 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1527363
TrendForce (2024年):近眼顯示的市場趨勢技術分析TrendForce 2024 Near-Eye Display Market Trend and Technology Analysis |
||||||
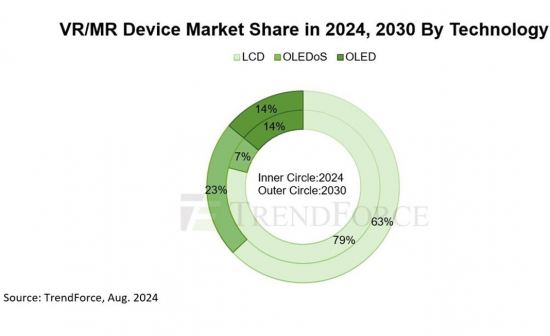
TrendForce:2030年VR/MR設備出貨量將達3,700萬台,OLEDoS和LCD佔據高階和主流市場
根據TrendForce最新報告,隨著庫存清理,近眼顯示器(NED)出貨量預計在未來幾年將增加。在高階VR/MR市場,OLEDoS的技術佔有率預計到2030年將上升至23%,而在主流市場,LCD將繼續佔據近眼顯示器63%的佔有率。
TrendForce 將 VR/MR 裝置定義為近眼顯示器,即透過單一顯示器提供沉浸式體驗的裝置。強調透明性、將虛擬和現實使用區域融為一體的設備被歸類為AR設備。
TrendForce指出,VR/MR已經在娛樂和遊戲領域奠定了堅實的基礎。此外,Apple Vision Pro 將於 2024 年推出,預計將為 VR/MR 應用開闢新途徑。目前存在的高定價和有限服務內容的問題預計會隨著時間的推移而改善。因此,TrendForce預測,到2030年,VR/MR設備出貨量將達到3,730萬台,2023年至2030年複合年增長率為23%。
廠商策略將推動OLEDoS在VR/MR市場的普及
Sony和蘋果在 Apple Vision Pro 上的合作確立了 OLEDoS 在高階 VR/MR 市場的主導地位。此次合作凸顯了業界對高解析度 VR/MR 設備的追求,並提升了 OLEDoS 的知名度。
OLEDoS採用CMOS和高亮度OLED元件,實現高發光效率,使OLEDoS產品的基本解析度達到3,000 PPI以上。 TrendForce 指出,CMOS 製造的複雜性和低產量使得 OLEDoS 顯示器的製造成本更高,限制了採用的成長。
TrendForce也指出,除了國外企業積極投資OLEDoS領域外,SeeYa、京東方等中國廠商也緊跟在後。這有望促進該技術未來在VR/MR設備市場的擴展,並有助於降低CMOS技術的成本和提高良率。 OLEDoS在高階市場仍有潛力,TrendForce預計其市佔率將從2024年的7%成長到2030年的23%。開發資源投資與迭代顯示規格增強 LCD 競爭力
在主流近眼顯示器市場,由於Meta對成本效益的重視,LCD技術仍佔主導地位。然而,隨著更高清晰度和影像品質的進步,1,200 PPI LCD 產品將面臨其他技術的競爭。 TrendForce預計2024年LCD近眼顯示器產品出貨量為680萬片,較2023年減少5.6%。
TrendForce指出,LCD的複雜元件仍有最佳化的空間。例如,改進液晶材料以減少眩暈,更新背板技術將解析度提高到 1,500 PPI 以上。京東方在LCD在近眼顯示器的應用上投入了大量資金,在VR/MR設備中LCD顯示規格不斷更新和迭代,確保該技術在中低價市場保持強勁競爭力。 TrendForce預測,到2030年,LCD技術將佔據63%的市佔率。
OLED的市佔率維持在13-15%。
發光材料沉積後無法完全覆蓋螢幕,這會在使用VR/MR設備時惡化紗門效果。 TrendForce表示,OLED在高階市場的競爭力不如OLEDoS,性價比也不如LCD產品。此外,OLED在VR/MR市場的應用高度依賴特定製造商,從長遠來看限制了其滲透率。 TrendForce預計,2024年至2030年OLED在VR/MR市場的市佔率將維持在13-15%。
目錄
第1章 近眼顯示開發概要
- AR/VR/MR 的誕生
- 從現實到虛擬:虛擬和真實影像的連續光譜
- MR在行銷中的兩個主要意義
- 用於創建 XR 體驗的技術架構
- 聖杯:MR 的“鯨魚時刻”
- AR/VR/MR規格分析
- AR/VR/MR顯示技術路線圖
- AR/VR/MR 市場挑戰:高水準的 PPI
- 眼睛的最高解析度僅限於中心:從視網膜到中央凹
- 注視點顯示:有效地重新分配像素
- AR/VR/MR 顯示器面臨的挑戰:聚散調節衝突 (VAC)
- VR/MR設備顯示解決方案開發
- VR/MR 的關鍵指標: "失控" 的解析度要求
- VR/MR 困境:PPD/厚度與功耗權衡
- VR/MR光學技術重要指標:厚度
- VR/MR光學技術主要指標:FOV
- VR/MR困境:降低MPRT以降低顯示電阻
- 薄餅光學元件對於 VR/MR 技術至關重要
- Pancake 2.0:光學技術亮點
- Pancake 2.0:更薄
- Pancake 2.0:更有效率
- VR/MR光學系統現狀
- VR/MR顯示器:LCD和OLED
