 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1479762
高科技產業稀土:中國貿易禁令下的市場分析與預測Rare Earths Elements In High-Tech Industries: Market Analysis And Forecasts Amid China's Trade Embargo |
||||||
介紹
稀土是一組化學性質獨特的元素,由 17 種元素組成,是各種尖端技術和再生能源系統的重要組成部分。從電動車和風力渦輪機到智慧型手機和先進醫療設備,稀土在促進各行業的創新和永續發展方面發揮關鍵作用。
高新科技產業與替代能源產業發展趨勢
稀土在高科技和替代能源產業中的應用非常廣泛,涵蓋了對現代技術和再生能源解決方案的進步和效率至關重要的廣泛應用。下面我們就來詳細介紹一下。
報告涵蓋的高新技術產業
電子和通訊設備:稀土對於智慧型手機、電腦和平板顯示器等電子設備的生產至關重要。釹、鐠和鏑等元素用於揚聲器、硬碟和小型馬達的磁鐵。銪和鋱作為磷光體,有助於螢幕的生動顯示。
先進光學和雷射:釓、鉺和鐿用於光纖和雷射技術。這些元素對於高速網路傳輸和醫療雷射的精確度至關重要。
國防/航空航太:由釤製成的釤鈷磁鐵用於精確導引彈藥和衛星通訊系統。釔和鋱等稀土因其獨特的光學和磁性特性而被用於雷達系統和其他國防電子設備。
報告涵蓋的替代能源產業
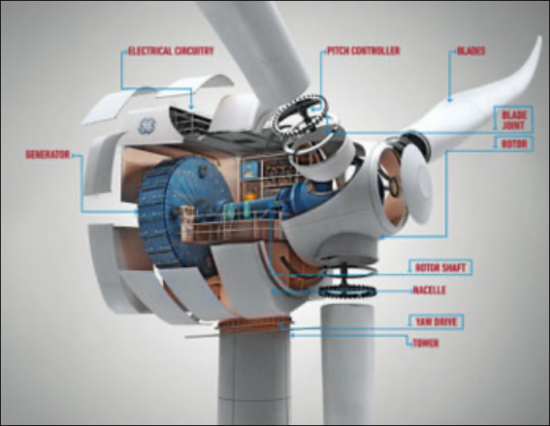
風力渦輪機:釹、鐠和鏑對於風力渦輪發電機的強力永磁體至關重要。即使在低風速下,這些磁鐵也能實現高效發電。
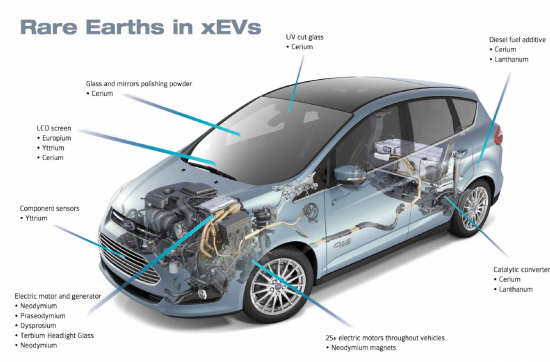
電動車(EV): NdFeB(釹鐵硼)磁鐵常用於電動車和混合動力車的牽引馬達。這種磁鐵的高性能有助於提高電動車的效率和續航里程。
太陽能板:雖然稀土不是太陽能電池的主要成分,但鈰等稀土氧化物被用來拋光太陽能板的玻璃。燈籠也用於生產儲存太陽能的先進電池。
能源儲存:鎳氫(NiMH)電池中使用了鑭和鈰等稀土,這對於再生能源儲存解決方案至關重要。這些元素有助於提高電池的容量和使用壽命,這對於再生能源的穩定供應至關重要。
趨勢
稀土 (REE) 在高科技和替代能源產業中的趨勢反映了它們作為各種應用中的關鍵成分日益增長的重要性。
一個值得注意的趨勢是電動車 (EV)、風力渦輪機和太陽能電池板等再生能源技術對稀土的需求不斷增長。隨著全球加速向清潔能源轉型,鐠鐠永磁體、催化劑和電池技術中使用的稀土需求預計將大幅增加。
此外,特別是考慮到地緣政治緊張局勢,人們越來越重視確保可持續和多樣化的稀土供應,以減輕供應鏈風險並減少對少數主導生產商的依賴。
另一個趨勢是尋找替代來源和回收方法,以解決與傳統稀土開採和加工相關的供應限制和環境問題。此外,材料科學和技術創新的進步正在幫助開發更高效、更環保的工藝,用於在各種應用中提取、純化和利用稀土。
整體而言,這一趨勢凸顯了稀土在高科技和替代能源產業發展中的重要作用,同時也凸顯了策略規劃和合作的必要性,以確保可持續和有彈性的供應鏈。
本報告審視並分析了全球稀土產業,提供了有關稀土產量、需求、市場動態、技術進步和未來前景的資訊。
目錄
第一章簡介
第二章 稀土產業
- 中國稀土產業
- 中國生產
- 中國稀土生產結構
- 中國稀土消費結構
- 中國稀土出口
- 中國稀土產業近期活動
- 其他地區稀土產業
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 南非
- 澳大利亞
- 格陵蘭
- 阿根廷
- 印度
- 俄羅斯
- 礦業公司簡介
第三章 稀土市場分析
- 概述
- 稀土市場
- 國內生產和消費
- 中國的生產與消費
- 全球稀土市場分析
第四章 對高新技術應用的影響
- 概述
- 半導體
- 硬碟機 (HDD)
- 行動、行動互聯網設備
- 固態照明 - LED/CFL
- 綠色科技
第五章 美國戰略金屬展望
- 稀土在國防領域的應用
- 稀土資源及潛在生產力
- 供應鏈問題
- 稀土定律
第六章 歐洲戰略金屬展望
- 重要性評估
- 2020年歐盟重要原料清單
- 當前和過去的努力
第七章 重構美國供應鏈
- 材料供應鏈的課題與機遇
- 價格上漲的影響:依應用分類
- 美國的 REE/REO 回收
Introduction
The report "Rare Earths Elements in High-Tech and Alternative Energy Industries: Market Analysis and Forecasts" presents a comprehensive exploration into the pivotal role of rare earth elements (REEs) within high-tech and alternative energy sectors.
Rare earth elements, a group of 17 chemically unique elements, are integral components in a wide array of cutting-edge technologies and renewable energy systems. From electric vehicles and wind turbines to smartphones and advanced medical devices, REEs play a vital role in enabling innovation and sustainability across various industries.
