|
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1563423
固體冷卻材料及系統 (PDRC、熱、熱電等) 的市場與技術 (2025-2045年)Solid State Cooling Materials and Systems PDRC, Caloric, Thermoelectric, Other: Markets, Technology 2025-2045 |
||||||
處於主導地位的蒸汽壓縮冷卻未來將不可避免地經歷S形曲線,預計20年內其市場佔有率將大幅下降。未來十年,許多固態冷卻新創公司預計將擴大市場佔有率,並被冷卻巨頭收購,為投資者提供主要退出途徑。
固態冷卻為冷卻帶來了許多新的創新,包括引入1kW 微晶片、更高溫度的6G 通訊基礎設施計劃、下一代柔性太陽能電池板,甚至是即使在50°C 的夏季也能保持涼爽的衣服前景是滿足需求的。固態冷卻是多功能智慧材料(包括結構電子產品)趨勢的一部分。
本報告提供固體冷卻材料及系統的市場調查,彙整新的固體冷卻技術概要,主要材料的R&D趨勢,技術藍圖,主要材料的市場規模的轉變·預測,案例研究,進入經營者,事業機會分析等資料。
目錄
第1章 摘要整理·結論
- 本報告的目的
- 調查方法
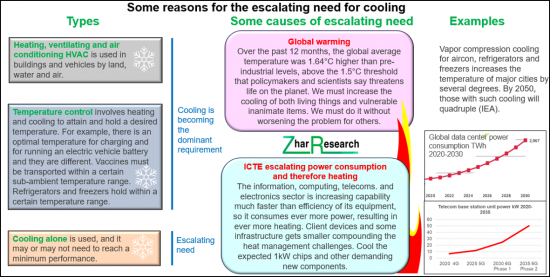
- 增加冷卻需求的多種原因
- 固態冷卻的本質以及為何它現在成為優先事項
- 散熱工具包,多功能趨勢,最佳固態散熱工具
- 18個主要結論
- 主要降溫技術:2000年-2045年
- 重要的熱量冷卻研究數量:依技術分類
- 固態冷卻研究的主要材料
- PDRC評估
- 電熱冷卻的評估
- 彈性熱量冷卻的評估
- 熱電冷卻的評估
- 冷卻路線圖:依市場/技術劃分
- 市場預測
- 背景預測
第2章 簡介
- 概要
- 冷卻需求往往較大且性質不同。
- 冷卻需求重大變更範例:2025-2045 年
- 冷卻技術將如何過渡到智慧材料
- 重塑空調,使其更節能、環保且價格實惠
- 廣泛使用和提議的不良材料:這對您來說是一個機會
- 2024 年公佈的固態冷卻競爭對手範例
第3章 PDRC (Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling)
- 概要
- PDRC 基礎知識
- 基於結構和成分的輻射冷卻材料
- 潛在優勢與應用
- 2024 年和 2023 年的其他重要進展
- PDRC 商業化的公司
- 3M USA
- BASF Germany
- i2Cool USA
- LifeLabs USA
- Plasmonics USA
- Radicool Japan, Malaysia etc.
- SkyCool Systems USA
- SolCold Israel
- Spinoff from University of Massachusetts Amherst USA
- SRI USA
- PDRC SWOT報告
第4章 自我適應型·轉換可能·調整可能·Janus型·反斯托克斯型的固體冷卻
- 整體概況/SWOT
- 輻射冷卻技術成熟度曲線
- 自適應且可切換的輻射冷卻
- 雙方協調輻射冷卻:SWOT 評估
- 反斯托克斯螢光冷卻:SWOT 評估
第5章 相位改變·熱冷卻
- 結構和鐵磁相變冷卻模式和材料
- 固態相變冷卻:在特定應用中可能與其他形式競爭
- 與熱量冷卻相關的物理原理
- 熱量冷卻的工作原理
- 熱電冷卻和熱冷卻的比較以及優越熱冷卻技術的鑑定
- 促進熱量冷卻使用的研究提案
- 電熱冷卻
- 磁熱冷卻:SWOT 評估
- 機械熱冷卻(彈性、壓力、扭轉)
- 多熱量冷卻
第6章 實行技術:超材料以及其他的先進性的光冷卻:新興材料和設備
- 超材料
- 先進的光子冷卻和加熱預防
第7章 與其他的固體冷卻的用戶及電力供給者的未來的熱電冷卻熱電發電
- 基礎知識
- 熱電材料
- 廣泛且靈活的熱電冷卻:有待解決的市場空白
- 建築物的輻射冷卻:2024 年熱電發電帶來的多功能性
- TEC 與 TEG 散熱問題:不斷發展的解決方案
- 熱電冷卻和冷卻發電方面的 20 項進展及 2024 年回顧
- 2023 年的進展
- 82 家 Peltier 熱電模組和產品製造商
Summary
Solid state cooling is now a superb investment with impressive research advances through 2024. Uniquely, the new Zhar Research report, "Solid State Cooling Materials and Systems PDRC, Caloric, Thermoelectric, Other: Markets, Technology 2025-2045" gives that new picture with PhD level analysis.