- PPD 圍繞 VR/MR 的競爭:從顯示器擴展到系統
- VST 顯示延遲問題
- 使顯示規格符合 VR/MR 要求
- AR 市場挑戰:永遠不會太小
- AR 市場挑戰:永不光明
- 光學系統的趨勢
- 光引擎與光學系統
- 光學分析狀況
- 顯示規格與 AR 需求保持一致
- AR(擴增實境)顯示技術矩陣
第2章 近眼顯示市場趨勢分析
- NED 市場規模分析(2024-2028 年)
- VR/MR 市場規模分析(2024-2028 年)
- AR市場規模分析(2024-2028)
- VR/MR 市場規模分析:LCD/OLEDoS(2024-2028 年)
- AR市場規模分析:OLEDoS/LEDoS(2024-2028)
第3章 近眼顯示技術概要
3.1 OLEDoS
- OLEDoS的基本流程
- OLEDoS技術現狀
- OLEDoS:PPI 和亮度進一步提升
- OLEDoS 分析:Sony/eMagin/Kopin/RAONTECH
- 鋁陽極製程作為高解析度 OLEDoS 的替代品
- 鋁陽極的採用可能會改變OLEDoS產業的分工
- 透明 OLEDOS:SOI 上的 OLED
- OLEDoS:2024 年從 AR 過渡到 VR/MR
3.2 LEDoS
- 擴增實境 (AR):LEDoS 製造流程
- LEDoS 技術組合路線圖
- 更新 LEDoS 設備和製造工藝
- 外延:基板材質與尺寸選項
- 晶片:2D/3D結構分析
- 晶片製造及後端晶片製造工藝
- ALD 鈍化
- 連接:溫度、壓力和精度非常重要的技術要素
- 接頭:CTE 不匹配
- 加入:尺寸不符問題
- 非常規鍵結:LED+單基板工藝
- LED 光源的內在限制:光集中的挑戰
- 片上光學:微光學是新焦點
- 全彩微顯示技術
- InGaN紅光技術
- 紅光困境:InGaN 還是 AlInGaP? ALD鈍化
- InGaN紅色LED:仍在開發中
- 全彩顯示:QD顏色轉換優缺點分析
- 全彩:QDCC透過NRET機制進一步發展
- QDCC 能夠實現高達 3,000 PPI 的高解析度
- 全彩顯示:RGB垂直堆疊
- 垂直堆疊 LEDoS 技術
- 垂直堆疊LEDoS技術面臨的挑戰
- 垂直堆疊LEDoS技術的優勢
- 垂直堆疊 LED PKG:顯示器的商業應用
- LEDoS 小型化的下一個 "戰場" :QDCC 與垂直堆疊
- 全彩化:多色/單色可調 LED
- 線/棒 LEDoS:進階 PPI 應用的效率優勢
- NED 的 LEDoS 技術評估
- 線材/棒材 LEDoS:優點與缺點
- LEDoS微顯示器主要技術分析
3.3液晶螢幕
- 主要 LCD 技術:色序
- LCD關鍵技術:Mini LED背光
- LCD(玻璃上)PPI 突破
- LCD(玻璃上)高幀率
- LCD背光革命:雷射
- LCD背光革命:雷射+HOE
- LCD技術發展綜述:充分釋放LCD潛力
- LCD與VR/MR保持競爭力: "武器庫" 豐富
3.4 矽基液晶
- LCOS:光引擎的小型化
- LCOS:顯示模組尺寸縮小至0.47cc
3.5 DLP
- DLP 的進一步發展:TRP(傾斜和滾動像素)技術
3.6 磅
- LBS:光引擎的生態系與小型化
- 雷射光束掃描 (LBS):尺寸/分辨率
3.7 OLED
- OLED 與其他技術之間的良性循環
- 垂直堆疊OLED驅動電路:OLED-on-OS-on-Si
第四章產業佈局及企業趨勢:最新情況
- XR 公司針對 LEDoS 的併購 (M&A) 策略概述
- Google 的併購策略(JDC/Raxium)
- Meta 的併購策略(InfiniLED/MLED)
- Apple 的併購策略(Luxvue/Tesoro)
- Porotech
- JBD
- 史丹
- 瑞索維
- Saphlux
- Mojo 願景
- 奧斯坦多
- LG OLEDoS 的歷史(2021-2024 年)
- Att合作,為企業進軍高階MR市場
- Apple Vision Pro 顯示器與光學元件
- Apple Vision Pro 外溢效應
- Apple Vision Pro 作為消費市場的生產力工具
- LCD 與 OLED 微顯示器之戰:Quest 3 與 Vision Pro
TrendForce: VR/MR Device Shipments to Reach 37 Million Units by 2030, with OLEDoS and LCD Dominating High-End and Mainstream Markets
