 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1636556
亞太地區電子廢棄物管理:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)APAC E-Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
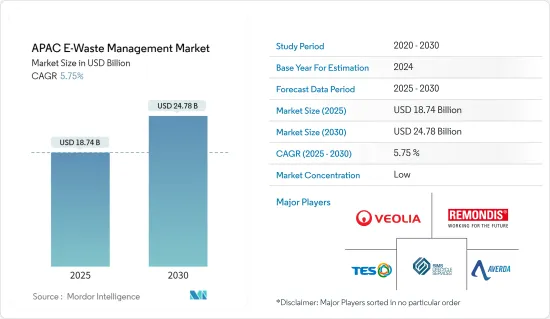
亞太地區電子廢棄物管理市場規模預計在 2025 年達到 187.4 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 247.8 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 5.75%。
由於科技的快速進步、消費性電子產品的日益普及以及強勁的經濟成長,亞太地區的電子廢棄物正在大幅增加。中國、印度和日本是主要貢獻者。
2023年8月,日本宣布與東南亞國協建立夥伴關係,共同因應電子廢棄物挑戰。該合作由環境部長會議建立,重點致力於制定電子廢棄物的法規。日本將透過2024財政年度預算支持建立廢棄物管理企業的註冊和認證制度。
該舉措旨在改善東南亞地區的電子廢棄物,由於廢棄物進口管理鬆懈,該地區受到環境污染和健康風險的困擾。日本也希望從電子廢棄物中回收有價值的金屬,以支持其電動車產業並緩解該國有限的金屬資源。
同時,2024年5月,韓國私募股權和環境相關企業增加了對垃圾掩埋場領域的投資。 Afilma Capital 以 5,000 億韓元(3.68 億美元)收購了領先的垃圾掩埋場營運商 Gentec。 Gentec 在忠清南道唐津市經營一個大型垃圾掩埋場。這種日益成長的興趣反映了人們對廢棄物管理的信心日益增強,也預示著電子廢棄物處理技術可能取得進步。
亞太地區電子廢棄物管理市場趨勢
印度EPR認證平台提升廢棄物垃圾回收效率
22會計年度,印度排放了超過160萬噸電子廢棄物,其中52.7萬噸被收集和處理。截至 2024 年 3 月,政府計劃推出一個用於交易生產者延伸責任 (EPR) 證書的線上平台,以應對這一日益嚴峻的挑戰。強制實施 EPR 要求生產商負責回收廢棄的產品,從而鼓勵生產更多可回收和可再利用的產品。
中央污染控制委員會 (CPCB) 正在監督該平台,以提高 EPR 認證市場的透明度和效率。公司可以透過內部管理廢棄物或從超過回收標準的營業單位獲得 EPR 證書來履行其回收義務。 CPCB 將根據未達到 EPR 目標的環境補償百分比為這些證書制定指導方針和價格。
自 2022 年《電子廢棄物(管理)規則》中引入 EPR 規定以來,政府已處理了 5,615 份 EPR 申請,核准了4,865 份,收到了 285 份來自回收商的申請,並批准了 196 份。值得注意的是,政府已經超額完成了 10.5 億噸廢棄電器及電子設備(WEEE)的回收目標。政府目前正尋求利用即將推出的平台來加強這些努力。
中國在北京舉辦活動重點關注電子廢棄物創新與永續性工作
業內專家表示,2022年,全球最大的電子廢棄物生產國中國排放了超過1,200萬噸電子廢棄物。時間快轉到2024年4月,北京捷佳苑外交居住(DRC)舉辦了一場活動,展示中國在廢棄物分類和回收方面的突破。此次博覽會展示了尖端的人工智慧廢棄物分類機,並介紹了由再生材料製成的產品。值得注意的是,該活動包括針對兒童的互動活動,並強調了回收的重要性。
這項活動由北京市對外環境衛生服務中心主辦,凸顯了中國利用人工智慧、物聯網、巨量資料和雲端運算領域的進步對抗電子廢棄物的決心。這次訪問由中國公共外交協會下屬的中國國際新聞傳播中心組織,是受新冠肺炎疫情影響暫停的媒體交流活動的一部分。節目匯集了來自 90 多個國家的 100 多名記者,重點關注媒體交流並深入了解中國正在發生的發展。
透過這樣的展示和舉措,中國正在建立自己在永續電子廢棄物管理技術方面處於領先地位的形象。這項戰略措施旨在加強中國的全球地位,擴大其在國際環境對話中的軟實力和影響力。
亞太地區電子廢棄物管理產業概況
亞太地區電子廢棄物管理市場正面臨威立雅集團、Remondis 和 Averda 等主要參與者以及 Sims Recycling Solutions 和 TES-AMM 的激烈競爭。威立雅集團和利蒙迪斯尤其突出,他們專注於先進的回收技術,並不斷擴大服務組合以處理不同的電子廢棄物流。
這些市場領先的公司優先考慮永續性,並與地方政府夥伴關係加強電子廢棄物收集和回收基礎設施。 Attero 是印度電子廢棄物產業的主要企業,擁有廣泛的收集網路和最先進的回收方法。這些公司透過對技術、監管環境和永續實踐的策略關注,推動了亞太地區電子廢棄物市場的發展,為更高效、更環保的電子廢棄物管理鋪平了道路。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 調查結果
- 調查前提
- 研究範圍
第2章調查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究階段
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場洞察
- 當前市場狀況
- 科技趨勢
- 供應鏈/價值鏈分析洞察
- 產業監管見解
- 洞察產業技術進步
第5章 市場動態
- 市場促進因素
- 科技的快速進步導致電子垃圾數量增加
- 都市化和工業化
- 市場限制
- 回收成本高
- 電子廢棄物的複雜性
- 市場機會
- 回收技術的進步
- 官民合作關係
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 購買者/消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
第6章 市場細分
- 依材料類型
- 金屬
- 塑膠
- 玻璃
- 其他材料
- 依排放源類型
- 家用電子電器
- 工業電子
- 家電
- 其他
- 按應用
- 垃圾掩埋場
- 回收利用
- 其他用途
- 按國家
- 中國
- 日本
- 印度
- 韓國
- 其他亞太地區
第7章 競爭格局
- 市場集中度概覽
- 公司簡介
- Veolia Group
- Remondis
- Averda
- Sims Recycling Solutions
- TES-AMM
- Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd
- Blue Planet Environmental Solutions Pte Ltd
- ECO Recycling Ltd(Ecoreco)
- Attero
- JOMAR Life Research Laboratory
- 其他公司
第8章 市場機會與未來趨勢
第 9 章 附錄
The APAC E-Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 18.74 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 24.78 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.75% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Asia-Pacific region is experiencing a significant rise in electronic waste due to rapid technological advancements, increased adoption of consumer electronics, and strong economic growth. China, India, and Japan are major contributors.
In August 2023, Japan announced a partnership with ASEAN countries to address e-waste challenges. This collaboration, established during an environment ministers' meeting, focuses on developing regulations for e-waste disposal. Japan will assist in creating registration and certification systems for waste management businesses, funded through its fiscal year 2024 budget.
This initiative aims to improve e-waste handling in Southeast Asia, which has struggled with environmental contamination and health risks due to lax waste import regulations. Japan also seeks to recover valuable metals from e-waste, supporting its electric vehicle industry and mitigating its limited domestic metal resources.
Meanwhile, in May 2024, South Korea's private equity and environmental firms increasingly invested in the landfill sector. Affirma Capital acquired Jentec, a major landfill operator, for KRW 500 billion (USD 368 million). Jentec operates a large landfill in Dangjin, South Chungcheong Province. This growing interest reflects increased confidence in waste management and suggests potential advancements in e-waste treatment technologies.
APAC E-Waste Management Market Trends
India's Upcoming EPR Certificate Platform to Boost E-Waste Recycling Efficiency
In the financial year 2022, India produced over 1.6 million metric tons of e-waste, with 527 thousand metric tons being collected and processed. As of March 2024, the government plans to roll out an online platform for trading Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) certificates to combat this escalating challenge. EPR mandates hold producers accountable for recycling their products post-disposal, thereby promoting the creation of more recyclable and reusable goods.
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) oversees this platform to boost transparency and efficiency in the EPR certificate market. Companies can fulfill recycling obligations by managing waste internally or procuring EPR certificates from entities surpassing their recycling benchmarks. The CPCB will set the guidelines and pricing for these certificates, pegged to a percentage of the environmental compensation for unmet EPR targets.
