亟待升級。同時,旨在加強製造業的「印度製造」宣傳活動刺激了新工廠和工業設施的建設,進一步拉動了對EPCM服務的需求。
「印度製造」計畫的全球推出標誌著印度重新關注製造業。該舉措的主要目標是將印度定位為全球製造業的頂級競爭者。自成立以來,印度政府迎來了多項改革,以加強製造、設計、創新和新興企業。在全球經濟低迷的背景下,印度以7.5%的成長速度成為成長最快的經濟體,且成長速度持續加快。 「印度製造」、「數位印度」、「100 個智慧城市」和「印度技能」等舉措在推動這一成長方面發揮關鍵作用。
「印度製造」的具體目標是將印度融入全球供應鏈,並強調印度企業在全球舞台上發揮作用的必要性。印度大幅開放經濟,向外國直接投資(FDI)開放國防、鐵路、建築、保險、退休基金和醫療設備等產業。此舉使印度成為世界上最開放的經濟體之一。為進一步改善營商環境,印度政府優先考慮改善營商便利度。重點在於簡化法規並創造更容易營商的環境。利用技術,政府已將 14 項服務整合到 eBiz 入口網站中,以簡化各個政府機構的核准流程。 「印度製造」的影響已經顯現。
總體而言,印度正在見證「印度製造」計劃的實際成效,包括經濟指標上升、外國投資增加和製造業擴張。在智慧城市使命、Bharatmala Pariyojana、Sagarmala Project和Make in India的共同努力下,印度的基礎設施正在重建。這項雄心勃勃的議程將加強城市和工業的能力,為工程、採購和施工管理服務打開大門。隨著印度深化融入全球供應鏈並改善商業環境,印度正在成為重要的製造業和基礎設施中心,為我正在努力的持續經濟成長和發展奠定了基礎。
由於投資和舉措增加,印度能源和公共產業行業需求激增
印度仍然受到電網不可靠的困擾,很大一部分人口沒有連網,每天都面臨停電的情況。印度電力產業因其多樣化的能源來源而在全球脫穎而出。除煤炭、天然氣、石油、核能等傳統能源來源外,我們還利用風能、太陽能、水力發電、都市垃圾、生質能等新能源來源。在向清潔能源轉型的推動下,印度政府正在對該產業進行重大改革。這包括升級基礎設施和投資綠色能源,包括風能和太陽能。
印度政府認知到私人投資的重要作用,並推出了多項獎勵計劃來加強該行業。印度的雄心勃勃的目標是在 10 年內將二氧化碳排放減少 45%,到 2030 年 50% 的電力來自可再生能源,並最終在 2070 年實現碳中和。這些目標和印度強勁穩定的經濟成長為能源公司提供了良好的前景。
印度的2030年願景包括5億千瓦的清潔能源產能,其中2.8億度將來自太陽能。截至2023年2月,印度總發電量為412.21GW,其中約100GW來自清潔能源。值得注意的是,印度風電裝置容量位居亞洲第二,僅次於中國。它也是世界上成長第五快的太陽能市場和最具成本效益的太陽能生產國。
在全球範圍內,印度在可再生能源發電方面排名第四。政府已在未來五年內投入 420 億美元的累計,用於促進創新和擴大能源產業。印度在世界銀行 2019 年營商便利度-獲得電力研究中取得了 89.4 分的驕人成績。此分數評估與電網連接的便利性、供應的可靠性、電價的透明度和電價。順便說一下,丹麥的得分稍高一些,為90.2。
展望未來,印度製定了雄心勃勃的離岸風力發電計劃,目標是到2022年建立5GW計劃,到2030年建立30GW項目。併網太陽能屋頂計畫的目標是到2022年實現40GW的屋頂太陽能發電(RTS)計劃容量。主要重點是研究、開發和示範(RD&D),以加強新能源和可再生能源的引進。新能源和可再生能源部(MNRE)積極推動研究和開發,以提高能源技術、材料和當地生產能力。
整體而言,印度電力產業正在經歷重大變革時期,能源結構多元化,並明顯專注於清潔能源。這種轉變正在刺激基礎設施的重大加強並吸引大量投資。印度有著減少碳排放、增加可再生能源產能並最終實現碳中和的明確目標,已成為對能源公司有吸引力的後起之秀。積極的政府措施進一步增強了這種吸引力,包括促進創新和促進行業成長的慷慨資金和支持政策。隨著印度加強其能源格局並採用更多的再生能源,它正在鞏固其作為永續能源全球領跑者的地位。這承諾為其公民提供更可靠的電力供應,並強調印度對全球環境目標的承諾。
印度EPCM(工程、採購和施工管理)產業概況
印度的工程、採購和施工管理 (EPCM) 市場分散,參與者眾多。雖然主要企業,但市場分散,不少中小企業積極進入市場,特別是專業領域和區域市場。該領域的一些知名公司包括 Larsen &Toubro (L&T)、Tata Projects Limited、Punj Lloyd Group、Reliance Infrastructure Limited 和 GMR Group。
其他好處:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章簡介
- 研究成果
- 研究場所
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
第3章執行摘要
第4章市場動態
- 市場概況
- 市場促進因素
- 可再生能源計劃
- 政府舉措
- 市場限制因素
- 監管和官僚障礙
- 建築材料成本上漲
- 市場機會
- 採用智慧基礎設施技術
- 價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 買家/消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭公司之間敵對關係的強度
- PESTLE分析
- 洞察市場創新
第5章市場區隔
- 按服務
- 設計
- 採購
- 建造
- 其他服務
- 按行業分類
- 住宅、基礎設施(交通)、能源和公共產業
- 產業
- 基礎設施(交通)
- 能源/公共產業
第6章 競爭狀況
- Market Concetration Overview
- 公司簡介
- Larsen & Toubro(L&T)
- Tata Projects Limited
- Punj Lloyd Group
- Reliance Infrastructure Limited
- GMR Group
- Afcons Infrastructure Limited
- Hindustan Construction Company(HCC)
- NCC Limited(Nagarjuna Construction Company)
- IVRCL Limited
- KEC International
- Gammon India Limited
- Simplex Infrastructures Limited
- Rays Power Infra Limited
- Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Ltd
- Salasar Techno Engineering Ltd(STEL)
第7章 未來趨勢
The India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management Market size is estimated at USD 69.28 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 126.91 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 12.87% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- India's engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) market is pivotal in the nation's infrastructure landscape. This market presents a spectrum of trends, challenges, and opportunities spanning diverse industries. India's EPC market has grown robustly and is fueled by ambitious infrastructure blueprints and industrial advancements. Bolstered by governmental impetus and private investments, the market's compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is poised to maintain its vigor in the coming years. Noteworthy investments are channeled into the Bharatmala project for road construction, the modernization of the railway network, and initiatives like the Smart Cities Mission. In addition, there is a notable surge in renewable energy projects, spanning solar, wind, and other avenues.