This report delves into the intricate dynamics of the REEs market, examining factors such as global supply chain resilience, evolving demand patterns, pricing dynamics, and geopolitical influences.
By providing in-depth insights and forecasts, the report aims to empower stakeholders with the knowledge and strategic insights necessary to navigate the complex landscape of high-tech and alternative energy industries amid challenges such as supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
High-Tech and Alternative Energy Industries Trends
The utilization of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) in high-tech and alternative energy industries is extensive, covering a wide range of applications essential for the advancement and efficiency of modern technologies and renewable energy solutions. Here's a detailed exploration:
High-Tech Industries Discussed in Report::
Electronics and Communication Devices: REEs are pivotal in manufacturing smartphones, computers, flat-screen monitors, and other electronic devices. Elements like neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium are used in magnets for speakers, hard drives, and small motors. Europium and terbium contribute to the vibrant displays of screens through their role in phosphors.
Advanced Optics and Lasers: Gadolinium, erbium, and ytterbium are used in optical fibers and laser technology. These elements are crucial for high-speed internet transmission and precision in medical lasers.
Defense and Aerospace: Samarium-cobalt magnets, made from samarium, are utilized in precision-guided munitions, and satellite communication systems. REEs like yttrium and terbium are used in radar systems and other defense electronics due to their unique optical and magnetic properties.
Alternative Energy Industries Discussed in Report
Wind Turbines: Neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium are essential for the powerful permanent magnets in the generators of wind turbines. These magnets allow the turbines to generate electricity efficiently, even at low wind speeds.

Electric Vehicles (EVs): The traction motors in electric and hybrid vehicles often use neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets. The high performance of these magnets contributes to the efficiency and range of EVs.

Solar Panels: While REEs are not major components in photovoltaic cells, certain rare earth oxides like cerium are used for polishing the glass of solar panels. Additionally, lanthanum is used in the production of advanced batteries that store solar energy.
