 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1687179
太陽能逆變器:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Solar PV Inverters - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
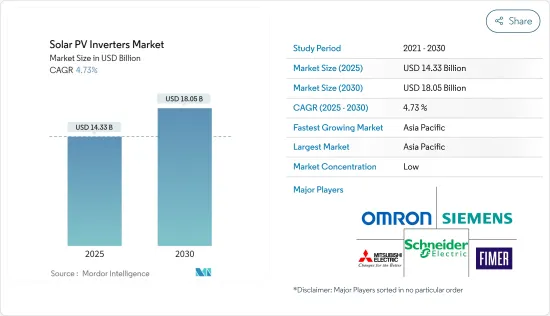
預計 2025 年太陽能逆變器市場規模為 143.3 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 180.5 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 4.73%。
受訪的市場在2020年受到了新冠肺炎疫情的影響,但目前已恢復到疫情前的水平。
預計預測期內對太陽能的需求不斷成長將推動太陽能逆變器市場的成長。預計不斷增加的投資和雄心勃勃的太陽能目標將推動所研究市場的成長。然而,預計預測期內串列型逆變器的技術缺陷將會阻礙太陽能光電逆變器市場的成長。
預計預測期內,太陽能光電逆變器的產品創新和最新技術的採用將為太陽能光電逆變器市場創造有利的成長機會。亞太地區佔據市場主導地位,預計在預測期內將以最高的複合年成長率成長。這一成長得益於印度、中國和澳大利亞等地區國家的投資增加和政府的支持政策。
太陽能逆變器市場趨勢
集中式逆變器市場預計將佔據市場主導地位
集中逆變器是大型併網設備。它常用於額定輸出功率超過100kWp的太陽能發電系統。落地式或地面安裝的逆變器將從太陽能電池陣列收集的直流電轉換為交流電以用於並聯型。這些設備的容量範圍從大約 50kW 到 1MW,可在室內和室外使用。
中央逆變器由一個DC-AC轉換級組成。為了擴大 MPP(最大功率點)電壓範圍,一些逆變器還具有 DC-DC 升壓級。可以使用低頻變壓器來升高交流電壓並隔離輸出。然而,這會降低效率並增加逆變器的尺寸、重量和成本。
中央逆變器的最大輸入電壓通常為1,000V。然而,一些現代中央逆變器的輸入電壓已經達到1,500V。這些逆變器可支援高達 1,500V 電壓的光伏陣列,並且需要更少的 BOS(系統平衡)組件。
中央逆變器可以是單片式的(具有單一動力傳動系統和多個 MPPT 追蹤器),也可以是模組化的(具有多個動力傳動系統)。模組化逆變器更為複雜,但如果一個或多個模組發生故障,則可以維持降低的輸出,並且可以使用多 MPPT 或主從控制方法。多 MPPT 系統對每個浮動陣列使用單獨的轉換器和 MPPT,從而增加部分陰影條件下的整體能量收集。在主從方法中,控制器模組始終處於開啟狀態。當陣列中有更多的電力可用時,它會命令從屬模組打開,從而在低輻射環境下最大限度地提高逆變器的效率。
中央逆變器用於公用事業規模的應用,因此必須產生與其所使用的電網相同的電壓和頻率。由於世界各地的電網標準不同,允許製造商自訂這些參數以滿足相數的特定要求,而生產的集中式逆變器大部分都是三相逆變器。
2022年1月,陽光電源在阿布達比世界未來能源高峰會上推出了全新1+X中央模組化逆變器,輸出容量為1.1兆瓦。本款1+X模組化逆變器可組合8台單元,達到8.8MW的輸出功率,並配備DC/ESS介面,可連接能源儲存系統(ESS)。
因此,預計電力需求的增加、政府對電力產業脫碳的舉措以及中央逆變器成本的下降將在預測期內推動該產業的成長。
亞太地區佔市場主導地位
亞太地區在 2021 年佔據了太陽能逆變器市場的主導地位,預計未來仍將繼續保持主導地位。預計大部分需求將來自中國,中國也是世界上最大的太陽能生產國。
在中國,人們越來越重視具有零電壓穿越(ZVRT)功能的太陽能逆變器。為了滿足該系統的標準,太陽能發電廠必須持續運作而不發生故障。由於該國是世界上太陽能發電量最大的國家,因此這項措施具有更重要的意義。
隨著世界各地,特別是亞太地區對工業化造成的污染的擔憂日益加劇,該地區的太陽能發電獲得了顯著發展勢頭。作為《巴黎協定》承諾的一部分,印度政府設定了一個雄心勃勃的目標,即在2022年實現175吉瓦的可再生能源裝置容量。在這175吉瓦中,100吉瓦將用於太陽能發電,而這其中的40吉瓦(40%)將透過分散式和屋頂規模的太陽能發電工程來實現。為了實現這一宏偉目標,政府於 2019 年啟動了多個新計劃,包括太陽能屋頂第二階段、PM-KUSUM 和超大型可再生能源發電園區 (UMREPP) 的開發。
印度太陽能發電潛力超過750GW,該國《2047年能源安全情境》顯示,到2047年,印度太陽能發電裝置容量可達479GW左右。印度太陽輻射強,太陽能發電已實現市電平價,推動光伏成為主流能源來源,公用事業和屋頂光伏領域的裝置容量不斷提升。
截至 2021 年 11 月,陽光電源自 2014 年以來已在印度出貨超過 10 GW 的太陽能逆變器。這是由於全國對太陽能的需求不斷增加。 2022年3月,陽光電源將印度工廠產能擴大至每年10GW。預計製造業的如此大規模發展將在預測期內推動所研究市場的成長。
因此,由於中國、印度和馬來西亞等國家推出的各種政府舉措,預計亞太地區將在預測期內主導太陽能逆變器市場。
光電逆變器產業概況
太陽能逆變器市場比較分散。市場的主要企業(不分先後順序)包括 FIMER SpA、施耐德電氣 SE、西門子股份公司、三菱電機株式會社、歐姆龍株式會社。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 研究範圍
- 市場定義
- 調查前提
第 2 章執行摘要
第3章調查方法
第4章 市場概況
- 介紹
- 2027 年市場規模與需求預測
- 最新趨勢和發展
- 政府法規和政策
- 市場動態
- 驅動程式
- 限制因素
- 供應鏈分析
