 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1686611
核子反應爐退役:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Nuclear Power Reactor Decommissioning - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
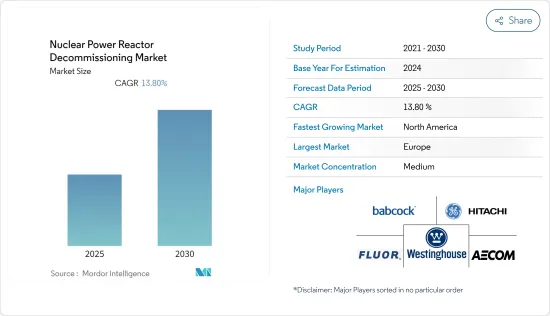
預計預測期核子反應爐退役市場將以 13.8% 的複合年成長率成長。
該市場在 2020 年受到 COVID-19 疫情的一定程度影響,但正在復甦並達到疫情前的水平。
推動市場成長的關鍵因素是越來越多的核子反應爐達到退役年齡、可再生能源(即風能和太陽能)價格下降以及對環境問題的日益敏感。
然而,由於政府的優惠政策而延長核能發電廠的使用壽命預計會阻礙市場的成長。
預計德國、英國和韓國等多個國家的核能淘汰政策將為國內外公司創造機會,提供開發符合國家需求的除役市場所需的專業知識。
北美預計將成為核能發電反應器退役成長最快的市場,其中美國是該地區的主要退役熱點之一。
核子反應爐退役市場趨勢
預計商用爐領域將佔據市場主導地位。
截至2022年10月,全球共有32個國家運作437座商業核能發電廠。美國擁有最大的核能發電能力,核能發電其他國家都多。法國擁有世界第二大核能發電能力,核能發電量也高居世界第二。
商業核能發電廠的關閉和除役受到多種因素的影響,包括經濟、監管和社會因素。太陽能和風能等替代能源的使用壽命結束和成本下降等主要資訊使得核能的成本競爭力下降。 2011年福島核電事故發生後,世界各地的核能安通訊協定都進行了升級,導致基礎設施升級相關的額外成本以及與營運和維護成本的增加。因此,許多老式商用核子反應爐的營運商選擇除役運行壽命為 40 年的老舊核子反應爐,並透過基礎設施升級將其生命再延長 20 年。
世界各國政府的政策措施也導致核能發電廠的關閉。許多政府已計劃減少國家能源結構中的核能。此類監管政策在擁有充足可再生能源且對商業核能發電廠營運的環境影響和潛在風險深感擔憂的西方國家十分普遍。
作為一項國家政策,德國計劃在2022年底前關閉所有核子反應爐。 2017年,瑞士決定逐步淘汰該國的核能發電廠。 2020年9月,比利時政府簽署協議,重申2025年逐步淘汰核電的承諾。西班牙承諾在2030年關閉其七座運作中的商業核子反應爐中的四座,在未來五年內關閉剩餘三座,到2035年徹底淘汰核能發電。
隨著可再生能源技術的發展和經濟性的提高,核能發電得到了大規模成長。世界各國正在建造龐大的可再生能源基礎設施,以抵銷對核子反應爐的需求。核能發電正在被可再生能源發電所取代,這導致核子反應爐的關閉。因此,再生能源來源發展的激增對全球核子反應爐退役市場起到了重大推動作用。
因此,由於上述因素,預計商用核子反應爐將在預測期內佔據研究市場的主導地位。
北美可望實現強勁成長
北美是世界上運作核子反應爐數量最多的地區之一。由於美國、加拿大和墨西哥的需求,核子反應爐退役市場預計將顯著成長。
美國是最大的核能發電國之一,佔2021年全球核能發電的30%。該國核子反應爐在2021年生產了778.15 TWh的電力,比2020年略有下降1.48%。
截至 2022 年 8 月,美國共有 92 座核子反應爐在運作,總合容量為 94.7 GWe,分佈在 30 個州,由 30 家電力公司使用。兩座核子反應爐正在興建中,總合容量為223萬千瓦。
美國的核能時代即將結束,核能發電廠除役已成為重要的產業。私人公司收購了這些工廠,並接管了許可證、責任、除役基金和廢棄物處理合約。約有 41 座核子反應爐、總合容量為 1,997 萬千瓦的反應器被關閉,最近關閉的是密西根州的帕利塞茲核電廠,該核電廠於 2022 年 5 月關閉。 2021 年 12 月,Holtec International 獲得美國核能管理委員會的批准,收購、除役和拆除位於密西根州科弗特的帕利塞茲核電廠。預計到2030年將有約198座核子反應爐關閉。
美國的核子反應爐正在老化。美國美國核能管理委員會(NRC) 透過後續許可證續約 (SLR) 計畫考慮將營運許可證延長 60 至 80 年的申請。然而,最近一些核電廠業主選擇在45至50年後提前退休。
低成本頁岩氣發電的激烈競爭,損害了國內核能產業的競爭力。創紀錄的低批發電價,加上高成本延長(PLEX)升級,導致核能發電廠提前退役。
多年來,加拿大一直在核能研究和技術領域處於領先地位,出口加拿大開發的核子反應爐系統。 2021年,加拿大核能發電廠發電量為92.6TWh,約佔總發電量的15%。安大略省 19 座運轉核子反應爐(總合容量 13,624 兆瓦)和 6 座核子反應爐(總合容量 214 萬千瓦)於 2022 年 8 月關閉。
截至2022年8月,加拿大有多種研究和原型核子反應爐已不再使用並已關閉。這些核子反應爐目前處於安全儲存狀態,等待最終除役。這些核子反應爐包括 WR-1、Chalk River 實驗室 (CRL) 的 NRX核子反應爐、CRL 的 MAPLE-1 和 MAPLE-2(多用途應用物理晶格實驗)核子反應爐、魁北克省貝坎庫爾的 Gentilly 1核能發電廠、安大略省羅爾夫頓的核能發電示範 (NPD)核子反應爐以及安大略省金站的道格拉斯角核能發電廠。預計這些將在預測期內推動加拿大核子反應爐退役市場的需求。
因此,預計預測期內北美核子反應爐退役市場將顯著成長。
核子反應爐退役業概況
核子反應爐退役市場相當分散。市場的主要企業(不分先後順序)包括巴布科克國際集團、福陸公司、通用電氣日立核服務公司、AECOM 和西屋電氣公司。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章 引言
- 研究範圍
- 調查前提條件
第2章執行摘要
第3章調查方法
第4章 市場概述
- 介紹
- 2027 年市場規模與需求預測
- 核能發電量預測
- 近期趨勢和發展
- 市場動態
- 驅動程式
- 限制因素
- 供應鏈分析
- 波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭
第5章市場區隔
- 核子反應爐類型
- 壓水式反應爐
- 加壓重水反應器
- 沸水式反應爐
- 高溫反應爐
- 液態金屬快滋生反應器
- 其他核子反應爐
- 按應用
- 商業動力反應爐
- 原型爐
- 研究反應器
- 按容量
- 100MW以下
- 100-1000 MW
- 超過1000MW
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 亞太地區
- 歐洲
- 南美洲
- 中東和非洲
第6章競爭格局
- 併購、合資、合作與協議
- 主要企業策略
- 公司簡介
- Babcock International Group PLC
- James Fisher & Sons PLC
- NorthStar Group Services Inc.
- Fluor Corporation
- GE Hitachi Nuclear Services
- Studsvik AB
- Enercon Services Inc.
- Orano Group
- Aecom
- Bechtel Group Inc.
- Westinghouse Electric Company
第7章 市場機會與未來趨勢
The Nuclear Power Reactor Decommissioning Market is expected to register a CAGR of 13.8% during the forecast period.

Although the market studied was moderately impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, it has been recovering and reached pre-pandemic levels.
The major factors driving the market's growth are the increasing number of nuclear reactors reaching operational retirement, declining prices of renewable power generation sources (i.e., wind and solar), and growing sensitivity toward environmental issues.
However, the lifetime extension of nuclear power plants with favorable government policies is expected to hinder the market's growth.
Nuclear phase-out policies in several countries, such as Germany, the United Kingdom, and South Korea, are expected to create opportunities for foreign and domestic players to provide the necessary expertise for the country's needs to develop their decommissioning market.
North America is expected to be the fastest-growing market for nuclear power reactor decommissioning, with the United States being one of the significant decommissioning hotspots in the region.
Nuclear Power Reactor Decommissioning Market Trends
Commercial Reactors Segment is Expected to Dominate the Market
As of October 2022, 437 commercial nuclear power plants were in operation across 32 countries. The United States had the largest nuclear electricity generation capacity and generated more nuclear electricity than any other country. France has the second-largest nuclear electricity generation capacity and second-highest nuclear electricity generation.
Several factors are responsible for the shutdown and decommissioning of commercial nuclear power plants, including economic, regulatory, and social factors. Some primary factors, such as the end of operational life and the fall in the cost of alternative energy generation sources, like solar and wind, made nuclear energy less cost-competitive. Following the Fukushima disaster of 2011, nuclear safety protocols have been upgraded across the world, which levied additional costs for the upgradation of infrastructure and increased operations and maintenance costs. Due to this, operators of many older commercial reactors, which have an operating life of 40 years and can be extended by 20 more years with infrastructural upgrades, are opting to decommission older units.
The policy-level initiatives from governments across the world have also led to the shutdown of nuclear power plants. The governments in many countries planned to reduce nuclear power in the energy mix of their countries. Such regulatory policies are prevalent among Western European states with a strong renewable portfolio and serious concerns about the environmental footprint and potential risk of operating commercial nuclear power plants.
As per its national policy, Germany plans to shut down all its reactors by the end of 2022. In 2017, Switzerland voted to phase-out nuclear power plants from the country. In September 2020, the Belgian government signed an agreement reaffirming its commitment to phasing-out nuclear power by 2025. Spain declared that it will close four of its seven operating commercial reactors by 2030 and close the rest three reactors within the next five years, completely phasing out nuclear generation by 2035.
The development of renewable energy technologies and increasing economic viability have led to its massive development. Countries across the world are creating huge infrastructures pertaining to renewable power, which has offset the requirement for nuclear reactors. Nuclear power generation is being replaced by renewable energy sources, which led to the closure of nuclear reactors. Therefore, the surge in the development of renewable energy sources is a big boost for the global nuclear reactor decommissioning market.
Therefore, due to the aforementioned factors, commercial rectors are expected to dominate the market studied during the forecast period.
North America is Expected to Witness Significant Growth
North America is one of the largest regions in terms of operable reactors worldwide. The nuclear power reactor decommissioning market is expected to witness significant growth due to the demand from the United States, Canada, and Mexico.
The United States is one of the largest nuclear power producers, accounting for 30% of the global nuclear power generated in 2021. The country's nuclear reactors produced 778.15 TWh of electricity in 2021, representing a slight decline of 1.48% from 2020.
As of August 2022, the United States has 92 operating nuclear power reactors with a combined capacity of 94.7 GWe in 30 states, used by 30 different power companies. Two reactors are under construction with a total of 2.23 GWe.
As the era of nuclear power winds down in the United States, the decommissioning of nuclear power plants is becoming a significant industry. Private companies are acquiring these plants, taking over their licenses, liability, decommissioning funds, and waste contracts. Around 41 reactors with a combined capacity of 19.97 GW were shut down, the latest being the Palisades nuclear plant in Michigan shut down in May 2022. In December 2021, HoltecInternational received approval from the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to acquire the Palisades plant in Covert, Michigan, to decommission and dismantle the plant. Around 198 reactors are expected to shut down by 2030.
The nuclear reactor fleet of the United States is aging. The United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) is considering applications for extending operating licenses beyond 60 to 80 years with its subsequent license renewal (SLR) program. However, some plant owners recently opted for early retirement of their nuclear units at 45 to 50 years old.
Intense competition from electricity generation using low-cost shale gas hurt the competitiveness of the nuclear power industry in the country. Record low wholesale electricity prices and the high cost of life extension (PLEX) upgrades have together driven early nuclear plant retirements.
For many years, Canada has been a leader in nuclear research and technology, exporting reactor systems developed in Canada. In 2021, Canada generated 92.6 TWh of electricity from nuclear power plants, accounting for about 15% of the total electricity generation mix. In Ontario, 19 operable reactors with a combined capacity of 13,624 MW and around six reactors with a combined capacity of 2.14 GW were shut down in August 2022.
As of August 2022, Canada has a variety of research and prototype power reactors that are no longer in use and have been shut down. These reactors are in a safe storage state and awaiting final decommissioning. Some of these reactors include the WR-1, the NRX reactor at Chalk River Laboratories (CRL), the MAPLE-1 and MAPLE-2 (Multipurpose Applied Physics Lattice Experiment) reactors at CRL, the Gentilly-1 nuclear generating station in Becancour, QC, the Nuclear Power Demonstration (NPD) reactor in Rolphton, ON, and the Douglas Point nuclear-generating station in Kincardine, ON. These are expected to drive the demand for the Canadian nuclear power reactor decommissioning market during the forecast period.
Therefore, North America is expected to witness significant growth in the nuclear power reactor decommissioning market during the forecast period.
Nuclear Power Reactor Decommissioning Industry Overview
The nuclear power reactor decommissioning market is moderately fragmented. Some of the major players in the market (in no particular order) are Babcock International Group PLC, Fluor Corporation, GE Hitachi Nuclear Services, AECOM, and Westinghouse Electric Company.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Scope of Study
- 1.2 Study Assumptions
2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4 MARKET OVERVIEW
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Market Size and Demand Forecast in USD million, till 2027
- 4.3 Nuclear Power Generation Forecast in TWh, till 2027
- 4.4 Recent Trends and Developments
- 4.5 Market Dynamics
- 4.5.1 Drivers
- 4.5.2 Restraints
- 4.6 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes Products and Services
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Reactor Type
- 5.1.1 Pressurized Water Reactor
- 5.1.2 Pressurized Heavy Water Reactor
- 5.1.3 Boiling Water Reactor
- 5.1.4 High-temperature Gas-cooled Reactor
- 5.1.5 Liquid Metal Fast Breeder Reactor
- 5.1.6 Other Reactor Types
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Commercial Power Reactor
- 5.2.2 Prototype Power Reactor
- 5.2.3 Research Reactor
- 5.3 By Capacity
- 5.3.1 Below 100 MW
- 5.3.2 100-1000 MW
- 5.3.3 Above 1000 MW
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.2 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3 Europe
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Mergers and Acquisitions, Joint Ventures, Collaborations, and Agreements
- 6.2 Strategies Adopted by Leading Players
- 6.3 Company Profiles
- 6.3.1 Babcock International Group PLC
- 6.3.2 James Fisher & Sons PLC
- 6.3.3 NorthStar Group Services Inc.
- 6.3.4 Fluor Corporation
- 6.3.5 GE Hitachi Nuclear Services
- 6.3.6 Studsvik AB
- 6.3.7 Enercon Services Inc.
- 6.3.8 Orano Group
- 6.3.9 Aecom
- 6.3.10 Bechtel Group Inc.
- 6.3.11 Westinghouse Electric Company