Shake up
Nothing is forever and the dominant vapor compression cooling will be subject to the inevitable S curve, sharply losing share within 20 years. Long before that, within ten years, many solid-state cooling startups starting to take share will be bought by the cooling giants playing catch-up, this providing an excellent exit for investors.
Serving new needs
Solid-state cooling will serve the many new needs for cooling such as 1kW microchips arriving, planned hotter 6G Communications infrastructure, next generation flexible solar panels and even apparel that cools well in the lethal 50C summers arriving. Solid-state cooling is part of the trend to multifunctional smart materials including structural electronics: vapor compression is not.
Latest research is important
This commercially-oriented 339-page report has 292 research advances assessed from 2024 and 2023, 102 companies mentioned, ten SWOT appraisals, 33 new infograms, 17 forecast lines 2025-2045. The primary focus is on the technologies judged to have the largest commercial potential 2025-2045 - radiative cooling into the atmospheric window, notably the variant called passive daytime radiative cooling, the many forms of caloric cooling and thermoelectric cooling being reinvented. Multi-mode and multifunctional forms are revealed and new enabling technologies such as metamaterial cooling explained.
Lucid insights
The 30-page Executive Summary and Conclusions is sufficient in itself, presenting roadmaps 2025-2045, those 17 forecast lines, many new pie charts, comparisons, SWOTs, radical new needs. See projections such as best cooling temperature differences and cooling power achievements likely 2025-2045 by technology. Which two caloric cooling technologies win? See the most promising materials for each technology ranked from research and latest company initiatives and some toxigen issues that are an opportunity for you.
The 26-page Introduction puts it in context such as emerging countries such as Saudi Arabia and India being in hotter locations just as global warning is added. See the new cooling needs from ever hotter microchips graphed, telecommunications base station and data center power escalation graphed. Here are the allied technologies such as thermal conductors shown in maturity curves 2025, 2035, 2045 and the solid-state cooling options they support. See how the need for vapor compression will be eased by adding some of the new technologies. However, this is an unbiassed report, so the chapter ends with detail on two examples of competition for solid state cooling that emerged in 2024. The rest of the report is much more detailed with two chapters on different forms of radiative cooling, one on the enabling metamaterials, one on caloric cooling and one on emerging new forms of thermoelectric cooling.
Chapter 3 "Passive Daylight Radiative Cooling" takes 98 pages, massively important because, taking no power, it is easily integrated into apparel and buildings. This technology combines radiative cooling into the atmospheric window with reflection of heat. Exactly how does it work in structures and fabrics? Smart windows, invisible facades and remarkable other applications being progressed? See how ten companies commercialising PDRC. The materials involved are very closely examined. Can it be coloured without compromise? Transparent, aerogel, porous, ceramic and meta-material forms? Overall, the 13 most important formulations of material for PDRC are prioritised, particularly incorporating the research breakthroughs in 2024.
Chapter 4 (30 pages) takes you into allied technologies and advanced functionalities of PDRC with, "Self-adaptive, switchable, tuned, Janus and anti-Stokes solid state cooling". This includes two-way radiative cooling, use of fluorescence and different materials such as vanadium salts and liquid crystal. As with all the other chapters, enjoy SWOT appraisals, diagrams and analysis, not rambling text.
Chapter 5, "Phase change and particularly caloric cooling" compares the cooling obtained by phase changes between solid, liquid and gas and the feeble cooling between different solid crystalline states. However, this chapter then almost entirely focuses on the exciting solid-state one - caloric cooling by alteration of ferroic state. See magnetocaloric, elastocaloric, twistocaloric, barocaloric and electrocaloric compared and why an additional liquid option is not promising. Learn how latest research leads us to look particularly closely at the complementary technologies electrocaloric and elastocaloric, the winning materials from latest research and the issues to overcome before successful commercialisation such as sometimes toxigen intermediaries, moving parts or high voltages. Nonetheless, the potential on a 20-year view is shown to be considerable.