Since the inception of EPR directives in the E-Waste (Management) Rules of 2022, the government has processed 5,615 EPR applications, approving 4,865, and has received 285 applications from recyclers, granting 196. Notably, the government has already surpassed its recycling goal of 1.05 billion metric tons for Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE). It is now looking to bolster these efforts with the upcoming platform.
China Highlights E-Waste Innovations and Sustainability Initiatives at Beijing Event
Industry experts note that in 2022, China, the world's largest producer of electronic waste, churned out over 12 million metric tons. Fast-forward to April 2024, when the Qijiayuan Diplomatic Residence Compound (DRC) in Beijing set the stage for an event spotlighting China's waste sorting and recycling strides. The exhibition featured cutting-edge AI-driven waste-sorting machinery and showcased products crafted from recycled materials. Notably, the event included interactive activities for children, emphasizing the importance of recycling.
Hosted by the Beijing Municipal Center for Foreign-related Environment Sanitation Services, the event underscored China's resolve to combat e-waste, leveraging advancements in AI, IoT, big data, and cloud computing. The China International Press Communication Center (CIPCC), under the China Public Diplomacy Association (CPDA), facilitated this visit as part of a media exchange initiative reignited after a pause during the COVID-19 pandemic. The program hosted 100+ journalists from 90+ nations, focusing on media exchange and offering insights into China's ongoing developments.
Through such showcases and initiatives, China is crafting a narrative of being a frontrunner in sustainable e-waste management technology. This strategic move aims to bolster China's global standing, amplifying its soft power and influence in international environmental dialogues.
APAC E-Waste Management Industry Overview
The e-waste management market in Asia-Pacific sees intense competition, with major firms like Veolia Group, Remondis, and Averda, alongside Sims Recycling Solutions and TES-AMM, leading the charge. Veolia Group and Remondis, in particular, stand out for their emphasis on advanced recycling technologies and broadening service portfolios to handle diverse electronic waste streams.
These market leaders prioritize sustainability, forging partnerships with local governments to bolster e-waste collection and recycling infrastructure. Attero, a prominent player in India's e-waste landscape, has a widespread collection network and cutting-edge recycling methods. Collectively, these firms are propelling the APAC e-waste market forward through a strategic focus on technology, regulatory adherence, and sustainable initiatives, paving the way for a more efficient and eco-conscious e-waste management landscape.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Deliverables
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
- 1.3 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Technological Trends
- 4.3 Insights into Supply Chain/Value Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Insights into Governement Regualtions in the Industry
- 4.5 Insights into Technological Advancements in the Industry
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Market Drivers
- 5.1.1 Rapid Technological Advancements Drive Increasing E-Waste Volumes
- 5.1.2 Urbanization and Industrialization
- 5.2 Market Restraints
- 5.2.1 High Cost of Recycling
- 5.2.2 Complexity of E-Waste
- 5.3 Market Opportunities
- 5.3.1 Advancements in Recycling Technologies
- 5.3.2 Public-Private Partnerships
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 5.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Material Type
- 6.1.1 Metal
- 6.1.2 Plastic
- 6.1.3 Glass
- 6.1.4 Other Materials
- 6.2 By Source Type
- 6.2.1 Consumer Electronics
- 6.2.2 Industrial Electronics
- 6.2.3 Household Appliances
- 6.2.4 Other Sources
- 6.3 By Application
- 6.3.1 Landfill
- 6.3.2 Recycled
- 6.3.3 Other Applications
- 6.4 By Country
- 6.4.1 China
- 6.4.2 Japan
- 6.4.3 India
- 6.4.4 South Korea
- 6.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 Veolia Group
- 7.2.2 Remondis
- 7.2.3 Averda
- 7.2.4 Sims Recycling Solutions
- 7.2.5 TES-AMM
- 7.2.6 Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd
- 7.2.7 Blue Planet Environmental Solutions Pte Ltd
- 7.2.8 ECO Recycling Ltd (Ecoreco)
- 7.2.9 Attero
- 7.2.10 JOMAR Life Research Laboratory*
- 7.3 Other Companies