- The nation is also witnessing the development and expansion of thermal, hydroelectric, and nuclear power plants alongside a bolstered power transmission network. Key initiatives such as the Smart Cities Mission, AMRUT, and Bharatmala underscore India's commitment to infrastructure growth. Furthermore, the nation's rapid industrialization and urbanization fuel an escalating demand for enhanced infrastructure. Lastly, the liberalization of FDI policies is drawing in international EPC players, who are also embracing cutting-edge construction technologies and project management tools.
India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Market Trends
Infrastructure Development Driving Demand For EPC Services
The Indian government has embarked on ambitious infrastructure programs, notably the Smart Cities Mission, Bharatmala Pariyojana for highways, and the Sagarmala Project for ports. The Smart Cities Mission aims to elevate cities by enhancing core infrastructure, ensuring a high quality of life, fostering a clean and sustainable environment, and implementing 'Smart' Solutions. Emphasizing sustainable and inclusive growth, the mission focuses on compact areas, aiming to create a replicable model to guide other cities. This initiative is not just about transforming individual cities but about catalyzing a nationwide movement toward smarter urban centers.
These initiatives underscore India's commitment to infrastructure development, presenting significant opportunities for EPCM services. With urbanization surging, there is a critical need for upgraded urban infrastructure, from metro rail systems to airports and smart city projects. In tandem, the "Make in India" campaign, aimed at bolstering manufacturing, is spurring the construction of new plants and industrial facilities, further driving the demand for EPCM services.
The global launch of the "Make in India" initiative marked India's renewed focus on manufacturing. The primary goal of this initiative is to position India as the top choice for global manufacturing. Since its inception, the Indian government has spearheaded numerous reforms to bolster manufacturing, design, innovation, and startups. Amidst a globally subdued economic landscape, India has emerged as the fastest-growing economy, boasting a growth rate of 7.5% that continues to accelerate. Initiatives like "Make in India," "Digital India," "100 Smart Cities," and "Skill India" have played a pivotal role in driving this growth.
"Make in India" specifically targets integrating India into the global supply chain, emphasizing the need for Indian companies to excel on a global stage. India has significantly liberalized its economy, opening sectors like defense, railways, construction, insurance, pension funds, and medical devices to foreign direct investment (FDI). This move has positioned India as one of the most open economies worldwide. To further enhance the business environment, the Indian government has prioritized improving the ease of doing business. The focus is on simplifying regulations to foster a conducive environment for businesses. Leveraging technology, the government has integrated 14 services into the eBiz portal, streamlining clearances from various government agencies. The impact of "Make in India" is already evident.
Overall, India is witnessing tangible outcomes from its "Make in India" initiative, with economic indicators on the rise, foreign investments increasing, and the manufacturing sector expanding. The concerted efforts of the Smart Cities Mission, Bharatmala Pariyojana, Sagarmala Project, and Make in India are reshaping India's infrastructure. This ambitious agenda bolsters urban and industrial capabilities and opens up significant avenues for engineering, procurement, and construction management services. With India's deepening integration into global supply chains and ongoing efforts to improve its business environment, the nation is on track to emerge as a pivotal manufacturing and infrastructure hub, setting the stage for sustained economic growth and development.
