 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1636256
廢棄物回收服務 -市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢/統計、成長預測(2025-2030)Waste Recycling Services - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
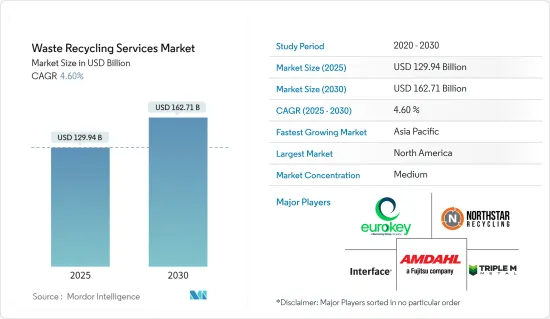
廢棄物回收服務市場規模預計到 2025 年為 1,299.4 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 1,627.1 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)複合年成長率為 4.6%。
主要亮點
- 對永續性的需求不斷成長和人口的快速成長正在推動廢棄物回收服務市場的發展。
- 現代經濟中廢物的數量和複雜性不斷增加,日益使生態系統和人類健康面臨風險。據估計,全球整體每年收集112億噸固態廢棄物,其有機物腐爛產生的溫室氣體排放量約佔全球溫室氣體排放的5%。特別是,電氣和電子設備排放的廢棄物含有有害物質,這已成為已開發國家和開發中國家的首要問題。
- 從缺乏收集系統到處理方法不當,廢棄物管理不善會導致空氣污染、水源和土壤污染。不當的垃圾掩埋場進一步污染飲用水,造成健康風險和疾病傳播。散落的碎片危害生態系統,電子廢棄物和工業廢棄物中的有害物質對城市健康和環境造成負擔。
- 第一個解決方案在於最大限度地減少廢棄物。當廢棄物不可避免時,重點就會轉移到材料和能源回收以及再製造和回收。尤其是回收利用可以節省大量資源。例如,回收一噸紙可以節省 17 棵樹和 50% 的正常用水量。此外,回收業是重要的就業來源,在巴西、中國和美國僱用了超過 1,200 萬人。
- 2024年3月15日,環境、森林和氣候變遷部(MOEFCC)在印度官方公報上公佈了《2024年塑膠廢棄物管理(修訂)規則》,該規則進一步細化了《2016年塑膠廢棄物管理規則》 。這些修正案一宣布立即生效,突顯了印度對抗塑膠污染的承諾。因此,地方政府機構正在加緊努力,盡量減少廢棄物並推廣回收服務。
廢棄物回收服務的市場趨勢
廢棄物回收活動活性化的地方政府部門
根據聯合國環境規劃署 (UNEP) 的最新報告,預計城市產生的廢棄物將猛增三分之二,相關成本將在一代人內幾乎翻倍,確保永續且負擔得起的未來。 ,迫切需要大幅減少廢棄物的產生。
聯合國環境規劃署的報告預測,全球都市固態廢棄物產生量將從2023年的23億噸增加到2050年的38億噸。如果考慮到廢棄物管理不當的深遠影響(污染、健康危害、氣候變遷等),估計費用將上升至 3,610 億美元。如果不迅速解決廢棄物管理問題,到 2050 年,全球每年的成本可能飆升至驚人的 6,403 億美元,各國將實施城市廢棄物回收舉措,這凸顯了優先考慮這一問題的緊迫性。
中國作為世界第二人口大國,面臨工業、農業和生活部門每年排放超過100億噸廢棄物的巨大挑戰。生態環境部於 2024 年 1 月發布的這項資料凸顯了這個問題的嚴重性。不過,中國生活廢棄物也有正面進展。為了改善生活條件並增強經濟效益,像趙這樣的公司正在採取創新方法。我們正在招募針對困難廢棄物的獨特方法,例如從特定地區收集廢棄物,焚燒不可回收的廢棄物為都市區提供電力,以及在焚燒前對果皮進行發酵和脫水。
沙烏地阿拉伯投資回收公司 (SIRC) 宣布計劃投資垃圾焚化發電工廠,以符合該國在 2030 年實現 3GW垃圾焚化發電能力的野心。 SIRC 的一個重點是提高垃圾焚化發電過程的成本效率。因此,地方政府正在採取各種舉措來促進回收。
亞太地區市場將顯著成長
亞洲經濟的快速成長和都市化加劇了人們對固態廢棄物產生和管理的擔憂。使問題更加複雜的是,亞洲國家和地區儘管位於同一地理區域,但在廢棄物管理和材料循環計劃方面擁有獨特的方法。
隨著世界走向循環經濟,廢棄物管理在亞太市場越來越受到關注。根據聯合國區域發展中心的報告,2014年該地區產生的塑膠廢棄物量為7,000萬噸至1.04億噸。預計由於原生塑膠消費量的不斷增加,到2030年這數字可能飆升至1.4億噸。
儘管對再生塑膠的需求不斷增加,但該地區缺乏廢棄物基礎設施。然而,合作、監管和投資方面的共同努力正在克服這一障礙,實現循環經濟的願景。
機械回收在亞太地區,特別是在東北亞和印度半島已佔有一席之地。目前該地區機械回收裝置容量超過每年1800萬噸。其中,中國佔該產能的66%,其次是印度,佔比約8%。 2012年至2022年間,該地區機械回收能力加倍,並自2018年以來維持年均約4%的成長率。根據 ICIS 預測,機械回收產量預計將大幅飆升,從 2023 年的每年 1,200 萬噸增至 2040 年的每年 3,500 萬噸。這使得亞太地區需要付出巨大的努力來減少每天產生的廢棄物。
廢棄物回收服務業概況
廢棄物回收服務市場分散。競爭格局多元化且充滿活力。各種公司競相提供回收服務、廢棄物收集、分類、加工和處置。市場的主要企業包括 Eurokey Recycling Ltd、Northstar Recycling、Triple M Metal LP、Amdahl Corp. 和 Interface Inc.。
中小企業在廢棄物回收服務市場中也發揮著重要作用,提供專業服務或針對特定地區或廢棄物流。
其他好處
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月分析師支持
目錄
第1章簡介
- 調查先決條件
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
- 分析方法
- 調查階段
第3章執行摘要
第4章市場動態與洞察
- 目前的市場狀況
- 市場動態
- 促進因素
- 對永續性的需求不斷成長推動市場
- 人們對環境問題的興趣日益濃厚
- 抑制因素
- 影響市場的監管因素
- 影響市場的基礎建設挑戰
- 市場機會
- 市場驅動的技術進步
- 促進因素
- 價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 政府法規、貿易協定和舉措
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭公司之間的敵對關係
- 廢棄物回收服務市場的技術開發
- COVID-19 對市場的影響
第5章市場區隔
- 依產品
- 紙/紙板
- 金屬
- 塑膠
- 玻璃
- 電池/電子產品
- 其他
- 按來源
- 地方政府(住宅和商業設施)
- 工業的
- 其他來源
