 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1644316
歐洲快速消費品物流-市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Europe FMCG Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
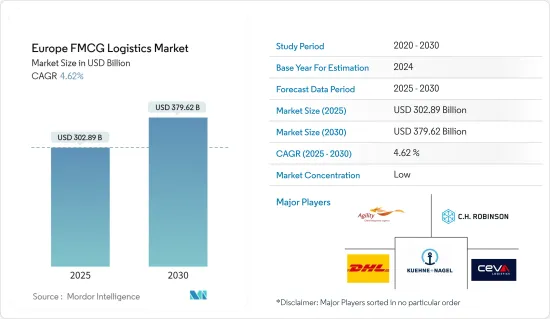
2025年歐洲快速消費品物流市場規模預估為3,028.9億美元,預估至2030年將達到3,796.2億美元,預測期間(2025-2030年)的複合年成長率為4.62%。
新冠疫情從根本上擾亂了歐洲公路貨運市場的供需。幾乎整個歐洲都受到了影響,但影響分為不同的階段。隨著市場適應新的政府規定,封鎖和跨境限制的影響也隨著時間的推移而演變。
受歐洲電子商務快速成長的推動,2021年歐洲物流投資成長至456.2億歐元(476億美元)。推動市場成長的關鍵參數包括經濟成長、人口成長和工業化。然而,政府缺乏致力於開發海港和公路網路的新興市場,以及透過增加地產地銷重組供應鏈,阻礙了市場的成長。
2020 年,西歐佔據歐洲快速消費品物流市場的最大市場佔有率,預計預測期內該地區將為市場供應商提供若干成長機會。物流業併購活動的增多、物流供應商對卡車車隊的重視程度的提高以及共享經濟的日益普及,可能會對該地區快速消費品物流市場的成長產生重大影響。
歐洲快速消費品物流市場趨勢
歐洲電子商務銷售額快速成長
許多電子商務企業儘管最初資本很少,但卻實現了更大的擴張。第三方物流使零售商能夠透過電子商務更有效地與客戶互動。業內專家預測,到2023年,電子商務將佔英國全部零售的25%。在西歐,目前 10.2% 的零售額來自線上銷售,而東歐這一比例為 5.0%。目前,西班牙和義大利的網路零售額僅佔總零售額的5%左右,預計未來五年這兩個市場的網路零售額成長率將是西歐市場中最快的,年成長率分別為17%和21%。同樣,在中東歐,羅馬尼亞、俄羅斯和匈牙利預計表現最佳,年均成長率為17.5%。
法國和義大利是高度成熟的高階市場,佔歐洲市場的很大佔有率。越來越多的醫藥製藥公司正在進入電子商務領域。因此,他們正在試圖確定如何在應對諸多監管限制的同時最好地滿足不斷成長的需求。雖然保健和美容產品(如膳食補充劑和化妝品)可以在網上銷售,而且幾乎沒有監管限制(儘管有一些重要的要求,需要告知潛在消費者產品的特性和價格),但藥品電子商務的限制要嚴格得多。
在某些情況下,缺乏法律監管會為考慮進入電子商務領域(例如醫療設備產業)的不確定性。同時,當局繼續監督和執法。經常有報導稱,一些網站(包括在國外經營的網站)因向義大利消費者提供處方箋或非法藥品而被禁。西班牙是第13大電子商務市場,2021年銷售額達272億美元,超過義大利和俄羅斯。西班牙電商市場將以17%的增幅,為2021年全球15%的成長率做出貢獻。與西班牙一樣,未來幾年全球電子商務銷售額預計將成長。隨著新市場的出現,預計未來幾年全球成長將繼續。中東和東南亞將推動這一發展,因為其中階不斷壯大,而線下基礎設施則落後。
英國脫歐對物流市場的影響
經過多年談判,英國已脫離歐盟。許多專家表示,這可能會對歐洲的供應鏈和物流業產生重大影響。打擊歐洲貿易
在英國脫歐前,貨物和物資在歐洲範圍內流通,沒有太多中斷,實現了供應鏈正常運作所必需的平穩過渡。英國脫歐後,經濟、海關和行政將發生變化,導致貨運產生額外的費用和關稅。這可能會對供應鏈的運作產生重大影響。
歐盟是世界第二大貿易區,英國脫歐將帶來供應鏈成本增加。這不僅會影響歐洲內部貿易,而且預計還將對該地區的物流業產生重大影響。
英國的貨物運輸大部分都是透過道路運輸進行的。透過公路運輸進口和出口英國英國的大部分貨物都由海外運輸商處理(其中許多車輛在波蘭、愛爾蘭和羅馬尼亞註冊)。相反,英國的運輸業佔歐盟所有運輸活動的 8%。
英國脫歐後,英國運輸商可能面臨多重障礙。此外,額外的關稅和海關程序將導致供應鏈延遲並增加所有運輸方式的成本。
透過歐洲港口營運的英國物流公司也將失去英國作為歐盟成員國期間享有的優惠。同樣,其他歐洲遠洋運輸公司在英國港口裝貨時也將受到英國新規章制度的約束。
歐洲快速消費品物流產業概況
歐洲快速消費品物流市場競爭激烈,細分化,參與企業眾多。隨著全球快速消費品銷售的增加,對高效率物流服務供應商的需求也隨之增加。由於快速消費品必不可少,預計未來幾年需求將持續成長。預計未來幾年快速消費品物流服務供應商的商機將會擴大。市場由 DHL 集團、CH Robinson Worldwide Inc.、Kuehne+Nagel International AG、Agility Logistics、CEVA Logistics、FedEx、XPO Logistics、Nippon Express、DB Schenker、Hellmann Worldwide Logistics 和 APL Logistics 等知名主要參與者組成。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 調查前提條件
- 研究範圍
第2章調查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究階段
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場洞察
- 當前市場狀況
- 價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 科技趨勢
- 洞察區域電子商務產業
- 政府法規和舉措
- 洞察歐洲第三方物流和宅配、快遞和小包裹市場
- COVID-19 對快速消費品物流市場的影響
第5章 市場動態
- 驅動程式
- 限制因素
- 機會
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第6章 市場細分
- 按服務
- 運輸
- 倉儲、配送和庫存管理
- 其他附加價值服務
- 按產品類型
- 飲食
- 個人護理
- 家居用品
- 其他耗材
- 按國家
- 德國
- 英國
- 荷蘭
- 法國
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 波蘭
- 比利時
- 瑞典
- 歐洲其他地區
第7章 競爭格局
- 市場集中度概覽
- 公司簡介
- DHL Group
- CH Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- Kuehne+Nagel International AG
- Agility Logistics
- CEVA Logistics
- FedEx
- XPO Logistics
- Nippon Express
- DB Schenker
- Hellmann Worlwide Logistics
- APL Logistics*
第8章 市場機會與未來趨勢
第 9 章 附錄
