 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1645101
東南亞氫氣生產:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Southeast Asia Hydrogen Generation - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
價格
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
簡介目錄
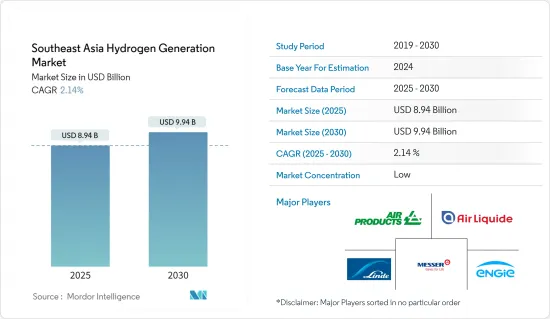
東南亞氫氣市場規模預計在 2025 年為 89.4 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 99.4 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 2.14%。
主要亮點
- 從中期來看,預計預測期內,政府的支持性政策、脫硫、溫室氣體排放政策以及鼓勵氫氣生產和消費等因素將推動東南亞地區的氫氣生成市場的發展。
- 同時,氫能能源儲存的高生產成本預計將抑制氫氣產量的成長。
- 然而,從核能、風能、太陽能、生質能、水力發電和地熱能等再生能源來源中提取氫氣的技術進步,再加上氫氣作為燃料的使用日益增多,可能會為未來幾年氫氣生成市場提供有利的成長機會。
- 預計預測期內,印尼東南亞氫氣生產市場將顯著成長。這是得益於政府的支持政策和投資。
東南亞氫氣市場趨勢
綠色氫氣是重要組成部分
- 綠色氫氣是透過電解過程產生的,該過程利用電將水分解為氫和氧。過程中使用的電力來自風能、太陽能和水力發電等再生能源來源。因此,生產的氫氣是純粹“綠色”的,並且產生極少的二氧化碳排放。
- 2023年,該地區的氫氣產量將達到約360萬噸。這種氫主要用於精製過程和氨、甲醇等化學物質的合成。值得注意的是,幾乎所有氫氣都是透過天然氣蒸氣重組生產的,沒有採用任何碳捕獲、利用和儲存 (CCUS) 技術。
- 巨額投資證明了東南亞綠氫能的宏偉前景。例如,2024年10月,TTCL公共有限公司贏得了一份價值12億泰銖的契約,在老撾建立一座綠色氫工廠。該計劃旨在透過利用可再生能源來提高老撾的氫氣生產能力。
- 2024 年 2 月,馬來西亞最大的綠氫計劃——位於霹靂州的一座 60 兆瓦浮體式太陽能發電廠,從私人投資者手中獲得了 18.8 億馬幣(3.936 億美元)的投資。這些投資凸顯了東南亞地區對綠氫日益成長的需求。
- 該地區正試圖減少重工業(主要是石化、鋼鐵和發電)的排放,這導致措施超越了綠色氫氣的生產和使用。因此,對綠氫基礎設施的投資正在加速,東南亞各地出現了合作計劃。預計這一勢頭將為該地區的脫碳目標和能源轉型努力做出重大貢獻。
- 2024 年 10 月,Senoko Energy 與 Gentari 簽署了一份合作備忘錄,探討從馬來西亞進口氫氣到新加坡,目標是到 2029 年將其整合到 Senoko 的燃氣渦輪機資產中。此次合作將大幅減少碳排放,支持新加坡實現2050年淨零目標。
- 此外,鋼鐵製造商 Meranti 宣布計劃於 2023 年在泰國建造東南亞首家綠色扁平鋼廠。該廠將使用氫氣取代煤炭,並採用可再生能源電弧爐技術生產綠色鋼鐵。計畫預計於2027年投入營運,年產能達200萬噸,每年減少二氧化碳排放400萬噸。
- 根據國際可再生能源機構(IRENA)的數據,到2023年,東南亞的可再生能源裝置容量將以越南(46,012兆瓦)領先,其次是泰國(12,547兆瓦)、馬來西亞(9,052兆瓦)、菲律賓(7,832兆瓦)和新加坡(1,147兆瓦)。廣泛的可再生能源基礎設施為綠色氫氣生產提供了堅實的基礎。
- 由於這些因素,預計預測期內綠色氫氣領域將對氫氣生產市場產生重大影響。
印尼經濟快速成長
