 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1687782
東協低溫運輸物流:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)ASEAN Cold Chain Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
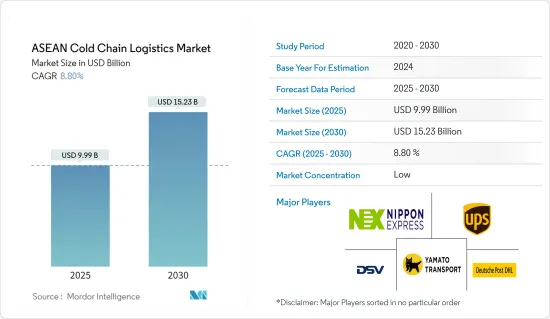
2025年東協低溫運輸物流市場規模預估為99.9億美元,預估至2030年將達152.3億美元,預測期間(2025-2030年)複合年成長率為8.8%。
主要亮點
- 城市人口的增加和消費者態度的改變正在推動對冷藏保管和運輸的需求。東南亞的冷藏/冷凍產品市場正在快速成長。
- 食品分銷正迅速從傳統市場轉向超級市場和便利商店。冷藏和冷凍產品很容易採購,主要經銷商都提供冷藏卡車運輸服務。
- 各地低溫運輸服務品質參差不齊。由於缺乏冷藏,食物也可能變質。據估計,東南亞90%的食物廢棄物發生在運輸過程中。
- 雖然印度的低溫運輸業務尚處於起步階段,但它是低溫運輸倉儲和物流領域最有前景的行業之一。
- 到2027年,印度將成為世界第五大經濟體。作為全球市場上成熟且重要的參與者,印度對供應鏈基礎設施的投資可能會在未來幾年增加。
- 幸好,印度政府正在透過各種補貼和激勵措施推動低溫運輸產業的發展,並鼓勵私人參與。食品加工工業部(MoFPI)啟動了低溫運輸、加值和保鮮基礎設施計畫。
- 東南亞國協收入水準的提高和生活方式的改變是這些地區肉類消費和生產成長的重要因素。印尼和越南是主要的成長動力。
東協低溫運輸物流市場趨勢
清真食品推動市場
- 近年來,全球品牌開始轉向伊斯蘭經濟,以利用不斷上升的購買力和不斷變化的消費者支出重點。東協地區約有2.6億穆斯林,主要居住在印尼、馬來西亞、泰國、菲律賓、新加坡、緬甸和汶萊。過去十年,全部區域舉辦了一系列清真生活方式活動和宣傳活動,激發了人們對伊斯蘭旅行、食品、時尚和化妝品的興趣。
- 韓國食品巨頭 SPC 集團有意進軍馬來西亞,以期搶佔全球清真食品產業 2 兆美元的市場。在與新加坡接壤的馬來西亞柔佛州,SPC集團宣布計劃投資 400 億韓元(約 3,000 萬美元)建造清真認證工廠。根據韓國媒體報道,該設施將設有一個港口,為貨物運往東南亞和中東地區提供路線。
- 由於清真食品大部分為肉類,因此必須存放在經過各國政府清真認證的低溫運輸倉庫中。最近,政府推出了多項旨在發展清真產業的政策,包括為清真產業建立經濟特區(KEK)。
- 此外,國家伊斯蘭教經濟和金融委員會 (KNEKS) 與聯合利華印尼等公司之間的合作預計將促進該國的清真產業的發展。馬來西亞政府也正在採取多項措施,力爭成為清真市場的全球市場領導者。清真產業總體規劃和清真園區是政府最近的進展。所有這些清真舉措正在推動東南亞國協的低溫運輸物流。
肉類消費成長推動東協低溫運輸物流
- 東南亞人口不斷成長、收入不斷提高、都市化和零售業的發展,導致肉類消費和飼料進口量增加。該地區五大新興市場為印尼、馬來西亞、菲律賓、泰國和越南。
- 近年來肉類消費量不斷增加,魚貝類是肉類消費和生產的最大來源,同時也滿足了部分飼料需求。每個東南亞國家對肉類的偏好各有不同,這從消費量和生產量就可以看出。
- 馬來西亞是東南亞國家中家禽業產值最高的國家,並且擁有大型生產設施。
- 東南亞國協對清真食品的需求不斷成長,原因有很多。一個重要因素是該地區穆斯林人口的成長。隨著越來越多的人遵守伊斯蘭飲食習慣,對清真認證食品的需求也日益成長。
- 此外,消費者對食品來源及其加工方式的認知和意識也不斷增強。許多人(不僅是穆斯林)都選擇清真認證的產品,因為人們認為這些產品品質更高、更衛生、更安全。
- 東協地區的旅遊業也正在顯著成長,其中包括來自穆斯林占多數國家的遊客。這些遊客在旅行時尋找清真食品,從而產生了對清真認證餐廳和食品的需求。
- 為了滿足日益成長的需求,東南亞國協的公司正在積極尋求食品清真認證。清真認證保證產品符合要求的標準並依照伊斯蘭飲食法規進行製作。該認證為消費者提供了保證,並幫助公司進入利潤豐厚的清真市場。
東協低溫運輸物流產業概況
東協低溫運輸物流市場是一個分散的市場,由全球和本地參與者混合組成。本地中小型企業以較小的車隊和儲存空間服務市場。在一些國家,例如新加坡,DHL、日本通運等全球性企業佔有強大的市場佔有率。此外,全球參與者正在投資市場並收購當地企業,以擴大在該地區的業務。
此外,日本物流企業也加強在東協地區的活動,透過在東南亞國協各國家為製造業和流通業建立陸上運輸樞紐,推動供應鏈建構。該公司也參與低溫運輸開發,並積極投資新鮮農產品、鮮花、化妝品和消費品的物流。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章 簡介
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 市場覆蓋
第2章調查方法
- 分析方法
- 研究階段
第3章執行摘要
第4章 市場洞察
- 當前市場狀況
- 市場動態
- 驅動程式
- 低溫運輸物流需求不斷增加
- 擴大該地區的國際貿易
- 限制因素
- 缺乏適當的基礎設施和設施
- 低溫運輸物流高成本
- 機會
- 生鮮產品需求不斷增加
- 市場驅動的技術進步
- 驅動程式
- 冷凍設施的技術趨勢和自動化
- 政府法規和舉措
- 日本在東協低溫運輸產業中的作用思考與說明
- 產業價值鏈洞察
- 產業吸引力-波特五力分析
- 新進入者的威脅
- 購買者/消費者的議價能力
- 供應商的議價能力
- 替代品的威脅
- 競爭對手之間的競爭強度
- 排放標準和法規對低溫運輸產業的影響
- 深入了解冷藏倉庫使用的冷媒和包裝材料
- 深入了解印尼和馬來西亞的清真標準和認證
- 氣候和溫度控制儲存見解
- COVID-19 市場影響
第5章 市場區隔
- 按服務
- 貯存
- 運輸
- 附加價值服務(速凍、貼標、庫存管理等)
- 按溫度
- 常溫
- 冷藏
- 冷凍
- 按應用
- 園藝(新鮮水果和蔬菜)
- 乳製品(牛奶、冰淇淋、奶油等)
- 肉類和魚類
- 加工食品
- 製藥、生命科學、化學
- 其他用途
- 按地區
- 新加坡
- 泰國
- 越南
- 印尼
- 馬來西亞
- 菲律賓
- 其他東南亞國協
第6章 競爭格局
- 市場集中度概覽
- 公司簡介
- Nippon Express
- United Parcel Service of America