The Europe FMCG Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 302.89 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 379.62 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.62% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

The COVID-19 crisis fundamentally disrupted the demand and supply in the European road freight market. While virtually all of Europe was affected, the impact had distinct phases. The effects of lockdowns and border crossing restrictions evolved as time passed and the market adjusted to the government's new rules.
Logistics investments in Europe went up to EUR 45.62 billion (USD 47.60 billion) in 2021, driven by the massive e-commerce growth in Europe. Key parameters promoting market growth include economic growth, increasing population, and industrialization. However, the lack of the government's commitment to developing seaports or road networks and reconfigured supply chains, with the growing local production and consumption units, are hampering the market growth.
Western Europe had the largest market share in the FMCG logistics market in Europe in 2020, and the region will offer several growth opportunities to market vendors during the forecast period. Increasing M&A in the logistics industry, growing focus on truck platooning by logistics vendors, and increasing adoption of sharing economy will significantly influence FMCG logistics market growth in this region.
Europe FMCG Logistics Market Trends
E-commerce Sales to Rise at a High Pace in Europe
Numerous e-commerce businesses witnessed more significant operational expansion even though they functioned on a shoestring initially. Third-party logistics allows retailers to unleash greater sophistication before their customers on the deals made through the e-commerce mode. According to industry experts, e-commerce will likely account for 25% of the total retail sales in the United Kingdom by 2023. In Western Europe, 10.2% of retail sales are online, while 5.0% are online in Eastern Europe. With only around 5% of the total retail sales currently made online in Spain and Italy, these two markets are expected to see the most substantial online retail sales growth of all the Western European markets over the next five years at 17% per annum and 21% per annum, respectively. Likewise, Central and Eastern Europe may witness an average growth of 17.5% annually, with Romania, Russia, and Hungary performing the strongest.
France and Italy are highly established premium markets that contribute to significant shares in the European market. More and more healthcare and pharmaceutical companies are entering the e-commerce world. As a result, they find themselves attempting to identify the most suitable way to meet ever-burgeoning demand while dealing with numerous regulatory restrictions. While wellness and beauty products, such as nutrition supplements and cosmetics, may be sold online with few regulatory restrictions (although there are still several critical requirements to inform potential consumers about the characteristics of the products and their prices), e-commerce of medicines is subject to considerably more conditions.
