 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1685873
印尼可再生能源:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030)Indonesia Renewable Energy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
價格
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
簡介目錄
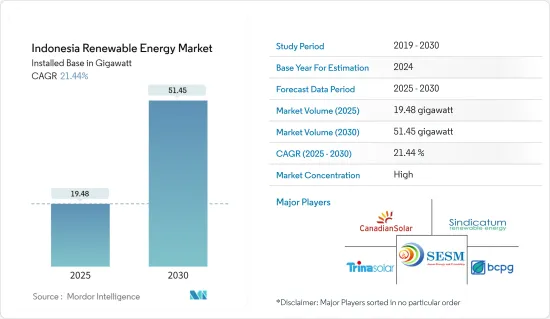
預計印尼可再生能源市場裝置規模將從 2025 年的 19.48 吉瓦成長至 2030 年的 51.45 吉瓦,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 21.44%。
主要亮點
- 從中期來看,印尼政府對可再生能源發電的興趣日益濃厚,以及政府的優惠政策預計將推動市場發展。
- 另一方面,依賴石化燃料作為能源供應以及石油和天然氣領域計劃和投資增加等因素預計將抑制該國的可再生能源市場。
- 然而,智慧電網和電池儲能系統(BESS)的整合,以提高電能品質和促進波動的風能和太陽能發電工程,預計將在印尼的可再生能源市場創造一些商機。
印尼可再生能源市場趨勢
太陽能:預計將實現顯著成長
- 印尼政府設定的目標是,2025年,可再生能源發電%,到2050年,這一比例將達到31%。目前,全國約13%的發電量來自可再生能源發電,主要是水力發電和地熱發電。
- 據印尼能源與礦產資源部(MEMR)稱,印尼的太陽能發電潛力約為 207GW。印尼政府優先發展包括太陽能在內的可再生能源。
- 根據印尼能源與礦產資源部預測,2022年印尼太陽能發電裝置容量約為190.06兆瓦,較2021年的155.29兆瓦成長22.39%。國際可再生能源機構(IRENA)預測,到2030年,印尼太陽能光電裝置容量容量將大幅擴張,主要得益於政府和印尼國家電力公司(PLN)的舉措。
- 作為其 2017 年可再生能源未來藍圖(REmap) 計畫報告的一部分,IRENA 指出,到 2030 年,印尼有潛力安裝 47GW 的太陽能光電容量。
- 印尼的太陽能光電發電容量正在公共產業規模、住宅和商業屋頂以及離網規模上成長,以取代高成本的柴油發電,預計將推動該國的太陽能成長。
- 2021 年 9 月,能源和礦產資源部 (MEMR) 頒布了屋頂太陽能光電淨計量立法,將淨計量係數從約 0.65 提高到 100。這使太陽能系統所有者能夠以與從電網購買電力相同的價格獲得他們輸入電網的電力的剩餘信用額度。預測期內,此類政府措施可能會增加印尼對太陽能的需求。
- 因此,由於這些因素,預計太陽能產業在預測期內將大幅成長。
可再生能源政策的進步可望推動市場
- 經過幾十年的發展,印尼的新能源和可再生能源(NRE)近年來發展勢頭強勁。印尼在開發新能源和可再生能源方面落後於其他國家。該國過去擁有豐富的石油和天然氣資源,因此 NRE 開發是一種選擇,而不是優先事項。
- 當印尼的石油和天然氣蘊藏量開始枯竭時,印尼政府開始將注意力轉向NRE領域。 2005年,該國首次成為石油淨進口國。
- 因此,2007年頒布的《能源法》制定了一項政策,將對石化燃料(主要是煤炭和石油)的依賴轉向更環保和永續的能源,例如太陽能、風能、水力發電、地熱能和生質能。
- 根據緬甸能源礦產資源部資料,緬甸地熱能蘊藏量龐大,為2,390萬千瓦,水力發電蘊藏量超過9,400萬千瓦。此外,該國的生質能潛力超過 3,260 萬千瓦,沼氣潛力為每天 20 萬桶。
- 可再生能源計劃預計包括6060萬千瓦風力發電、2.08億千瓦太陽能和1790萬千瓦海洋和潮汐能。隨著可再生能源技術的快速發展,其潛力可能會更大。
- 根據國際可再生能源機構預測,2022年可再生能源總設備容量約為1,248萬千瓦,較2021年的1,153萬千瓦成長8.18%。
- 因此,由於這些因素,預計政府制定的越來越多的政策將在預測期內推動該國的可再生能源市場。
印尼可再生能源產業概況
印尼的可再生能源市場是一體化的。市場的主要企業包括(不分先後順序)加拿大太陽能公司、Syndicatum 再生能源公司、天合光能公司、PT Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur 和 BCPG 公共有限公司(BCPG)。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究範圍
- 市場定義
- 調查前提
第2章執行摘要
第3章調查方法
第4章 市場概述
- 介紹
- 可再生能源結構(2022年)
- 可再生能源裝置容量及2028年預測
- 近期趨勢和發展
- 政府法規和政策
- 市場動態
- 驅動程式
- 該國自然景觀具有巨大的可再生能源潛力
- 政府支持政策和舉措
- 限制因素
- 缺乏對基礎建設的投資
- 驅動程式
- 供應鏈分析
- PESTLE分析
第5章市場區隔
- 來源
- 太陽的
- 風
- 水力發電
- 生質能源
- 其他
第6章競爭格局
- 合併、收購、合作及合資
- 主要企業策略
- 公司簡介
- Canadian Solar Inc.
- Sindicatum Renewable Energy Company Pte Ltd.