- 隨著印尼轉向可再生能源以實現 2060 年淨零排放目標,氫能逐漸成為人們關注的焦點。憑藉豐富的資源和優越的地理位置,印尼有望成為氫氣生產(尤其是來自可再生能源的綠色氫氣)的地區領導者。
- 根據《2024 年印尼氫能展望》的研究結果,由於對氨的需求增加,預計到 2060 年印尼的氫氣需求將增加到約 200 萬噸/年 (MTPA)。
- 據世界鋼鐵協會稱,印尼的鋼鐵產量預計將從 2019 年的 856 萬噸穩步成長至 2023 年的 1,680 萬噸。鋼鐵產量的成長支撐了不斷成長的工業需求,並推動了對傳統石化燃料的更清潔替代品(主要是綠色氫氣)的需求。
- 印尼正將重點轉向可再生能源,以實現其 2060 年淨零排放目標。氫能是這轉變的核心。印尼利用其豐富的資源和優越的位置,正在將自己打造成為該地區氫氣生產的強國,特別是在生產由可再生能源提供的綠色氫氣方面。
- 例如,2024 年 10 月,勝科工業透過其子公司勝科公用事業私人有限公司與 PT PLN Energi Primer Indonesia 簽署協議,在印尼蘇門答臘島建立綠色氫氣生產設施。該廠預計每年生產 10 萬噸,成為東南亞最大的綠氫能計畫。該計劃旨在創建連接蘇門答臘、廖內群島和新加坡的區域綠氫中心。
- 2024 年 10 月,PT Pertamina Power Indonesia(「Pertamina NRE」)、PT Pertamina Geothermal Energy Tbk(「PGE」)和 Genvia 簽署了一份合作備忘錄 (MoU),鞏固了夥伴關係。兩家公司合作的重點是利用先進的固體氧化物電解槽(SOEL) 技術和地熱熱源生產綠色氫氣。該合作備忘錄包括 Jembia 尖端高溫 SOEL 技術的技術和經濟評估,旨在最佳化綠色氫氣生產的能源消耗。
- 此外,PT Kilang Pertamina Internasional 計劃在西巴布亞的賓圖尼灣建造一座藍氨工廠。該工廠計劃於2030年開始營運,目標藍氨生產能力約為875,000 TPA(噸/年),預計將滿足約150,000 TPA的藍氫需求。該設施的設計日處理量為 9,000 萬標準立方英尺天然氣(MMSCFD)。
- 因此,由於上述因素,預計預測期內印尼將在東南亞氫氣生產市場中見證顯著成長。
東南亞氫氣生產產業概況
東南亞氫氣市場正在整合。該市場的主要企業(不分先後順序)包括林德公司 (Linde PLC)、梅塞爾Group Limited (Messer Group GmbH)、液化空氣集團 (Air Liquide SA)、空氣產品及化學品公司 (Air Products and Chemicals Inc.) 和 Engie SA。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 研究範圍
- 市場定義
- 調查前提
第 2 章執行摘要
第3章調查方法
第4章 市場概況
- 介紹
- 2029 年市場規模與需求預測(美元)
- 最新趨勢和發展
- 政府法規和政策
- 市場動態
- 驅動程式
- 精製和工業領域的需求增加
- 政府優惠政策
- 限制因素
- 氫能能源儲存的資本成本高
- 驅動程式
- 供應鏈分析
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
- 投資分析
第5章 市場區隔
- 按來源(定性分析)
- 藍氫
- 綠色氫氣
- 灰色氫氣
- 依技術分類
- 蒸汽甲烷重整 (SMR)
- 煤炭氣化
- 其他技術
- 按應用
- 精製
- 化學處理
- 鋼鐵生產
- 其他用途
- 按地區
- 印尼
- 馬來西亞
- 越南
- 新加坡
- 其他東南亞地區
第6章 競爭格局
- 併購、合資、合作與協議
- 主要企業策略
- 公司簡介
- Linde Plc
- Air Liquide SA
- Messer Group GmbH
- Engie SA
- Cummins Inc.