India's Energy And Utilities Segment Experiencing Surge in Demand, Driven by Increased Investments and Initiatives
India still grapples with an unreliable power grid, leaving a significant portion of its populace unconnected and facing daily power outages. The country's power sector stands out globally for its diverse energy sources. India harnesses traditional avenues like coal, natural gas, oil, and nuclear power alongside newer options such as wind, solar, hydropower, municipal waste, and biomass. Driven by a commitment to transition to clean energy, the Indian government is spearheading a substantial industry overhaul. This includes revamping infrastructure and channeling investments into green energy, notably wind and solar power.
Recognizing the pivotal role of private investment, the Indian government has rolled out several incentive schemes to bolster the sector. Setting ambitious targets, India aims to slash carbon emissions by 45% by the end of the decade, source 50% of its electricity from renewables by 2030, and ultimately achieve carbon neutrality by 2070. These targets and India's robust and consistent economic growth present lucrative prospects for energy companies.
India's vision for 2030 includes a 500 GW clean energy capacity, with a significant 280 GW from solar power. As of February 2023, India's total generation capacity stood at 412.21 GW, with approximately 100 GW attributed to clean sources. Notably, India boasts the second-highest wind power capacity in Asia, trailing only China. It also holds the title of the world's fifth-fastest-growing solar energy market and the most cost-efficient producer of solar power.
On the global stage, India ranks fourth in renewable energy generation. The government has earmarked a substantial USD 42 billion over the next five years to foster innovation and scale up the energy sector. India's commitment to enhancing its energy landscape is underscored by its impressive score of 89.4 in the World Bank's 2019 Ease of Doing Business - Getting Electricity survey. This score evaluates the ease of connecting to the grid, supply reliability, tariff transparency, and electricity pricing. For context, Denmark secured a slightly higher score of 90.2.
Looking ahead, India has laid out ambitious plans for offshore wind energy, aiming to establish 5 GW of projects by 2022 and a substantial 30 GW by 2030. The "Grid Connected Solar Rooftop Program" is set on achieving a 40 GW capacity for rooftop solar (RTS) projects by 2022. The key focus is on research, development, and demonstration (RD&D) to bolster the adoption of new and renewable energy. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) actively promotes R&D to advance energy technologies, materials, and local production capabilities.
Overall, India's power sector is undergoing a significant transformation, a diverse energy mix, and a notable focus on clean energy. This shift is spurring substantial infrastructure enhancements and drawing in considerable investments. With clear targets to slash carbon emissions, ramp up renewable energy capacity, and ultimately achieve carbon neutrality, India emerges as an attractive prospect for energy firms. The government's proactive steps bolstered this appeal, such as generous funding and supportive policies, which nurture innovation and foster sectoral growth. As India fortifies its energy landscape and embraces more renewables, the country is on track to cement its position as a global frontrunner in sustainable energy. This promises a more dependable power supply for its citizens and underscores India's commitment to worldwide environmental objectives.
India Engineering, Procurement, And Construction Management (EPCM) Industry Overview
The Indian engineering, procurement, and construction management (EPCM) market features a fragmented landscape, hosting numerous players. Although dominant players exist, the market is fragmented, with many small to mid-sized companies actively participating, especially in specialized sectors or regional markets. Prominent entities in this sector include Larsen & Toubro (L&T), Tata Projects Limited, Punj Lloyd Group, Reliance Infrastructure Limited, and GMR Group.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Renewable Energy Projects
- 4.2.2 Government Initiatives
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Regulatory and Bureaucratic Hurdles
- 4.3.2 Increase in Cost of Construction Material
- 4.4 Market Opportunities
- 4.4.1 Adoption of Smart Infrastructure Technologies
- 4.5 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.7 PESTLE Analysis
- 4.8 Insights into Technology Innovation in the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Engineering
- 5.1.2 Procurement
- 5.1.3 Construction
- 5.1.4 Other Services
- 5.2 By Sectors
- 5.2.1 Residential Industrial, Infrastructure (Transportation), and Energy and Utilities
- 5.2.2 Industrial
- 5.2.3 Infrastructure (Transportation)
- 5.2.4 Energy and Utilities
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concetration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Larsen & Toubro (L&T)
- 6.2.2 Tata Projects Limited
- 6.2.3 Punj Lloyd Group
- 6.2.4 Reliance Infrastructure Limited
- 6.2.5 GMR Group
- 6.2.6 Afcons Infrastructure Limited
- 6.2.7 Hindustan Construction Company (HCC)
- 6.2.8 NCC Limited (Nagarjuna Construction Company)
- 6.2.9 IVRCL Limited
- 6.2.10 KEC International
- 6.2.11 Gammon India Limited
- 6.2.12 Simplex Infrastructures Limited
- 6.2.13 Rays Power Infra Limited
- 6.2.14 Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Ltd
- 6.2.15 Salasar Techno Engineering Ltd (STEL)