In some cases, legislation absence raises questions and creates a high uncertainty level for those considering entering the e-commerce field (e.g., those in the medical device industry). At the same time, authorities continue to enact oversight and enforcement. There are frequent reports of websites that are banned because they offer prescription-only medicines or even illegal medicines to Italian consumers (this includes websites operating abroad). Spain is the 13th largest market for e-commerce, with a revenue of USD 27.2 billion in 2021, placing it ahead of Italy and Russia. With an increase of 17%, the Spanish e-commerce market contributed to a worldwide growth rate of 15% in 2021. Like in Spain, global e-commerce sales are expected to increase over the following years. As new markets emerge, global growth will continue over the upcoming years. East and Southeast Asia will propel this development with their growing middle class and lagging offline infrastructure.
Impact of Brexit on the Logistics Market
The UK left the European Union (EU) after years of negotiations. Many experts say it could significantly affect Europe's supply chain and logistics sector. It will harm European trade.
Before Brexit, goods and supplies moved across Europe without much interruption, resulting in a smooth transition essential for the supply chain functioning. Post-Brexit, there will be economic, customs, and administrative changes, and additional charges and duties will be imposed on shipments. It will significantly affect the supply chain functioning.
The EU is the world's second-largest trading bloc, and Brexit will result in incremental costs in the supply chain. It will not only impact intra-Europe trade but also hugely affect the logistics industry in the region.
Road haulage is the dominant mode of freight transport within the UK. Most goods imported to and exported from the UK by road are handled by overseas haulers (with vehicles mostly registered in Poland, Ireland, and Romania). Conversely, the UK haulers account for 8% of the total haulage activity in the EU.
Those UK haulers could face several hurdles post-Brexit. Also, additional tariffs and customs clearance procedures cause delays in supply chains and increase costs for all transport modes.
The UK logistics companies operating through European ports will also lose the benefits they received while members of the EU. Similarly, other European maritime transport companies will adhere to new UK rules and regulations while shipping in ports in the country.
Europe FMCG Logistics Industry Overview
The Europe FMCG Logistics Market is highly competitive and fragmented, with many players. With Increasing FMCG sales worldwide, the demand for efficient logistics service providers also increased with the increasing sales. As FMCG products are essential, their demand will likely keep growing in the coming years. The opportunity for FMCG logistics service providers is expected to grow in the coming years. Some existing significant players in the market include - DHL Group, C.H. Robinson Worldwide Inc., Kuehne + Nagel International AG, Agility Logistics, CEVA Logistics, FedEx, XPO Logistics, Nippon Express, DB Schenker, Hellmann Worldwide Logistics and APL Logistics.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Value Chain / Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.3 Technological Trends
- 4.4 Insights into E-Commerce Industry in the Region
- 4.5 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.6 Insights on 3PL market and Courier, Express, and Parcel Mrkets in Europe
- 4.7 Impact of Covid-19 on FMCG Logistics Market
5 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 5.1 Drivers
- 5.2 Restraints
- 5.3 Opportunities
- 5.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 5.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 5.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 5.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 5.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 5.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
6 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 6.1 By Service
- 6.1.1 Transportation
- 6.1.2 Warehousing, Distribution, and Inventory Management
- 6.1.3 Other Value-added Services
- 6.2 By Product Category
- 6.2.1 Food and Beverage
- 6.2.2 Personal Care
- 6.2.3 Household Care
- 6.2.4 Other Consumables
- 6.3 By Country
- 6.3.1 Germany
- 6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 6.3.3 Netherlands
- 6.3.4 France
- 6.3.5 Italy
- 6.3.6 Spain
- 6.3.7 Poland
- 6.3.8 Belgium
- 6.3.9 Sweden
- 6.3.10 Rest of Europe
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 7.2 Company Profiles
- 7.2.1 DHL Group
- 7.2.2 C.H. Robinson Worldwide Inc.
- 7.2.3 Kuehne + Nagel International AG
- 7.2.4 Agility Logistics
- 7.2.5 CEVA Logistics
- 7.2.6 FedEx
- 7.2.7 XPO Logistics
- 7.2.8 Nippon Express
- 7.2.9 DB Schenker
- 7.2.10 Hellmann Worlwide Logistics
- 7.2.11 APL Logistics*