- Air Products and Chemicals Inc.
- Taiyo Nippon Sanso Holding Corporation
- Enapter Srl
- 市場排名/佔有率分析
- 其他著名公司名單
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
- 技術進步
簡介目錄
Product Code: 50002211
The Southeast Asia Hydrogen Generation Market size is estimated at USD 8.94 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 9.94 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 2.14% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- Over the medium term, factors such as supportive government policies and regulations for desulphurization, greenhouse gas emissions, and encouraging the production and consumption of hydrogen are likely to drive the hydrogen generation market in the Southeast Asian region during the forecast period.
- On the other hand, the high production costs of hydrogen energy storage are expected to restrain the growth of hydrogen generation.
- Nevertheless, technological advancements in extracting hydrogen from renewable sources including nuclear, wind, solar, biomass, hydro, and geothermal coupled with the rising applications of hydrogen as a fuel, are poised to unlock lucrative growth opportunities for the hydrogen generation market in the years ahead.
- Indonesia is expected to witness significant growth in the Southeast Asian hydrogen generation market during the forecast period. Owing to to supportive goverment policies and investments.
Southeast Asia Hydrogen Generation Market Trends
Green Hydrogen is a Significant Segment
- Green hydrogen is produced through a process called electrolysis, which uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. The electricity used in this process comes from renewable sources such as wind, solar, or hydropower. This ensures that the hydrogen produced is genuinely "green" and has minimal carbon emissions.
- In 2023, the region's hydrogen production reached approximately 3.6 million tons. This hydrogen was predominantly utilized in refining processes and the synthesis of chemicals like ammonia and methanol. Notably, almost all of this hydrogen was produced via natural gas steam reforming, which did not incorporate carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technology.
- Significant investments evidence the ambitious outlook for green hydrogen in Southeast Asia. For instance, in October 2024, TTCL Public Company Limited secured a THB 1.2 billion contract to establish a green hydrogen plant in Laos. This project aims to enhance Laos's hydrogen production capacity using renewable energy.
- Further, in February 2024, Malaysia's largest green hydrogen project, a 60MW plant in Perak state powered by floating solar, secured 1.88 billion ringgit (USD 393.6 million) from private investors. This kind of investments highlights the rising demand for the green hydrogen market in the Southeast Asia region.
- The region's attempt to minimize emissions, mainly from heavy industries like petrochemicals, iron and steel, and power generation, are resulting in measures to exceed green hydrogen production and usage. As a result, investments in green hydrogen infrastructure are accelerating, and collaborative projects are emerging across Southeast Asia. This momentum is expected to significantly contribute to the region's decarbonization goals and energy transition efforts.
- In October 2024, Senoko Energy and Gentari signed an MoU to explore importing hydrogen gas from Malaysia to Singapore, aiming to integrate it into Senoko's gas turbine assets by 2029. This collaboration seeks to reduce carbon emissions significantly, supporting Singapore's 2050 Net Zero target.
- Moreover, In 2023, Meranti, a steel manufacturer, announced plans to build Southeast Asia's first green flat steel plant in Thailand. The plant will use hydrogen to replace coal and employ electric arc furnace technology powered by renewable energy to produce green steel. Expected to be operational by 2027, the facility will have an annual production capacity of 2 million tons, reducing carbon emissions by 4 million tons annually.
- According to International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) In 2023, Southeast Asia saw significant renewable energy capacities, with Vietnam leading at 46,012 MW, followed by Thailand at 12,547 MW, Malaysia at 9,052 MW, the Philippines at 7,832 MW, and Singapore at 1,147 MW. This substantial renewable energy infrastructure provides a strong foundation for green hydrogen production.
- Therefore, owing to such factors, the green hydrogen segment is likely to significantly impact the hydrogen generation market during the forecast period.
Indonesia to Witness Significant Growth
- As Indonesia pivots towards renewable energy to achieve its net-zero emissions goal by 2060, hydrogen energy is emerging as a focal point. With its abundant resources and strategic positioning, Indonesia is poised to become a regional leader in hydrogen production, particularly in green hydrogen, which is derived from renewable sources.