Energy Storage: REEs like lanthanum and cerium are used in nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, which are crucial for renewable energy storage solutions. These elements help improve the battery's capacity and longevity, essential for the stability of renewable energy sources.
Trends
The trends in Rare Earth Elements (REEs) within high-tech and alternative energy industries reflect their increasing importance as critical components in various applications.
One prominent trend is the growing demand for REEs in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy technologies such as wind turbines and solar panels. As the global transition toward cleaner energy sources accelerates, the demand for REEs used in NdPr permanent magnets, catalysts, and battery technologies is expected to rise significantly.
Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on securing sustainable and diversified REE supplies to mitigate supply chain risks and reduce dependence on a few dominant producers, particularly in light of geopolitical tensions.
Another trend is the exploration of alternative sources and recycling methods to address supply constraints and environmental concerns associated with traditional REE mining and processing. Furthermore, advancements in material science and technological innovations are driving the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly processes for extracting, refining, and utilizing REEs in various applications.
Overall, the trends underscore the critical role of REEs in advancing high-tech and alternative energy industries while highlighting the need for strategic planning and collaboration to ensure a sustainable and resilient supply chain.
About This Report
Rare Earths Elements in High-Tech and Alternative Energy Industries report covers a wide range of topics related to the production, demand, market dynamics, technological advancements, and future prospects of REEs. Specifically, the report include:
Market Analysis: An overview of the global REE market, including historical trends, current market size, and growth projections, detailing market drivers, challenges, and opportunities.
Industry Trends: Exploration of key trends shaping the demand for REEs in high-tech and alternative energy sectors, such as electric vehicles, renewable energy technologies, consumer electronics, and advanced manufacturing.
Supply Chain Analysis: Examination of the REE supply chain, including major producers, mining projects, processing facilities, and distribution networks. This section also discusses geopolitical factors, trade policies, and supply chain risks affecting REE availability.
Application Segmentation: Detailed analysis of REE applications across various industries, highlighting their uses in magnets, batteries, catalysts, lighting, electronics, and other high-tech products.
Technology Innovation: Exploration of technological advancements and research initiatives aimed at improving REE extraction, processing, recycling, and substitution. This section also covers innovations in material science, manufacturing processes, and product design to enhance REE efficiency and sustainability.
Regulatory Environment: Overview of regulatory frameworks, environmental regulations, and policies impacting REE mining, production, trade, and usage. This section also addresses sustainability standards, responsible sourcing initiatives, and compliance requirements for REErelated industries.
Market Forecasts: Forecasting of future trends and growth opportunities in the REE market, including projections for demand, supply, prices, and market shares. This section provides insights into emerging technologies, market disruptions, and investment prospects in the REE sector.
Competitive Landscape: Analysis of key players in the REE industry, including mining companies, processors, manufacturers, and end-users. This section includes company profiles, market strategies, competitive positioning, and partnerships in the REE value chain. Overall, the comprehensive report aims to provide stakeholders with actionable insights, strategic recommendations, and data-driven analyses to navigate the complex landscape of REEs in high-tech and alternative energy industries.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction
- 1.1. Rare Earth Element Characteristics
- 1.2. Rare Earth Element Resources
- 1.3. Overview of Rare Earth Element Applications
Chapter 2. Rare Earth Industry
- 2.1. China' Rare Earth Industry
- 2.1.1. China's Production
- 2.1.2. China Rare Earth Production Structure
- 2.1.3. China Rare Earth Consumption Structure
- 2.1.4. China Export of Rare Earths
- 2.1.5. Recent Activities Of China's Rare Earth Industry
- 2.1.5.1. Consolidation Of China's Rare Earth Industry
- 2.1.5.2. Export Quotas
- 2.2. Rest Of World's Rare Earth Industry
- 2.2.1. UNITED STATES
- 2.2.1.1. Mountain Pass
- 2.2.1.2. Utah Rare Earth Project
- 2.2.1.3. Bear Lodge Rare-Earth Project
- 2.2.1.4. Elk Creek
- 2.2.1.5. Bokan-Dotson Ridge
- 2.2.1.6. Diamond Creek
- 2.2.1.7. Lemhi Pass
- 2.2.2. CANADA
- 2.2.2.1. MacLeod Lake Project
- 2.2.2.2. Hoidas Lake
- 2.2.2.3. Benjamin River Project
- 2.2.2.4. Douglas River Project
- 2.2.2.5. Nechalacho Rare Earth Element Project
- 2.2.2.6. Archie Lake
- 2.2.2.7. Bulstrode Rare Earth Property
- 2.2.2.8. Mount Copeland
- 2.2.2.9. Cross Hills Newfoundland
- 2.2.2.10. Kipawa
- 2.2.2.11. Strange Lake
- 2.2.2.12. Ytterby
- 2.2.2.13. Grevet REE
- 2.2.2.14. Turner Falls
- 2.2.3. SOUTH AFRICA
- 2.2.3.1. Steenkampskraal Mine South Africa
- 2.2.4. AUSTRALIA
- 2.2.4.1. Nolans Bore
- 2.2.4.2. Mount Weld
- 2.2.4.3. Jungle Well/ Laverton
- 2.2.5. GREENLAND
- 2.2.5.1. Kvanefjeld Project
- 2.2.6. ARGENTINA
- 2.2.6.1. Cueva del Chacho
- 2.2.6.2. Susques Property - Jujuy Province
- 2.2.6.3. John Galt Project
- 2.2.7. INDIA
- 2.2.7.1. Indian Rare Earth
- 2.2.8. RUSSIA
- 2.2.8.1. Kutessay II
- 2.2.1. UNITED STATES
- 2.3. Profiles of Mining Corporations
Chapter 3. Rare Earth Market Analysis
- 3.1. Overview
- 3.2. Rare Earth Market
- 3.2.1. Domestic Production and Consumption
- 3.2.2. China Production and Consumption
- 3.3. Global Rare Earth Market Analysis
Chapter 4. Impact on Hi-Tech Applications
- 4.1. Overview
- 4.1.1. Rare Earth Market By Application
- 4.1.2. NdPr Magnets
- 4.2. Semiconductors
- 4.2.1. Technology Impacted
- 4.2.1.1. High-k Dielectrics
- 4.2.1.2. Polishing Powders
- 4.2.2. Rare Earth Material Used
- 4.2.3. Market Forecast of Impacted Semiconductor Devices/Materials
- 4.2.1. Technology Impacted
- 4.3. Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
- 4.3.1. Technology Impacted
- 4.3.1.1. Neo Magnets for HDDs
- 4.3.1.2. High Strength Glass Substrates
- 4.3.1.3. Polishing Materials
- 4.3.2. Rare Earth Material Used
- 4.3.3. Market Forecast of Impacted HDD Devices/Materials
- 4.3.1. Technology Impacted
- 4.4. Mobile and Mobile Internet Devices
- 4.4.1. Technology Impacted
- 4.4.2. Rare Earth Material Used
- 4.4.3. Market Forecast of Impacted Mobile Devices/Materials
- 4.5. Solid State Lighting - LED/CFL
- 4.5.1. Technology Impacted
- 4.5.1.1. Phosphors for Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
- 4.5.1.2. Phosphors for Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL)
- 4.5.2. Rare Earth Material Used
- 4.5.3. Market Forecast of Impacted LED Devices/Materials
- 4.5.1. Technology Impacted
- 4.6. Green Technology
- 4.6.1. Technology Impacted
- 4.6.1.1. Magnets for Hybrid Vehicle Electric Motors and Brakes
- 4.6.1.2. Neo Magnets for Wind Turbines
- 4.6.1.3. Cerium for Catalytic Converters for Automobiles
- 4.6.2. Rare Earth Material Used
- 4.6.3. Market Forecast of Impacted Green Devices/Materials
- 4.6.4. Other Green Technologies
- 4.6.1. Technology Impacted
Chapter 5. U.S Strategic Metal Perspective
- 5.1. The Application of Rare Earth Metals in National Defense
- 5.2. Rare Earth Resources and Production Potential
- 5.3. Supply Chain Issues
- 5.4. Rare Earth Legislation
Chapter 6. European Strategic Metal Perspective
- 6.1. Assessing Criticality
- 6.2. The 2020 EU Critical Raw Materials List
- 6.3. Current And Past Initiatives
Chapter 7. Rebuilding a U.S. Supply Chain
- 7.1. Materials Supply Chain Challenges And Opportunities
- 7.2. Impact of Price Hikes by Application
- 7.2.1. REE/REO Recycling In U.S.