In a report on solid state cooling, thermoelectrics might seem the dullest option - mature yet only achieving a market size of around one billion dollars. However, the closer look in this report reveals that this huge and precise cooling capacity even on a tiny scale is badly needed for some new needs. Learn how it can be boosted by using some of the other solid state cooling options on the hot side. In addition, see how wide area, low-cost thermoelectrics is a real, though not immediate, possibility when latest research is appraised in detail. This chapter 7, "Future thermoelectric cooling and thermoelectric harvesting as a user of and power provider for other solid-state cooling" (72 pages) ends with 82 manufacturers listed.
Zhar Research report, "Solid State Cooling Materials and Systems PDRC, Caloric, Thermoelectric, Other: Markets, Technology 2025-2045" is essential reading for those seeking to make or use the next generation of cooling technology and all in added value materials that seek large new opportunities.
CAPTION: Some reasons for the escalating need for cooling. Source, Zhar Research report, "Solid State Cooling Materials and Systems PDRC, Caloric, Thermoelectric, Other: Markets, Technology 2025-2045".

Table of Contents
1. Executive summary and conclusions
- 1.1. Purpose of this report
- 1.2. Methodology of this analysis
- 1.3. The many reasons for the escalating need for cooling
- 1.4. The nature of solid-state cooling and why it is now a priority
- 1.5. Cooling toolkit, trend to multifunctionality with best solid-state cooling tools shown red
- 1.6. 18 Primary conclusions
- 1.7. Typical best reported temperature drop achieved by technology 2000-2045 extrapolated
- 1.8. Number of important caloric cooling research advances 2024 and 2023 by technology revealing best options
- 1.9. Leading materials in number of latest research advances on solid state cooling
- 1.10. Appraisal of Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling PDRC
- 1.10.1. SWOT appraisal of PDRC
- 1.10.2. Popularity of materials by family in recent research on PDRC and allied radiative cooling
- 1.11. Appraisal of electrocaloric cooling
- 1.11.1. SWOT appraisal of electrocaloric cooling
- 1.11.2. Electrocaloric materials by popularity in research
- 1.12. Appraisal of elastocaloric cooling
- 1.13. Appraisal of thermoelectric cooling
- 1.13.1. SWOT appraisal of thermoelectric cooling, temperature control and harvesting
- 1.13.2. Formulation popularity of latest thermoelectric cooling technology
- 1.14. Cooling roadmap by market and by technology 2025-2045
- 1.15. Market forecasts 2025-2045 as tables with graphs
- 1.15.1. Cooling module global market by seven technologies $ billion 2025-2045
- 1.15.2. Terrestrial radiative cooling performance in commercial products W/sq. m 2025-2045
- 1.16. Background forecasts
- 1.16.1. Air conditioner value market $ billion 2025-2045 and by region
- 1.16.2. Global market for HVAC, refrigerators, freezers, other cooling $ billion 2025-2045
- 1.16.3. Refrigerator and freezer value market $ billion 2025-2045
- 1.16.4. Market for 6G vs 5G in 2 categories base stations units millions yearly 2025-2045
2. Introduction
- 2.1. Overview
- 2.2. Need for cooling becomes much larger and often different in nature
- 2.3. Examples of radical changes in the requirements for cooling 2025-2045
- 2.3.1. Escalation of demand for air conditioning and forthcoming changes in requirement
- 2.3.2. How 6G Communications from 2030 will bring new cooling requirements: infograms
- 2.3.3. Severe new microchip cooling requirements arriving
- 2.3.4. Other cooling problems and opportunities emerging in electronics and ICT
- 2.4. How cooling technology will trend to smart materials 2025-2045
- 2.5. Reinventing air conditioning to be lower power, greener, more affordable
- 2.7. Undesirable materials widely used and proposed: this is an opportunity for you
- 2.8. Examples of competition for solid state cooling announced in 2024
3. Passive daytime radiative cooling (PDRC)
- 3.1. Overview
- 3.2. PDRC basics
- 3.3. Radiative cooling materials by structure and formulation with research analysis
- 3.4. Potential benefits and applications
- 3.4.1. Overall opportunity and progress
- 3.4.2. Transparent PDRC for facades, solar panels and windows including 8 advances in 2024
- 3.4.3. Wearable PDRC, textile and fabric with 7 advances in 2024 and SWOT
- 3.4.4. PDRC cold side boosting power of thermoelectric generators
- 3.4.5. Color without compromise including advances in 2024
- 3.4.6. Aerogel and porous material approaches
- 3.4.7. Environmental and inexpensive PDRC materials development
- 3.5. Other important advances in 2024 and 2023
- 3.5.1. 24 important advances in 2024
- 3.5.2. Advances in 2023
- 3.6. Companies commercialising PDRC
- 3.6.1 3M USA
- 3.6.2. BASF Germany
- 3.6.3. i2Cool USA
- 3.6.4. LifeLabs USA
- 3.6.5. Plasmonics USA
- 3.6.6. Radicool Japan, Malaysia etc.