- According to the findings in the Indonesia Hydrogen Energy Outlook 2024, by 2060, Indonesia's hydrogen demand is expected to increase to around 2 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) due to the increasing demand for Ammonia.
- According to the World Steel Association, Indonesia's steel production has steadily increased from 8.56 million tonnes in 2019 to 16.8 million tonnes in 2023. This rising steel production underscores the growing industrial demand, which drives the need for hydrogen, mainly green hydrogen, as a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
- Indonesia is shifting its focus to renewable energy in pursuit of its net-zero emissions target for 2060. Central to this transition is hydrogen energy. Leveraging its rich resources and advantageous location, Indonesia is on track to establish itself as a regional powerhouse in hydrogen production, especially green hydrogen sourced from renewables.
- For instance, in October 2024, Sembcorp Industries, through its subsidiary Sembcorp Utilities Pte Ltd, signed an agreement with PT PLN Energi Primer Indonesia to establish a green hydrogen production facility in Sumatra, Indonesia. This facility will produce 100,000 metric tonnes annually, making it Southeast Asia's largest green hydrogen initiative. The project aims to create a regional green hydrogen hub connecting Sumatra, the Riau Islands, and Singapore.
- In October 2024, PT Pertamina Power Indonesia ("Pertamina NRE"), PT Pertamina Geothermal Energy Tbk ("PGE"), and Genvia solidified their partnership by signing a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU). Their collaboration centers on green hydrogen production, utilizing advanced solid oxide electrolyzer (SOEL) technology alongside geothermal heat sources. The MoU includes a technical and economic assessment of Genvia's state-of-the-art high-temperature SOEL technology, with the goal of optimizing energy consumption in green hydrogen production.
- Additionally, PT Kilang Pertamina Internasional planned to construct a blue ammonia facility in Bintuni Bay, West Papua Province. The plant is expected to commence operations in 2030, aiming for a blue ammonia production capacity of around 875,000 TPA (tons per annum) of blue ammonia, which is expected to create a demand for blue hydrogen of around 150,000 TPA. The facility is designed to process 90 million standard cubic feet per day (MMSCFD) of natural gas.
- Therefore, based on the above-mentioned factors, Indonesia is expected to witness significant growth in the Southeast Asia hydrogen generation market during the forecast period.
Southeast Asia Hydrogen Generation Industry Overview
The Southeast Asia hydrogen generation market is consolidated. Some of the major players in the market (in no particular order) include Linde PLC, Messer Group GmbH, Air Liquide SA, Air Products and Chemicals Inc., Engie SA, among others.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Market Size and Demand Forecast in USD, till 2029
- 4.3 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.4 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.5 Market Dynamics
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.5.1.1 Increasing Demand From Refining And Industrial Sector
- 4.5.1.2 Favourable Government Policies
- 4.5.2 Restraints
- 4.5.2.1 High Capital Costs For Hydrogen Energy Storage
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes Products and Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Source (Qualitative Analysis)
- 5.1.1 Blue Hydrogen
- 5.1.2 Green Hydrogen
- 5.1.3 Grey Hydrogen
- 5.2 Technology
- 5.2.1 Steam Methane Reforming (SMR)
- 5.2.2 Coal Gasification
- 5.2.3 Other Technologis
- 5.3 Application
- 5.3.1 Oil Refining
- 5.3.2 Chemical Processing
- 5.3.3 Iron & Steel Production
- 5.3.4 Other Applications
- 5.4 Geography
- 5.4.1 Indonesia
- 5.4.2 Malaysia
- 5.4.3 Vietnam
- 5.4.4 Singapore
- 5.4.5 Rest of Southeast Asia
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Linde Plc
- 6.3.2 Air Liquide SA
- 6.3.3 Messer Group GmbH
- 6.3.4 Engie S.A.
- 6.3.5 Cummins Inc.
- 6.3.6 Air Products and Chemicals Inc.
- 6.3.7 Taiyo Nippon Sanso Holding Corporation
- 6.3.8 Enapter S.r.l.
- 6.4 Market Ranking/ Share Analysis
- 6.5 List of Other Prominent Companies
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
- 7.1 Technological Advancements
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219