- 7.2.1.1. Overall Process
- 7.2.1.2. Recycling RE Magnets
- 7.2.1.3. Recycling Phosphors
- 7.2.1.4. Company Programs
- 7.2.1. REE/REO Recycling In U.S.
TABLES
- 1.1. Selected Rare Earth Element Bearing Products
- 1.2. Rare Earths Elements And Some Of Their End Uses
- 2.1. World Mine Production and Reserves
- 2.2. Global Rare Earth Supply/Demand
- 2.3. China's Rare Earth Export Volume And Export Amount
- 2.4. Rare Earth Projects Outside China
- 3.1. U.S. Rare Earth Statistics
- 3.2. Rare Earth Prices
- 3.3. Rare Earth Elements: World Production
- 3.4. Rare Earth Oxide Demand-Supply
- 3.5. Rare Earth Composition By End Use
- 4.1. NdPr Oxide Supply Market Forecast
- 4.2. NdPr Oxide Demand Market Forecast
- 4.3. Forecast of Ceria CMP Slurry for Semiconductors
- 4.4. Market Forecast for Hard Disk Drives
- 4.5. Neodymium Consumption For Hard Disk Drives
- 4.6. Market Forecast For Ceria Slurry For Glass Disks
- 4.7. Shipment Forecast of Smartphones
- 4.8. Neodymium Consumption For Smartphones
- 4.9. Market Forecast of LEDs by Application
- 4.10. Demand of Rare Earths in LEDs
- 4.11. Shipment Forecast Of Electric Vehicles
- 4.12. Neodymium Consumption For Electric Vehicles
- 4-13. Shipment Forecast Of Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles
- 4-14. Ceria Consumption For Catalytic Converters
- 4-15. Shipment Forecast Of Wind Turbines
- 4-16. Neodymium Consumption For Wind Turbines
- 5.1. Rare Earth Elements: World Production And Reserves
- 7.1. NdFeB Permanent Magnet Supply Chain Steps
FIGURES
- 1.1. Periodic Table Of Rare Earth Elements
- 1.2. Abundance Of The Rare Earth Elements
- 1.3. Rare Earth Production Since 1950
- 1.4. China's Rare Earth Dominance
- 2.1. Rare Earth Proportion And Distribution In China
- 2.2. Production Of Rare Earth Concentrates Since 1987
- 2.3. Production Of Rare Earth Oxides Since 1994
- 2.4. China Mining Quota By Company
- 2.5. China Rare Earth Oxide Exports By Destination
- 2.6. China Rare Earth Metal Exports By Destination
- 2.7. China's Rare-Earth Exports
- 3.1. U.S. Distribution Of Refined Rare Earth Products
- 3.2. Rare-Earth Price Index
- 3.3. Comparison Of Rare Earth Consumption Between China And The World
- 3.4. Global Supply-Demand Forecast
- 3.5. REE Demand By Volume
- 3.6. REE Demand By Value
- 3.7. REE Applications Global
- 3.8. REE Applications U.S.
- 3.9. REE Composition By End Use
- 3.10. Approximate % Content Of Current And Prospective Ores
- 4.1. Application Market Share by Volume
- 4.2. High-Performance Magnet Share by Application
- 4.3. High-Performance Magnet Share by Application - 2030
- 4.4. Illustration of MOSFET and Gate Oxide
- 4.5. STI CMP Using Ceria
- 4.6. Hafnium Demand for Semiconductors
- 4.7. HDD Drive and Neo Magnets
- 4.8. REE Usage in Phosphors
- 4.9. Scattered Photon Extraction white LED
- 4.10. Supply Chain for Fluorescent Lighting
- 4.11. EV Rare Earths Applications
- 4.12. Wind Turbine Motor
- 4.13. Supply Chain for Permanent Magnets
- 4.14. Catalytic Converter for Automobiles
- 5.1. Global Rare Earth Reserves
- 6.1. Supply Of Strategic Metals To The European Union