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 歐洲
- 亞太地區
- 中東/非洲
- 南美洲
第6章 競爭狀況
- 市場集中度概覽
- 公司簡介
- Eurokey Recycling Ltd
- Northstar Recycling
- Triple M Metal LP
- Amdahl Corp.
- Interface Inc.
- Covanta
- Epson Inc.
- Collins & Aikman
- Xerox Corp.
- Fetzer Vineyards*
- 其他公司
第7章 市場的未來
第8章附錄
The Waste Recycling Services Market size is estimated at USD 129.94 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 162.71 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.6% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- The increasing demand for sustainability and rapid population growth drives the waste recycling services market.
- The modern economy's escalating waste volume and complexity are increasingly endangering ecosystems and human health. Globally, an estimated 11.2 billion tonnes of solid waste are collected annually, with the decay of its organic fraction contributing to about 5% of the world's greenhouse gas emissions. Notably, waste from electrical and electronic equipment, laden with new and hazardous substances, is emerging as a top challenge in both developed and developing nations.
- Poor waste management, spanning from absent collection systems to inadequate disposal methods, leads to air pollution and contaminates water and soil. Improper landfills further contaminate drinking water, posing health risks and disease transmission. Debris dispersal harms ecosystems, while hazardous substances from electronic and industrial waste strain both urban health and the environment.
- The primary solution lies in waste minimization. When waste is inevitable, the focus shifts to material and energy recovery, alongside remanufacturing and recycling. Recycling, in particular, offers significant resource savings. For instance, recycling a tonne of paper saves 17 trees and 50% of the water typically used. Additionally, the recycling industry is a significant job creator, employing over 12 million individuals across Brazil, China, and the United States.
- On March 15, 2024, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MOEFCC) announced the Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2024, in the Gazette of India, further refining the 2016 Plastic Waste Management Rules. Effective immediately upon publication, this amendment underscored India's commitment to combating plastic pollution. Hence, government bodies across various regions are intensifying efforts to minimize waste and promote recycling services.
Waste Recycling Services Market Trends
Municipal Segment Seeing an Upsurge in Waste Recycling Activities
With municipal waste projected to surge by two-thirds and its associated costs nearly doubling within a generation, a recent report by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) highlights the urgent need for a significant reduction in waste generation to ensure a sustainable and affordable future.