TrendForce's latest report reveals that shipments of near-eye displays are expected to increase year-by-year over the next few years following inventory clearance. It is anticipated that OLEDoS will dominate the high-end VR/MR market, with its technological share rising to 23% by 2030, while LCD will continue to occupy the mainstream market, holding a 63% share in near-eye displays.
TrendForce defines VR/MR devices as near-eye displays that achieve an immersive experience through a single display. Devices emphasizing transparency and the integration of virtual and real-world applications are classified as AR devices.
TrendForce notes that VR/MR has already established a solid foundation in the entertainment and gaming sectors. Furthermore, the introduction of Apple Vision Pro in 2024 is expected to open new avenues for VR/MR applications. Current issues of high pricing and limited service content are expected to improve over time. Therefore, TrendForce predicts that VR/MR device shipments could reach 37.3 million units by 2030, with a CAGR of 23% from 2023 to 2030.

Manufacturers' strategies drive OLEDoS penetration in the VR/MR market
The collaboration between Sony and Apple on the Apple Vision Pro has established OLEDoS as dominant in the high-end VR/MR market. This partnership highlights the industry's pursuit of high-resolution VR/MR devices and has increased attention on OLEDoS.
OLEDoS employs CMOS and top-emitting OLED components to achieve higher luminous efficiency, pushing the basic resolution of OLEDoS products to over 3,000 PPI. TrendForce notes that the complexity of CMOS manufacturing and its lower yield rates result in high production costs for OLEDoS displays, which limit its penetration growth.
TrendForce also indicates that, in addition to international companies actively investing in the OLEDoS field, Chinese manufacturers such as SeeYa and BOE are also following suit. This is expected to drive the future expansion of this technology in the VR/MR device market, helping to reduce costs and improve yield for CMOS technology. OLEDoS still has potential in the high-end market, with TrendForce estimating its market share will increase from 7% in 2024 to 23% in 2030.
