 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1642080
計劃物流-市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Project Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
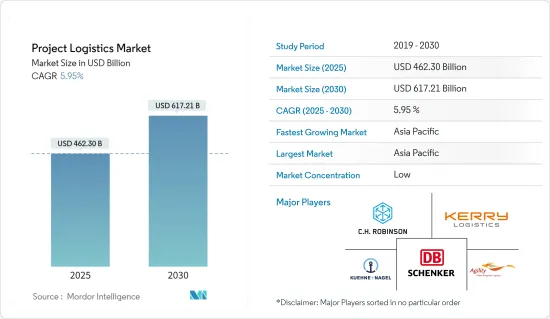
2025 年計劃物流市場規模估計為 4,623 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 6,172.1 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 5.95%。
計劃物流涉及整個計劃中貨物、材料和資訊的綜合管理和協調。運輸大型貨物需要專門的設備、基礎設施和經驗豐富的人員。處理具有特殊尺寸的貨物對於承運人而言始終是一個挑戰,但托運人和服務供應商在處理超大和重型貨物方面變得越來越熟練。零件和模組化包裝在不同地點生產並運送到最終目的地,需要仔細規劃。近年來,從早期規劃階段開始就讓運輸業者參與的趨勢日益明顯。
亞太地區引領計劃物流市場,預計將出現最高的成長率。基礎建設投資在亞太國家經濟發展中發揮關鍵作用,部分國家將國內基礎建設列為優先事項。
全球計劃物流網路 (GPLN) 等一些成熟的組織專門從事全球範圍內的計劃物流。 GPLN 成員從事廣泛的工業計劃,包括基礎設施和能源計劃,提供重型、超大和超限貨物的運輸、包裝/裝箱和起重等服務。
2020-2021 年,正值新冠疫情最嚴重時期,計劃物流領域對空運的需求很高,用於運輸全球必需品。
計劃物流市場趨勢
可再生能源的使用增加為計劃物流公司創造了機會
根據國際能源總署 (IEA) 最新報告,受政策支持擴大、石化燃料價格上漲和能源安全擔憂的推動,全球可再生能源發電能將在 2023 年成長三分之一。
預計明年這一成長動能將持續,使全球可再生能源發電裝置容量達到 4,500 吉瓦,相當於中國和美國的總合裝置容量。 2023年,全球可再生能源發電裝置容量預計將增加107吉瓦,絕對增量將超過440吉瓦,為有史以來最大增幅。
此次擴張正在全球主要市場進行,主要包括歐洲、美國、印度和中國。尤其是中國,預計在 2023 年和 2024 年將佔全球可再生能源發電新增產能的近 55%。
預計2023年風電裝置將強勁反彈,預測與前一年同期比較成長近70%。這是繼工業成長放緩之後出現的挑戰。成長改善的原因是,由於中國 COVID-19 限制措施以及歐洲和美國的供應鏈問題而推遲的計劃已完成。
然而,2024 年的成長程度將取決於政府提供更多的政策支持,以解決與授權和競標設計相關的障礙。與太陽能領域不同,風力發電機供應鏈的擴張速度不夠快,無法滿足中期不斷成長的需求。這主要是由於大宗商品價格上漲和供應鏈中的挑戰,影響了製造商的盈利。
這種可再生能源需求必然需要計劃物流,因為機械和其他零件非常大,因此需要單獨運輸然後在現場組裝。
模組化建築的發展推動市場
對永續基礎設施的需求正在推動高效、環保的建築技術的發展。傳統的建築方法可能已不足以滿足永續基礎設施的要求。模組化描述了一種解決傳統施工方法不靈活性的方法。採用模組化施工方法,可將建築成本降低 40%,並可實現場地準備和模組化/預製同時進行。
向模組化(異地)施工方法的轉變創造了新的市場,特別是對於人事費用低且預製土地充足的新興國家。在支援永續基礎設施發展方面,預製組裝式施工方法可大幅節省材料,例如與同等規模的傳統施工方法相比,可減少60%的鋼骨、56%的混凝土和77%的模板。
然而,模組化預製概念仍存在挑戰,包括規模經濟和運輸超過 ISO 貨櫃尺寸的模組化組件的複雜性。這種異地建設模式也為特定地理區域內的國際貿易開闢了機會,這取決於每個國家的競爭優勢。國際自由貿易的成長帶來更為廣闊的商機和新的貿易關係的潛力。國際和區域貿易也推動了工程、採購和建設(EPC)計劃的海外貿易的成長。海外EPC計劃採用模組化建造方式,將對計劃的貨物運輸發展和計劃物流的整體投資產生影響,包括國內和海外的物流成本。國內物流成本包括製造成本(加工、預拌混凝土、散裝材料、鋼筋和鋼材)。另一方面,海外物流成本包括船舶租賃費、燃油價格、外匯、距離、體積尺寸、保險、清關等。
計劃物流行業概況
計劃物流市場分為全球參與企業和中小型參與企業。大多數全球物流參與企業都有專門的計劃貨運部門來滿足市場的需求。本土參與企業在機隊規模、服務內容、服務業和技術方面的能力也日益增強。全球製造商都在異地生產大型和超大零件,這給重型運輸公司帶來了巨大的複雜性。擁有雄厚資本和資產的全球公司可以投資升級後的車輛並從中受益。同時,區域和地方企業也正在提出更好的行業解決方案,以支援客戶在規定時間內交付計劃的需求。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 調查結果
- 調查前提
- 研究範圍
第2章調查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究階段
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場概況
- 當前市場狀況
- 市場動態
- 驅動程式
- 可再生能源計劃對計劃物流的需求不斷增加
- 增加基礎建設投資
- 限制因素
- 初期資本投入高
- 驅動程式
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 產業價值鏈分析
- 政府法規和舉措
- 全球物流業(概況、LPI 得分、主要貨運統計等)
- 焦點 - 多式聯運在計劃貨物中的作用
- 洞察-石油與天然氣零售物流業
- 重型和大型貨物評論和說明
- 聚焦預製產業-計劃物流公司在運輸中的作用
- 深入了解重型貨物運輸客製化拖車製造商
- 關注合約物流和綜合物流的需求
第5章 市場區隔
- 服務
- 運輸
- 運輸
- 庫存管理和倉儲
- 其他附加價值服務
- 最終用戶
- 石油和天然氣、採礦和採石
- 能源動力
- 建設業
- 製造業
- 其他
- 地區
- 亞太地區
- 美洲
- 歐洲
- 中東和非洲
第6章 競爭格局
- 公司簡介
- Rhenus Logistics
- Bollore Logistics
- Agility Logistics
- EMO Trans
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Kuehne+Nagel International AG
- CH Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- Ceva Logistics
- NMT Global Project Logistics
- Rohlig Logistics
- Ryder System Inc.
- Expeditors International of Washington Inc.
- Megalift Sdn Bhd
- Dako Worldwide Transport GmbH
- CKB Logistics Group
- SAL Heavy Lift GmbH
- DB Schenker
- Kerry Logistics
- Deutsche Post DHL*
- 其他市場參與企業
- FLS 運輸服務、Crowley Logistics、Highland Forwarding Inc.、Kinetix International Logistics、Cole International Inc.、Hisiang Logistics Co. Ltd、Sea Cargo Air Cargo Logistics Inc.、Bati Group
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
第 8 章 附錄
- 主要國家按活動分類的 GDP 分佈
- 資本流動洞察 – 主要國家
- 經濟統計-運輸及倉儲業及其對經濟的貢獻(主要國家)
- 全球主要計劃清單(石油和天然氣、建築、基礎設施開發等)
- 貨物統計(運送方式、產品類型等)
第9章 免責聲明