- Deutsche Post DHL
- Yamato Transport Co. Ltd
- DSV Agility Logistics
- NYK(Yusen Logitics & TASCO)
- Tiong Nam Logistics
- Sinchai Cold Storage
- Jentec Storage Inc.
- JWD Logistics
- KOSPA
- PT. Pluit Cold Storage
- PT. Wahana Cold Storage
- Havi Logistics
- Royal Cargo
- Thai Max Co. Ltd
- MGM Bosco*
第7章:市場的未來
第 8 章 主要供應商和供貨商
- 儲存設備製造商
- 承運商
- 技術提供者
第 9 章 附錄
- 冷藏倉庫年度統計
- 冷凍食品進出口貿易資料
- 深入了解主要國家的食品運輸和儲存法規結構
- 洞察東南亞食品飲料產業
The ASEAN Cold Chain Logistics Market size is estimated at USD 9.99 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 15.23 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 8.8% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Key Highlights
- The growing urban population and changing consumer perception have boosted refrigerated storage and transport demand. The market for refrigerated/frozen products is rapidly growing in Southeast Asia.
- The distribution of food products is rapidly shifting from traditional markets toward supermarkets and convenience stores. Refrigerated and frozen products are easier to procure, as major distributors offer shipping via insulated trucks.
- The quality of local cold-chain services varies widely. Food products have been damaged due to the lack of refrigeration. It is estimated that 90% of Southeast Asia's food waste is created during transport.
- Indian cold chain business is still in its early stages, it is one of the most promising industries in the cold chain warehousing and logistics industry.
- By 2027, India will have the world's fifth-largest economy. Investment in India's supply chain infrastructure is likely to increase year on year since it is a well-established, important player in the global market.
- Fortunately, the Indian government is a driving factor in the development of the cold chain industry, encouraging private participation through a variety of subsidy programs and incentives. The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) has initiated a cold chain, value addition, and preservation infrastructure program.
- Rising income levels in ASEAN countries and lifestyle changes are key factors for the growth of meat consumption and production in these regions. Indonesia and Vietnam are mainly driving the growth.
ASEAN Cold Chain Logistics Market Trends
Hallal Food is offering traction to the market
- In recent years, global brands have begun to focus on the Muslim economy to capitalize on rising purchasing power and shifting consumer spending priorities. Around 260 million Muslims live in the ASEAN region, most of whom live in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines, Singapore, Myanmar, and Brunei. The number of halal lifestyle events and campaigns held across the region in the last decade stimulates interest in Islamic travel, foods, fashion, and cosmetics.