Investment in development resources and iteration of display specifications strengthen LCD competitiveness
In the mainstream near-eye display market, LCD technology remains dominant due to Meta's focus on cost-effectiveness. However, as these devices continue to pursue higher resolution and image quality, LCD products-with their 1,200 PPI-will face competition from other technologies. TrendForce estimates that in 2024, the shipment volume of LCD near-eye display products will be 6.8 million units, a 5.6% decrease compared to 2023.
TrendForce points out that there is still room for optimization in the complex components of LCD. For example, improving liquid crystal materials to reduce dizziness and upgrading backplane technology to boost resolution beyond 1,500 PPI. BOE has invested heavily in the application of LCD in near-eye displays, with continuous updates and iterations of LCD display specifications in VR/MR devices, ensuring this technology maintains strong competitiveness in the mid-to-low-end market. TrendForce forecasts that LCD technology will hold a 63% market share by 2030.
OLED market share to remain between 13% and 15%
Emission material cannot fully cover the screen after deposition, which exacerbates the screen door effect when using VR/MR devices. TrendForce indicates that OLED is less competitive than OLEDoS in the high-end market and cannot match the cost-effectiveness of LCD products. Additionally, the application of OLED in the VR/MR market relies heavily on specific manufacturers, limiting its long-term penetration rate. TrendForce estimates that from 2024 to 2030, the market share of OLED in the VR/MR market will remain between 13% and 15%.
Table of Contents
Chapter I. Near-Eye Display Development Overview
- The Birth of AR / VR / MR
- From Reality to Virtuality: The Continuous Spectrum of Virtual and Real Images
- Two Major Meanings of MR in Marketing
- Technical Architecture for Creating XR Experiences
- Holy Grail: "The Whale Moment" of MR
- AR / VR / MR Specification Analysis
- AR / VR / MR Display Technology Roadmap
- AR / VR / MR Market Challenges: High PPI
- Highest Resolution for Eyes is Limited to the Central Area:From the Retina to Fovea
- Foveated Display: Efficient Redistribution of Pixels
- AR / VR / MR Display Challenges: Vergence Accommodation Conflict (VAC)
- Development of VR / MR Device Display Solutions
- Key Indicators for VR / MR : The "Out of Control" Requirements of Resolution
- VR / MR Dilemma: Trade Off between PPD/Thickness and Power Consumption
- Key Indicators for VR / MR Optical Technology: Thickness
- Key Indicators for VR / MR Optical Technology: FOV
- VR / MR Dilemma: Reduced MPRT to Suppress Display Drag
- Pancake Optics Becomes a Must for VR / MR Technology
- Pancake 2.0: Highlights of the Optical Technology
- Pancake 2.0: Thickness Is Further Decreased
- Pancake 2.0: Efficiency Is Further Increased
- VR / MR Optic System Landscape
- VR / MR Displays: LCD vs. OLED
- PPD Competitions for VR / MR Extend from Displays to Systems
- Latency Issues of VST Displays
- Aligning Display Specifications with VR / MR Requirements
- AR Market Challenges- Never Too Small
- AR Market Challenges- Never Too Bright
- Optical System Trend
- Light Engine vs. Optical System
- Optical Analysis Landscape
- Aligning Display Specifications with AR Requirements
- Augmented Reality Display Technology Matrix
Chapter II. Near-Eye Display Market Trend Analysis
- 2024-2028 NED Market Size Analysis
- 2024-2028 VR / MR Market Size Analysis