The Project Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 462.30 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 617.21 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.95% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Project logistics encompasses the comprehensive management and coordination of goods, materials, and information throughout the entire process of a project. The transportation of large-sized cargo requires specialized equipment, infrastructure, and experienced personnel. Dealing with cargo of unique dimensions poses a constant challenge for transporters, but shippers and service providers are becoming more adept at handling oversized and heavyweight shipments. The complexity of manufacturing also contributes to the difficulty, as parts and modular packages are produced in various locations and then shipped to their final destinations, necessitating meticulous planning. In recent years, there has been a growing trend of involving transportation providers in the early stages of the planning process.
The Asian-Pacific region leads the market in project logistics and is expected to experience the highest growth rate. Infrastructure investment has played a significant role in the economic development of Asia-Pacific countries, with some nations prioritizing the advancement of their domestic infrastructure.
Several established organizations, such as the Global Project Logistics Network (GPLN), specialize in project logistics on a global scale. GPLN members handle a wide range of industrial projects, including infrastructure and energy projects, providing services such as transportation, packing/crating, and the lifting of heavy, oversized, and out-of-gauge cargo.
During the height of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020-21, air freight was in high demand within the project logistics sector for the transportation of essential items worldwide.
Project Logistics Market Trends
Increasing Usage of Renewable Energies Boosts Opportunities for Project Logistics Companies
According to the latest update from the International Energy Agency, global renewable power capacity is expected to increase by a third in 2023 due to factors such as growing policy support, higher fossil fuel prices, and concerns about energy security.
This growth will continue next year, with the world's total renewable electricity capacity reaching 4,500 gigawatts, equivalent to the combined power output of China and the United States. In 2023, global renewable capacity is projected to increase by 107 gigawatts, the largest absolute increase ever recorded, reaching over 440 gigawatts.
This expansion is happening in major markets worldwide, with Europe, the United States, India, and China leading the way. China, in particular, is expected to account for nearly 55% of global renewable power capacity additions in both 2023 and 2024.
Wind power installations are expected to experience a significant recovery in 2023, with a projected increase of nearly 70% compared to the previous year. This comes after a challenging period of slow growth in the industry. The improved growth can be attributed to the completion of projects that were delayed due to COVID-19 restrictions in China and supply chain issues in Europe and the United States.
However, the extent of growth in 2024 will depend on whether governments can offer more policy support to address obstacles related to permitting and auction design. Unlike the solar PV sector, the wind turbine supply chains are not expanding quickly enough to keep up with the growing demand in the medium term. This is primarily due to escalating commodity prices and difficulties in the supply chain, which are impacting the profitability of manufacturers.