- Trina Solar Ltd
- PT Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur
- BCPG Public Company Limited(BCPG)
- SEG Solar
- PT. ATW Solar Indonesia
- Fourth Partner Energy Private Limited
- Xurya Daya Indonesia
- TotalEnergies ENEOS
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
第 8 章智慧電網、電池能源儲存系統(BESS) 和可再生能源計劃的整合
簡介目錄
Product Code: 48850
The Indonesia Renewable Energy Market size in terms of installed base is expected to grow from 19.48 gigawatt in 2025 to 51.45 gigawatt by 2030, at a CAGR of 21.44% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- Over the medium term, the increasing interest of the Indonesian government toward renewable energy power generation and favorable government policies are expected to drive the market.
- On the other hand, factors, such as the country's dependence on fossil fuels for energy supply and an increasing number of projects and investments in the oil and gas sector, are expected to restrain the country's renewable energy market.
- Nevertheless, the integration of smart grids and battery energy storage systems (BESS) to improve the quality of power and facilitate the variable wind power and solar PV projects is expected to create several opportunities for the renewable energy market in Indonesia.
Indonesia Renewable Energy Market Trends
Solar Energy Is Expected to Witness Significant Growth
- The Indonesian government set a renewable energy target of 23% and 31% of the total electricity generation by 2025 and 2050, respectively. Around 13% of power generation nationwide comes from renewable energy resources, mainly hydroelectric and geothermal power production.
- Indonesia is rich in solar power, with a potential of around 207 GW, according to the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (MEMR). The Indonesian government is prioritizing the development of renewable energy sources, including solar.
- According to the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources, in 2022, the total installed on-grid solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity was approximately 190.06 MW, representing an increase of 22.39% compared to 155.29 MW in 2021. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) states that Indonesia is installing solar power capacity to grow significantly in scale by 2030, mainly driven by initiatives by the government and PLN (a state-owned electricity company).
- The IRENA identified the potential for Indonesia to deploy 47 GW of solar power capacity by 2030 as part of its 2017 Roadmap for a Renewable Energy Future (REmap) program report.
- The Indonesian solar power capacity is growing at the utility scale, on residential and commercial rooftops, and in off-grid settings to replace costly diesel-fueled generation, which is expected to drive solar power generation in the country.
- In September 2021, the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (MEMR) enacted the net metering legislation for rooftop PV, increasing the net metering factor from approximately 0.65 to 100. Thus, solar PV system owners will likely be given surplus credits for the power they inject into the grid, the same tariff rate for buying electricity from the network. Such government initiatives will likely increase the demand for solar energy in Indonesia during the forecast period.
- Therefore, due to such factors, the solar energy segment is expected to grow significantly during the forecast period.
Progressing Renewable Energy Policies Are Expected to Drive the Market
- After decades, the Indonesian New and Renewable Energy (NRE) has gained momentum in recent years. Indonesia lags in developing its new and renewable energy resources compared to other countries. The country's rich oil and gas resources in the past have made NRE development a choice instead of a priority.
- The government of Indonesia started paying attention to the NRE sector when Indonesian oil and gas reserves started depleting. The country became a net oil importer for the first time in 2005.
- Consequently, the Energy Law of 2007 set Indonesia's plan to shift its reliance on fossil fuels, mainly coal, and oil, toward more eco-friendly and sustainable means like solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass.
- The Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources data show that the country has enormous potential for geothermal energy at 23.9 GW and more than 94 GW of hydropower. The country also has a biomass potential of more than 32.6 GW and a biogas potential of 200,000 barrels per day.
- Renewable energy projects are estimated at 60.6 GW for wind energy, 208 GW for solar energy, and 17.9 GW for ocean and tidal energy. The potential could be substantially more immense with rapidly advancing renewable energy technology.
- According to the Internation Renewable Energy Agency, in 2022, the total installed renewable energy capacity was approximately 12.48 GW, representing an increase of 8.18% compared to 11.53 GW in 2021.
- Therefore, due to such factors, increasing policies set by the government are expected to drive the country's renewable energy market during the forecast period.
Indonesia Renewable Energy Industry Overview
The Indonesian renewable energy market is consolidated. Some of the key players in the market include (in no particular order) Canadian Solar Inc., Sindicatum Renewable Energy Company Pte Ltd, Trina Solar Co. Ltd, PT Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur, and BCPG Public Company Limited (BCPG)., among others.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of the Study
- 1.2 Market Definition
- 1.3 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Renewable Energy Mix, 2022
- 4.3 Renewable Energy Installed Capacity and Forecast in GW, till 2028
- 4.4 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.5 Government Policies and Regulations
- 4.6 Market Dynamics
- 4.6.1 Drivers
- 4.6.1.1 Immense Potential in Renewable sector due to Natural Landscape of the country
- 4.6.1.2 Supportive Government Policies and Initiatives
- 4.6.2 Restraints
- 4.6.3 Lack of Investment for Infrastructure Development
- 4.6.1 Drivers
- 4.7 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.8 PESTLE Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Source
- 5.1.1 Solar
- 5.1.2 Wind
- 5.1.3 Hydro
- 5.1.4 Bioenergy
- 5.1.5 Other Sources
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers, Acquisitions, Collaborations, and Joint Ventures
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Key Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Canadian Solar Inc.
- 6.3.2 Sindicatum Renewable Energy Company Pte Ltd.
- 6.3.3 Trina Solar Ltd
- 6.3.4 PT Sumber Energi Sukses Makmur
- 6.3.5 BCPG Public Company Limited (BCPG)
- 6.3.6 SEG Solar
- 6.3.7 PT. ATW Solar Indonesia
- 6.3.8 Fourth Partner Energy Private Limited
- 6.3.9 Xurya Daya Indonesia
- 6.3.10 TotalEnergies ENEOS
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS
8 The Integration Of Smart Grids And Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) with Renewable Energy Projects
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219