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第5章 市場區隔
- 按逆變器類型
- 集中式逆變器
- 串列型逆變器
- 微型逆變器
- 按應用
- 住宅
- 商業和工業
- 實用規模
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 南美洲
- 中東和非洲
第6章 競爭格局
- 併購、合資、合作、協議
- 主要企業策略
- 公司簡介
- FIMER SpA
- Schneider Electric SE
- Siemens AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Omron Corporation
- General Electric Company
- SMA Solar Technology AG
- Delta Energy Systems Inc.
- Enphase Energy Inc.
- SolarEdge Technologies Inc.
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
The Solar PV Inverters Market size is estimated at USD 14.33 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 18.05 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.73% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Although the market studied was affected by COVID-19 in 2020, it has recovered and reached pre-pandemic levels.
The growing demand for solar power is expected to stimulate the growth of the solar PV inverters market during the forecast period. Increasing investments and ambitious solar energy targets are expected to drive the growth of the market studied. However, technical drawbacks of string inverters are expected to hamper the growth of the solar PV inverters market during the forecast period.
Product innovation and adaptation of the latest technologies in solar PV inverters are anticipated to create lucrative growth opportunities for the solar PV inverters market during the forecast period. Asia-Pacific dominates the market, and it is expected to record the highest CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the increasing investments and supportive government policies in the countries of this region, including India, China, and Australia.
Solar PV Inverter Market Trends
Central Inverters Segment Expected to Dominate the Market
A central inverter is a large grid feeder. It is often used in solar photovoltaic systems with rated outputs over 100 kWp. Floor or ground-mounted inverters convert DC power collected from a solar array into AC power for grid connection. These devices range in capacity from around 50kW to 1MW and can be used indoors or outdoors.
A central inverter consists of one DC-AC conversion stage. Some inverters also have a DC-DC boost stage to increase their MPP (maximum power point) voltage range. Low-frequency transformers are sometimes used to boost the AC voltage and provide isolation at the output. However, this reduces efficiency and increases the inverter's size, weight, and cost.