The UNEP report forecasts that global municipal solid waste generation, which stood at 2.3 billion tonnes in 2023, will reach 3.8 billion tonnes by 2050. When considering the broader impacts of inadequate waste management-such as pollution, health hazards, and climate change-the estimated cost escalates to a substantial USD 361 billion. Failing to address waste management issues promptly could see this annual global cost soar to a monumental USD 640.3 billion by 2050, underscoring the pressing need for nations to prioritize municipal waste recycling initiatives.
China, the world's second most populous country, faces a monumental challenge, producing over 10 billion tons of waste annually, spanning industrial, agricultural, and domestic sectors. This data, released by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment in January 2024, underscores the scale of the issue. However, there are positive strides in China's domestic waste treatment. In an effort to enhance living conditions and bolster economic gains, companies like Zhao's are adopting innovative approaches. They are gathering waste from specific zones, incinerating non-recyclables to power urban areas, and employing unique methods for challenging waste, like fermenting and dehydrating fruit peels before incineration.
Saudi Investment Recycling Company (SIRC) announced plans to invest in waste-to-energy plants, aligning with the nation's ambition to achieve a 3GW waste-to-energy capacity by 2030. A key focus for SIRC is enhancing the cost-efficiency of waste-to-energy processes. Hence, regional governments are spearheading various initiatives to promote recycling endeavors.
Asia-Pacific Observing Significant Growth in the Market
Asia's rapid economic growth and urbanization are amplifying concerns about solid waste generation and management. Adding complexity, each Asian country and region boasts unique approaches to waste management and material-cycle policies despite their shared geographic region.
As the world pushes toward a circular economy, the spotlight on waste management in the Asia-Pacific market intensifies. The United Nations Centre for Regional Development reported that in 2014, the region generated a staggering 70-104 million tonnes of plastic waste. Projections indicate this number could surge to 140 million tonnes by 2030, propelled by a relentless rise in virgin plastic consumption.
While the demand for recycled plastics is on the upswing, the region grapples with a glaring deficit in waste infrastructure. However, concerted efforts in collaboration, regulation, and investment are underway, aiming to surmount this hurdle and actualize the circular economy vision.
In Asia-Pacific, mechanical recycling, especially in Northeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent, has a well-established presence. The region's current installed capacity for mechanical recycling stands at over 18 million tonnes annually. Notably, China leads, accounting for 66% of this capacity, with India following with an approximately 8% share. From 2012 to 2022, the region's mechanical recycling capacity doubled, and it has maintained an average annual growth rate of about 4% since 2018. Projections from ICIS indicate a significant surge in mechanical recycling output, from 12 million tonnes in 2023 to an estimated 35 million tonnes annually by 2040. With this, Asia-Pacific is making a surmountable effort to reduce the waste generated every day.
Waste Recycling Services Industry Overview
The waste recycling services market is fragmented in nature. The competitive landscape is diverse and dynamic. Various companies compete to provide recycling services, waste collection, sorting, processing, and disposal. Some key players in the market include Eurokey Recycling Ltd, Northstar Recycling, Triple M Metal LP, Amdahl Corp., and Interface Inc.
Small and medium-sized enterprises also play a significant role in the waste recycling services market, offering specialized services or catering to specific regions or waste streams.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS AND INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Increasing Demand for Sustainability Driving the Market
- 4.2.1.2 Environmental Concerns Driving the Market
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 Regulatory Factors Affecting the Market
- 4.2.2.2 Infrastructure Challenges Affecting the Market
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.2.3.1 Technological Advancements Driving the Market
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.3 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Government Regulations, Trade Agreements, and Initiatives
- 4.5 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Technological Developments in the Waste Recycling Services Market
- 4.7 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Paper & Paperboard
- 5.1.2 Metals
- 5.1.3 Plastics
- 5.1.4 Glass
- 5.1.5 Batteries & Electronics
- 5.1.6 Other Products
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Municipal (Residential and Commercial)
- 5.2.2 Industrial
- 5.2.3 Other Sources
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 North America
- 5.3.2 Europe
- 5.3.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.5 South America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Eurokey Recycling Ltd
- 6.2.2 Northstar Recycling
- 6.2.3 Triple M Metal LP
- 6.2.4 Amdahl Corp.
- 6.2.5 Interface Inc.
- 6.2.6 Covanta
- 6.2.7 Epson Inc.
- 6.2.8 Collins & Aikman
- 6.2.9 Xerox Corp.
- 6.2.10 Fetzer Vineyards*
- 6.3 Other Companies