- 2024-2028 AR Market Size Analysis
- 2024-2028 VR / MR Market Size Analysis :LCD/OLEDoS
- 2024-2028 AR Market Size Analysis :OLEDoS/LEDoS
Chapter III. Near-Eye Display Technology Overview
3.1 OLEDoS
- OLEDoS Basic Process
- OLEDoS Technology Landscape
- OLEDoS: Further Increases in PPI and Brightness
- OLEDoS Analysis: Sony / eMagin / Kopin / RAONTECH
- Al Anode Process as an Alternative to High-Resolution OLEDoS
- Adopting Al Anode May Change Division of Labor in OLEDoS Industry
- Transparent OLEDoS: OLED-on-SOI
- OLEDoS Shifts from AR to VR / MR in 2024
3.2 LEDoS
- Augmented Reality: LEDoS Manufacturing Process
- LEDoS Technology Portfolio Roadmap
- LEDoS Equipment and Manufacturing Process Upgrades
- Epitaxy: Substrate Materials and Size Options
- Chip: 2D / 3D Structural Analysis
- Chipmaking and Back-end Chipmaking Processes
- ALD Passivation
- Bonding: Temperature, Stress, and Precision are Key Technical Factors
- Bonding: CTE Mismatch
- Bonding: Size Mismatch Problem
- Non-conventional Bonding: LED + Single-substrate Process
- Intrinsic Limitations of LED Light Sources: Light Concentration Challenge
- On-chip Optics: Micro-optics is a New Focus
- Full Color Microdisplay Technologies
- InGaN Red Light Technology
- Red Light Dilemma: InGaN or AlInGaP?ALD Passivation
- InGaN Red LEDoS Are Still Under Development
- Full Color Display: QD Color Conversion Pros and Cons Analysis
- Full-colorization: QDCC To Be Further Advanced by NRET Mechanism
- QDCC Capable of High Resolution Up to 3,000 PPI
- Full Color Display: RGB Vertical Stacking
- Vertical Stacking LEDoS Technology
- Vertical Stacking LEDoS Technology Challenges
- Advantages of Vertical-stacking LEDoS Technology
- Vertically Stacked LED PKG: Commercial Application Aiming at Displays
- Next "Battlefield" for LEDoS Miniaturization: QDCC vs. Vertical Stacking
- Full-colorization: Multiple or One Color Tunable LED
- Wire/Rod LEDoS: An Edge in Efficiency for High PPI Applications
- LEDoS Technology Evaluation for NED
- Wire/Rod LEDoS: Pros and Cons
- LEDoS Microdisplay Key Technology Analysis
3.3 LCD
- Key LCD Technology: Color Sequential
- LCD Key Technology: Mini LED Backlight
- LCD (on Glass) PPI Breakthrough
- LCD (on Glass) High Frame Rate
- LCD Backlight Revolution: Laser
- LCD Backlight Revolution: Laser + HOE
- LCD Technological Development Summary: LCD Potential Fully Release
- LCD Maintain Competitiveness in VR / MR: The Abundant "Arsenal"
3.4 LCoS
- LCOS: Light Engine Miniaturization
- LCOS: Display Module Size Shrinks to 0.47cc
3.5 DLP
- DLP Further Advancement: Tilt-and-Roll Pixel (TRP) Technology
3.6 LBS
- LBS: Ecosystem and Light Engine Miniaturization
- Laser Beam Scanning: Size / Resolution
3.7 OLED
- Positive Cycle Between OLED and Other Technologies
- Vertical Stacking of OLED Driver Circuits: OLED-on-OS-on-Si
Chapter IV. Industry Layout and Player Dynamic Updates
- XR Companies M&A Strategies Overview for LEDoS
- Google M&A Strategies (JDC/Raxium)
- Meta M&A Strategies (InfiniLED/MLED)
- Apple M&A Strategies (Luxvue/Tesoro)
- Porotech
- JBD
- Sitan
- Raysolve
- Saphlux
- Mojo Vision
- Ostendo
- LG OLEDoS Advancement History (2021-2024)
- Collaborate to Enter the High-end MR Competition in Businesses
- Apple Vision Pro Display and Optic
- Apple Vision Pro Spillover Effect
- Apple Vision Pro as a Productivity Tool for Consumer Market
- Microdisplay Battle between LCD and OLED: Quest 3 vs. Vision Pro










![近眼設備中 Micro LED 的全球市場:趨勢、機遇和競爭分析 [2023-2028 年版]](/sample/img/cover/42/1277610.png)