- 3.6.7. SkyCool Systems USA
- 3.6.8. SolCold Israel
- 3.6.9. Spinoff from University of Massachusetts Amherst USA
- 3.6.10. SRI USA
- 3.7. PDRC SWOT report
4. Self-adaptive, switchable, tuned, Janus and Anti-Stokes solid state cooling
- 4.1. Overview of the bigger picture with SWOT
- 4.2. Maturity curve of radiative cooling technologies
- 4.3. Self-adaptive and switchable radiative cooling
- 4.3.1. The vanadium phase change approaches in 2024
- 4.3.2. Alternative using liquid crystal
- 4.4. Tuned radiative cooling using both sides: Janus emitter JET advances in 2024, 2023 and SWOT
- 4.5. Anti-Stokes fluorescence cooling with SWOT appraisal
5. Phase change and particularly caloric cooling
- 5.1. Structural and ferroic phase change cooling modes and materials
- 5.2. Solid-state phase-change cooling potentially competing with other forms in named applications
- 5.3. The physical principles adjoining caloric cooling
- 5.4. Operating principles for caloric cooling
- 5.5. Caloric compared to thermoelectric cooling and winning caloric technologies identified
- 5.6. Some proposals for work to advance the use of caloric cooling
- 5.7. Electrocaloric cooling
- 5.7.1. Overview and SWOT appraisal
- 5.7.2. Operating principles, device construction, successful materials and form factors
- 5.7.3. Electrocaloric material popularity in latest research with explanation
- 5.7.4. Giant electrocaloric effect
- 5.7.5. Electrocaloric cooling: issues to address
- 5.7.6. Six important advances and a review in 2024
- 5.7.7. 17 other advances in 2023
- 5.7.8. Notable earlier electrocaloric research
- 5.8. Magnetocaloric cooling with SWOT appraisal
- 5.9. Mechanocaloric cooling (elastocaloric, barocaloric, twistocaloric) cooling
- 5.9.1. Elastocaloric cooling overview: operating principle, system design, applications, SWOT
- 5.9.2. 19 elastocaloric advances in 2024
- 5.9.3. Barocaloric cooling
- 5.10. Multicaloric cooling
6. Enabling technology: Metamaterial and other advanced photonic cooling: emerging materials and devices
- 6.1. Metamaterials
- 6.1.1. Metamaterial and metasurface basics
- 6.1.2. The meta-atom, patterning and functional options
- 6.1.3. SWOT assessment for metamaterials and metasurfaces generally
- 6.1.4. Metamaterial energy harvesting may power metamaterial active cooling
- 6.1.5. Thermal metamaterial with 11 advances in 2024
- 6.4. Advanced photonic cooling and prevention of heating
7. Future thermoelectric cooling and thermoelectric harvesting as a user of and power provider for other solid-state cooling
- 7.1. Basics
- 7.1.1. Operation, examples
- 7.1.2. Thermoelectric cooling and temperature control applications 2025 and 2045
- 7.1.3. SWOT appraisal of thermoelectric cooling, temperature control and harvesting
- 7.2. Thermoelectric materials
- 7.2.1. Requirements
- 7.2.2. Useful and misleading metrics
- 7.2.3. Quest for better zT performance which is often the wrong approach
- 7.2.4. Some alternatives to bismuth telluride being considered
- 7.2.5. Non-toxic and less toxic thermoelectric materials, some lower cost
- 7.2.6. Ferron and spin driven thermoelectrics
- 7.3. Wide area and flexible thermoelectric cooling is a gap in the market for you to address
- 7.3.1. The need and general approaches
- 7.3.2. Advances in flexible and wide area thermoelectric cooling in 2024 and 2023
- 7.3.3. Wide area or flexible TEG research 40 examples from 2024 that may lead to similar TEC
- 7.4. Radiation cooling of buildings: multifunctional with thermoelectric harvesting in 2024
- 7.5. The heat removal problem of TEC and TEG - evolving solutions
- 7.6. 20 advances in thermoelectric cooling and harvesting involving cooling and a review in 2024
- 7.7. Advances in 2023
- 7.8. 82 Manufactures of Peltier thermoelectric modules and products