This renewable energy requirement incorporates project logistics as the machines and other parts are so huge that they are shipped separately and then assembled at the site.
Growing Modular Construction Driving The Market
The need for sustainable infrastructure is driving the development of construction technology that is efficient and environmentally friendly. The traditional construction method may no longer be sufficient to meet the requirements of sustainable infrastructure. Modularization offers a solution to the inflexibility of conventional construction methods. By using modular construction, the cost of construction can potentially be reduced by 40%, and activities can be carried out simultaneously on site preparation and modular prefabrication.
The shift towards modular (offsite) construction methods creates a new market, particularly for developing countries that have low labor costs and ample land for prefabrication areas. In terms of supporting sustainable infrastructure development, prefabrication methods can lead to significant material savings, such as 60% less steel, 56% less concrete, and 77% less formwork compared to conventional construction methods of a similar scale.
However, there are still challenges with the modular prefabrication concept, such as the economics of scale and the complexity of transporting modular components that exceed the size of ISO containers. This offsite construction model also opens up opportunities for international trade within specific geographical regions, depending on each country's competitive advantages. The growth of international free trade provides broader business opportunities and potential for new trading connections. International and regional trade also increases the overseas trading of engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) projects. The decision to use modular construction for overseas EPC projects impacts the development of project cargo movement and the overall investment in project logistics, including domestic and overseas logistics costs. Domestic logistics costs include manufacturing costs (fabrication, ready-mix concrete, bulk materials, rebar, and steel materials). In contrast, overseas logistics costs include vessel charter rates, bunker pricing, currency exchange, distance, volumetric sizing, insurance, and customs clearance.
Project Logistics Industry Overview
The project logistics market is fragmented, with the presence of global players and small- and medium-sized local players. Most global logistics players have a special project cargo division to meet the market needs and demand. Local players are also increasingly enhancing their capabilities in terms of fleet size, service offerings, industries served, and technology. Global manufacturers are making large and oversized components in the factory sites (off-site), which creates huge complexities for heavy cargo haulage companies. Global companies with high capital and assets can invest in upgraded fleets and benefit from this scenario. On the other hand, regional and local players are also coming up with better industry solutions to support the client's needs in executing the projects in the scheduled time.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Increasing Demand For Project Logistics From Renewable Energy Projects
- 4.2.1.2 Increasing Investments In Infrastructure
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 High Initial Capital Investment
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.3 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.6 Global Logistics Sector (Overview, LPI Scores, Key Freight Statistics, Etc.)
- 4.7 Spotlight - Role of Multimodal Transport in Project Cargo
- 4.8 Insights - Retail Oil and Gas Logistics Sector
- 4.9 Review and Commentary on Heavy and Large Dimension Shipments
- 4.10 Focus on the Prefabrication Industry - Role of Project Logistics Companies in Transportation
- 4.11 Insights into Customized Trailer Manufacturers for Moving Heavy Cargo
- 4.12 Spotlight on the Demand for Contract Logistics and Integrated Logistics
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Service
- 5.1.1 Transportation
- 5.1.2 Forwarding
- 5.1.3 Inventory Management and Warehousing
- 5.1.4 Other Value-added Services
- 5.2 End User
- 5.2.1 Oil and Gas, Mining, and Quarrying
- 5.2.2 Energy and Power
- 5.2.3 Construction
- 5.2.4 Manufacturing
- 5.2.5 Other End Users
- 5.3 Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 Americas
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.4 Middle-East and Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Overview (Market Concentration and Major Players)
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Rhenus Logistics
- 6.2.2 Bollore Logistics
- 6.2.3 Agility Logistics
- 6.2.4 EMO Trans
- 6.2.5 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 6.2.6 Kuehne + Nagel International AG
- 6.2.7 C.H. Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- 6.2.8 Ceva Logistics
- 6.2.9 NMT Global Project Logistics
- 6.2.10 Rohlig Logistics
- 6.2.11 Ryder System Inc.
- 6.2.12 Expeditors International of Washington Inc.
- 6.2.13 Megalift Sdn Bhd
- 6.2.14 Dako Worldwide Transport GmbH
- 6.2.15 CKB Logistics Group
- 6.2.16 SAL Heavy Lift GmbH
- 6.2.17 DB Schenker
- 6.2.18 Kerry Logistics
- 6.2.19 Deutsche Post DHL*
- 6.3 Other Players in the Market
- 6.3.1 FLS Transportation Services, Crowley Logistics, Highland Forwarding Inc., Kinetix International Logistics, Cole International Inc., Hisiang Logistics Co. Ltd, Sea Cargo Air Cargo Logistics Inc., and Bati Group
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 GDP Distribution, by Activity - Key Countries
- 8.2 Insights into Capital Flows - Key Countries
- 8.3 Economic Statistics - Transport and Storage Sector, and Contribution to Economy (Key Countries)
- 8.4 List of Major Global Projects (Oil and Gas, Construction, Infrastructure Development, Etc.)
- 8.5 Freight Statistics (Mode, Product Category, Etc.)