A central inverter typically has a maximum input voltage of 1,000V. However, some newer central inverters already come with 1,500V input voltage. These inverters allow PV arrays based on a maximum voltage of 1,500V, requiring fewer BOS (balance of system) components.
Central inverters can be monolithic (using a single power train and multi-MPPT tracker) or modular (using multiple power trains). Modular inverters are more complex but can maintain reduced power output if one or more modules fail and can use either a multi-MPPT or a master-slave control approach. The multi-MPPT system uses a separate converter and MPPT for each floating sub-array, increasing the overall energy harvest under partial shading conditions. In the master-slave approach, the controller module is always on. It commands the slave modules to switch on when more power is available from the array, which maximizes inverter efficiency in low-insolation environments.
As central inverters are used for utility-scale applications, they should produce the same voltage and frequency as that of the electric grid where they are used. As there are a lot of different electric grid standards worldwide, manufacturers are allowed to customize these parameters to match the specific requirements in terms of the number of phases; most central inverters manufactured are three-phase inverters.
In January 2022, Sungrow launched its new 1+X central modular inverter with an output capacity of 1.1MW at the World Future Energy Summit in Abu Dhabi. This 1+X modular inverter can be combined into eight units to reach a power of 8.8MW and features a DC/ESS interface for the connection of energy storage systems (ESS).
Therefore, the growing demand for electricity, the government's efforts to decarbonize the power sector, and the declining costs of central inverters are expected to drive the segment's growth during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific to Dominate the Market
Asia-Pacific dominated the solar PV inverter market in 2021, and it is expected to continue its dominance over the coming years. Most of the demand is expected to come from China, which is also the largest producer of solar energy in the world.
There has been an increased emphasis on solar inverters in China, providing a zero-voltage ride through (ZVRT) scheme. To meet the scheme norms, the solar PV power plants must continue to operate without breaking. This is even more significant as the country hosts the largest amount of solar power generation in the world.
With the rising concerns over pollution across the world due to industrialization, especially in Asia-Pacific, regional solar power generation gained considerable momentum. As part of the Paris Agreement commitments, the Government of India set an ambitious target of achieving 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022. Out of the 175 GW, 100 GW was earmarked for solar capacity with 40 GW (40%), which was expected to be achieved through decentralized and rooftop-scale solar projects. To achieve this huge target, the government launched several new programs in 2019, like the solar rooftop phase-2, PM-KUSUM, and the development of ultra mega renewable energy power parks (UMREPPs).
India's solar potential is more than 750 GW, and the country's energy security scenario 2047 shows a possibility of achieving around 479 GW of solar PV installed capacity by 2047. Solar power in India, bestowed with high solar irradiance, has already achieved grid parity that encourages the adoption of solar power as a mainstream energy source, pushing forward the capacity installations in the utility-scale and rooftop solar segments.
As of November 2021, Sungrow Power Supply Co. Ltd has shipped more than 10 GW of solar inverters in India since 2014. This is due to the increased demand for solar energy across the country. In March 2022, Sungrow increased its fab capacity in India to 10GW/annum capacity. Such a large development in the manufacturing sector is expected to boost the growth of the market studied during the forecast period.
Therefore, with various government initiatives launched by China, India, Malaysia, etc., Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the solar PV inverter market during the forecast period.
Solar PV Inverter Industry Overview
The solar PV inverters market is fragmented in nature. Some of the major players in the market (in no particular order) include FIMER SpA, Schneider Electric SE, Siemens AG, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and Omron Corporation.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Market Size and Demand Forecast in USD billion, till 2027
- 4.3 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.4 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 Market Dynamics
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.5.2 Restraints
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Inverter Type
- 5.1.1 Central Inverters
- 5.1.2 String Inverters
- 5.1.3 Micro Inverters
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Residential
- 5.2.2 Commercial and Industrial
- 5.2.3 Utility-scale
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.5 Middle East and Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 FIMER SpA
- 6.3.2 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.3.3 Siemens AG
- 6.3.4 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.3.5 Omron Corporation
- 6.3.6 General Electric Company
- 6.3.7 SMA Solar Technology AG
- 6.3.8 Delta Energy Systems Inc.
- 6.3.9 Enphase Energy Inc.
- 6.3.10 SolarEdge Technologies Inc.
- 6.3.11 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd








