 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1636213
建築廢棄物管理:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030)Construction Waste Management - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
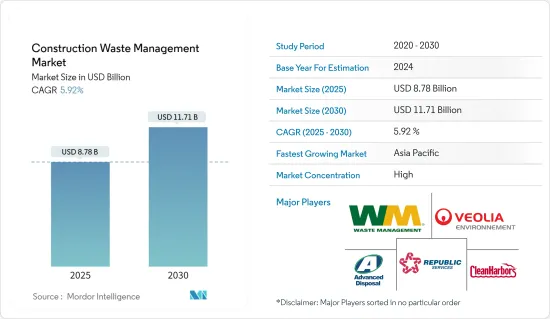
建築廢棄物管理市場規模預計到 2025 年為 87.8 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 117.1 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)複合年成長率為 5.92%。
主要亮點
- 快速都市化和對永續性的日益重視是建築廢棄物管理市場的主要促進因素。目前,儘管具有固有價值,但超過 75% 的建築材料廢棄物仍未回收。 2018 年,美國環保署 (EPA) 強調,家庭和企業產生的建築廢棄物是一般廢棄物的兩倍。美國在家庭廢棄物排放方面處於世界領先地位。
- 建築和拆除 (C&D)廢棄物類別涵蓋混凝土、瀝青、木材、磚塊、黏土瓦、石膏乾牆、瀝青瓦和金屬等材料。雖然混凝土和金屬很容易回收,但其他材料,特別是磚塊、粘土磚和石膏乾牆,很難重複利用,並且通常最終被扔進垃圾掩埋場。
- 隨著印度快速都市化進程,建築業越來越被認為是空氣污染的主要來源和資源的消耗大戶。特別是印度的資源開採率為每英畝1580噸,遠高於世界平均450噸。
- 《國家清潔空氣計畫》為印度131個無污染城市設定了嚴格目標,即在2026年將顆粒物污染減少40%。因此,有效管理建築和拆除 (C&D)廢棄物對於控制污染程度至關重要。
- 然而,最近的 CSE 審查凸顯了一個令人擔憂的趨勢:許多城市沒有能力系統、科學地管理拆除廢棄物。此外,2016年《拆建廢棄物管理條例》的通過進展緩慢,且執行過程中存在明顯差距。這凸顯了迫切需要全面的指導,以增強對制度設計和有效實施策略的理解。
- 儘管存在障礙,建築業在永續性方面取得了進展,成功地再利用了 75% 以上的廢棄物。回收活動佔廢棄物管理業務的 85% 以上,其重要性顯而易見,特別是考慮到美國僅回收其總廢棄物排放的三分之一。
- 隨著監管機構和建設公司加強控制廢棄物的力度,建築廢棄物管理市場可望擴大。精實建設和價值工程等方法從計劃一開始就致力於減少廢棄物,而後期規劃服務則提供有效的廢棄物清除和處置解決方案。
建築廢棄物管理市場趨勢
住宅建築廢棄物佔較大市場佔有率
住宅建築廢棄物是世界建築廢棄物問題的主要原因,凸顯了有效廢棄物管理的迫切性。預測表明,到 2025 年,全球建築廢棄物將增加到每年 22 億噸,主要來自住宅計劃和重建。
在美國,建築和拆除 (C&D)廢棄物(包括住宅廢棄物)佔該國廢棄物排放的 25%。該統計數據不僅突顯了住宅排放的廢棄物量,還顯示了商業和公共設施產生的廢棄物量。
住宅建築廢棄物中常見的材料包括木材、乾牆、混凝土和包裝材料。令人擔憂的是,運送到建築工地的材料中有大約 30% 變成了廢棄物,凸顯了該行業的材料效率低下。
建築廢棄物無法管理,影響嚴重,導致環境污染和資源枯竭。生態系統破壞和隨之而來的污染可能會產生深遠的後果,影響野生動物和公眾健康。
結合回收和再利用材料等永續做法是遏制住宅建築廢棄物快速增加的可行解決方案。精益建築和健全的廢棄物管理計劃等策略是顯著減少住宅建築廢棄物排放的有希望的方法。
亞太地區佔主要市場佔有率
亞洲的建築廢棄物管理因國家而異。日本、香港和新加坡等國家因其強調回收和妥善處置的先進系統而脫穎而出。韓國的回收率高達97%以上,令人驚嘆,台灣也取得了長足的進步,回收率也超過了50%。相較之下,許多開發中國家的回收率較低,往往依賴露天傾銷,這充滿了挑戰。
亞洲建築廢棄物管理的監管環境多種多樣,但它們的通用是都注重地方政府的責任。值得注意的是,印度等國家正在頒布法規以加強對廢棄物管理的監督。這些法規是綜合立法的一部分,旨在提高建築廢棄物的合規性和效率。
儘管取得了進展,亞洲在建築廢棄物管理方面仍面臨持續的挑戰。問題包括缺乏資金和標準化做法、非法傾倒和廢棄物處理基礎設施不足。此外,非正規廢棄物產業和複雜的政府責任(尤其是在開發中國家)進一步阻礙了有效的廢棄物管理。
亞洲的建築廢棄物管理市場預計未來將會成長。這種成長軌跡是由都市化進程的加速和對永續性的日益關注所推動的。回收技術的預期創新加上更嚴格的法規預計將顯著提高回收率。此外,建設公司和廢棄物管理營業單位之間加強合作預計將加強對廢棄物管理標準的遵守並促進循環經濟。
建築廢棄物行業概況
建築廢棄物管理市場較為分散。幾家主要企業正在競相為建築計劃提供高效且永續的廢棄物管理解決方案。該領域的著名公司包括廢棄物管理公司、威立雅環境公司、Clean Harbors公司、Republic Services公司和Advanced Disposal Services公司。這些公司提供廣泛的服務,包括廢棄物收集、回收、垃圾掩埋場管理和環境諮詢,幫助建設公司有效管理廢棄物,同時遵守監管要求和環境標準。
其他好處
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第1章簡介
- 調查先決條件
- 調查範圍
第2章調查方法
- 分析方法
- 調查階段
第3章執行摘要
第4章市場動態與洞察
- 目前的市場狀況
- 市場動態
- 促進因素
- 都市化和人口成長推動市場
- 經濟成長帶動市場
- 抑制因素
- 影響市場的法律規範
- 回收過程相關的高成本影響市場
- 機會
- 市場驅動的技術進步
- 促進因素
- 價值鏈/供應鏈分析
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 供應商的議價能力
- 消費者議價能力
- 新進入者的威脅
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭公司之間的敵對關係
- 廢棄物回收服務市場的技術開發
- COVID-19 對市場的影響
第5章市場區隔
- 依廢棄物類型
- 有害
- 無危險
- 按來源
- 住宅
- 非住宅
- 按材質
- 混凝土/磚
- 木頭
- 金屬
- 塑膠
- 玻璃
- 其他材料(土壤、乾牆、灰泥塗料等)
- 按地區
- 北美洲
- 美國
- 加拿大
- 墨西哥
- 北美其他地區
- 歐洲
- 英國
- 德國
- 法國
- 俄羅斯
- 義大利
- 西班牙
- 其他歐洲國家
- 亞太地區
- 印度
- 中國
- 日本
- 澳洲
- 其他亞太地區
- 南美洲
- 巴西
- 阿根廷
- 南美洲其他地區
- 中東/非洲
- 阿拉伯聯合大公國
- 南非
- 其他中東和非洲
- 北美洲
第6章 競爭狀況
- 市場集中度概況
- 公司簡介
- Waste Management
- Veolia Environment
- Clean Harbors
- Republic Services
- Advanced Disposal Services
- Biffa
- Covanta Holding
- Daiseki
- Hitachi Zosen
- 其他公司
第7章 市場的未來
第8章附錄
- 總體經濟指標
- 資本流動洞察(建築業投資)
- 對外貿易統計
The Construction Waste Management Market size is estimated at USD 8.78 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 11.71 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.92% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- Rapid urbanization and a growing emphasis on sustainability are the primary drivers of the construction waste management market. Currently, over 75% of construction material waste remains unrecycled despite its inherent value. In 2018, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) highlighted that construction waste doubled that of municipal waste from both households and businesses. The United States leads globally in household waste generation.
- The construction and demolition (C&D) waste category spans materials like concrete, asphalt, wood, brick, clay tiles, gypsum drywall, asphalt shingles, and metal. While concrete and metal are readily recyclable, others, especially brick, clay tiles, and gypsum drywall, face reusability challenges, often ending up in landfills.
- In India, amid rapid urbanization, the construction sector is increasingly recognized as a key source of air pollution and a substantial consumer of resources. Notably, India's resource extraction rate, at 1,580 tonnes per acre, far exceeds the global average of 450 tonnes per acre.
- The National Clean Air Programme has set a stringent target for the 131 non-attainment cities in India: a 40% reduction in particulate pollution by 2026. Consequently, effective management of construction and demolition (C&D) waste has become paramount in curbing pollution levels.
- However, a recent CSE review highlights a concerning trend: many cities lack the institutional readiness for systematic and scientific C&D waste management. Moreover, the adoption of the C&D Waste Management Rules of 2016 has been sluggish, with noticeable gaps in their execution. This underscores the urgent need for comprehensive guidance to enhance both the understanding of the system's design and the strategies for its effective implementation.
- Despite hurdles, the construction sector has shown progress in sustainability, managing to repurpose more than 75% of its waste. Notably, recycling activities account for over 85% of waste management jobs, underscoring their significance, especially when considering that the United States recycles only a third of its total waste output.
- With regulatory bodies and construction companies intensifying their efforts to curb waste, the construction waste management market is set for expansion. Approaches like lean construction and value engineering are honing in on waste reduction from the project's inception, while post-planning services are offering efficient waste removal and disposal solutions.
Construction Waste Management Market Trends
Residential Construction Waste Holds a Significant Share of the Market
Residential construction waste is a significant contributor to the global construction debris challenge, emphasizing the urgency of effective waste management. Projections suggest that annual construction waste worldwide will escalate to 2.2 billion tons by 2025, largely driven by residential projects and renovations.
Within the United States, construction and demolition (C&D) debris, including residential waste, constitute a striking 25% of the nation's total waste output. This statistic not only underscores the substantial waste from residential endeavors but also highlights the significant contributions from commercial and institutional construction.
Common materials in residential construction waste encompass wood, drywall, concrete, and packaging materials. Alarmingly, around 30% of materials delivered to construction sites end up as waste, accentuating the sector's material inefficiency.
The ramifications of unmanaged construction waste are dire, leading to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Ecosystem disruptions and subsequent pollution can have far-reaching consequences, affecting both wildlife and public health.
Embracing sustainable practices, like material recycling and reusing, presents a viable solution to curbing the surge in residential construction waste. Strategies such as lean construction and robust waste management plans hold promise in significantly reducing waste output during residential endeavors.
Asia-Pacific Holds a Significant Share of the Market
Construction waste management practices in Asia exhibit significant disparities across nations. Countries like Japan, Hong Kong, and Singapore stand out for their advanced systems, emphasizing recycling and proper disposal. South Korea boasts an impressive recycling rate exceeding 97%, while Taiwan has also made strides, surpassing a 50% recycling rate. In contrast, many developing nations grapple with low recycling rates, often resorting to open dumping, a practice laden with challenges.
Asia's regulatory landscape for construction waste management is diverse, with a common thread: a focus on local authorities' responsibilities. Notably, countries like India are enacting regulations to bolster oversight of waste management practices. These regulations, part of comprehensive acts, aim to enhance compliance and efficiency in handling construction waste.
Despite progress, Asia faces persistent challenges in construction waste management. Issues range from funding shortages and a lack of standardized practices to illegal dumping and inadequate waste processing infrastructure. Moreover, informal waste industries and complex governmental responsibilities further hinder effective waste management, particularly in developing nations.
Looking forward, Asia's construction waste management market is set for growth. This trajectory is fueled by rising urbanization and an amplified focus on sustainability. Anticipated innovations in recycling technologies, coupled with stricter regulations, are poised to significantly boost recycling rates. Moreover, increased collaboration between construction firms and waste management entities is expected to bolster compliance with waste management standards and foster a circular economy.
Construction Waste Management Industry Overview
The construction waste management market is fragmented in nature. Several key players are competing to provide efficient and sustainable waste management solutions for construction projects. Some notable companies in this space include Waste Management, Veolia Environment, Clean Harbors, Republic Services, and Advanced Disposal Services. These companies offer a range of services such as waste collection, recycling, landfill management, and environmental consulting to help construction firms effectively manage their waste while adhering to regulatory requirements and environmental standards.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS AND INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Urbanization and Population Growth Driving the Market
- 4.2.1.2 Economic Growth Driving the Market
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 Regulatory Frameworks Affecting the Market
- 4.2.2.2 High Costs Associated with the Recycling Process Affecting the Market
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.2.3.1 Technological Advancements Driving the Market
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.3 Value Chain/Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.5 Technological Developments in the Waste Recycling Services Market
- 4.6 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Waste Type
- 5.1.1 Hazardous
- 5.1.2 Non-hazardous
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Residential
- 5.2.2 Non-residential
- 5.3 By Material
- 5.3.1 Concrete & Bricks
- 5.3.2 Wood
- 5.3.3 Metal
- 5.3.4 Plastics
- 5.3.5 Glass
- 5.3.6 Other Materials (Soil, Drywall, Plaster, etc.)
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.2 Germany
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Russia
- 5.4.2.5 Italy
- 5.4.2.6 Spain
- 5.4.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 India
- 5.4.3.2 China
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Waste Management
- 6.2.2 Veolia Environment
- 6.2.3 Clean Harbors
- 6.2.4 Republic Services
- 6.2.5 Advanced Disposal Services
- 6.2.6 Biffa
- 6.2.7 Covanta Holding
- 6.2.8 Daiseki
- 6.2.9 Hitachi Zosen
- 6.3 Other Companies
7 FUTURE OF THE MARKET
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Macroeconomic Indicators
- 8.2 Insights into Capital Flows (Investments in Construction Sector)
- 8.3 External Trade Statistics