- SPC Group, a major South Korean food company, intends to grow into Malaysia to capture a portion of the USD 2 trillion worldwide halal food industry. In Johor, a Malaysian state bordering Singapore, SPC Group announced plans to invest 40 billion won (about USD 30 million) in the construction of a halal-certified factory. According to South Korean media, the facility will have a route to send goods throughout Southeast Asia and into the Middle East thanks to the location's ports.
- Since most halal food is meat products, they need to be stored in cold chain warehouses that are Halal-certified by the respective Governments. In recent times, several policies aimed at developing the halal industry have been demonstrated by the government, including the establishment of a Special Economic Zone (KEK) for the industry.
- In addition, the collaboration between the National Committee for Sharia Economics and Finance (KNEKS) and companies such as Unilever Indonesia is expected to boost the country's halal industry. The Malaysian government is also making many advancements to become a global market leader in the halal market. The halal industry's master plan and halal park are the recent advancements made by the government. All these halal initiatives are driving the cold chain Logistics in ASEAN countries.
Increase in Meat Consumption Propelling Cold Chain Logistics in ASEAN Countries
- Southeast Asia's expanding population and increasing incomes, urbanization, and retail sectors are contributing to rising meat consumption and growing imports of feedstuffs. The five key emerging markets within the region are Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- In recent years, meat consumption has also increased, although fish and seafood are the largest meat sources consumed and produced and are partially responsible for feedstuffs demand. Every Southeast Asian country has different meat preferences, as reflected by their levels of consumption and production.
- Malaysia has a sizable production apparatus in the poultry sector, which has the best production values among these Southeast Asian nations.
- The increasing demand for halal food products in ASEAN countries can be attributed to various factors. One of the key factors is the growing Muslim population in the region. As more people adhere to Islamic dietary practices, the demand for halal-certified food products has increased.
- Moreover, there has been a rise in awareness and consciousness among consumers regarding the source and preparation of their food. Many people, not just Muslims, are opting for halal-certified products as they perceive them to be of higher quality, more hygienic, and safer to consume.
- The ASEAN region has also witnessed a significant increase in tourism, including visitors from predominantly Muslim countries. These tourists seek halal food options during their travels, creating a demand for halal-certified restaurants and food products.
- To cater to this growing demand, businesses in ASEAN countries have been actively pursuing halal certification for their food products. Halal certification ensures that the products meet the required standards and are prepared in accordance with Islamic dietary laws. This certification assures consumers and helps businesses tap into the lucrative halal market.
ASEAN Cold Chain Logistics Industry Overview
The ASEAN cold chain logistics market's landscape is fragmented in nature, with a mix of global and local players. Small- and medium-sized local players still serve the market with small fleets and storage spaces. Some of the countries, like Singapore, have a strong presence of global players, like DHL and Nippon Express. Additionally, global players are investing in the market and acquiring local companies to increase their footprint in the region.
Furthermore, Japanese logistics companies strengthen their activities in the ASEAN region by setting up bases of land transportation in ASEAN countries for each country within the manufacturing and distribution industries, thereby pushing the construction of a supply chain. The companies are also involved in developing the cold chain and actively investing in logistics related to fruits and vegetables, flowers, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Market
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- 2.1 Analysis Methodology
- 2.2 Research Phases
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET INSIGHTS
- 4.1 Current Market Scenario
- 4.2 Market Dynamics
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.2.1.1 Increasing demand for cold chain logistics
- 4.2.1.2 Expansion of international trade in the region
- 4.2.2 Restraints
- 4.2.2.1 Lack of proper infrastructure and facilities
- 4.2.2.2 High cost associated to cold chain logistics
- 4.2.3 Opportunities
- 4.2.3.1 Growing demand for perishable goods
- 4.2.3.2 Technological advancements driving the market
- 4.2.1 Drivers
- 4.3 Technological Trends and Automation in Cold Storage Facilities
- 4.4 Government Regulations and Initiatives
- 4.5 Review and Commentary on Role of Japan in the ASEAN Cold Chain Industry
- 4.6 Insights into Industry Value Chain
- 4.7 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Impact of Emission Standards and Regulations in the Cold Chain Industry
- 4.9 Insights into Refrigerants and Packaging Materials Used in Refrigerated Warehouses
- 4.10 Insights into Halal Standards and Certifications in Indonesia and Malaysia
- 4.11 Insights into Ambient/Temperature-controlled Storage
- 4.12 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 By Service
- 5.1.1 Storage
- 5.1.2 Transportation
- 5.1.3 Value-added Services (Blast Freezing, Labeling, Inventory Management, etc.)
- 5.2 By Temperature
- 5.2.1 Ambient
- 5.2.2 Chilled
- 5.2.3 Frozen
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Horticulture (Fresh Fruits and Vegetables)
- 5.3.2 Dairy Products (Milk, Ice-cream, Butter, etc.)
- 5.3.3 Meats and Fish
- 5.3.4 Processed Food Products
- 5.3.5 Pharma, Life Sciences, and Chemicals
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 Singapore
- 5.4.2 Thailand
- 5.4.3 Vietnam
- 5.4.4 Indonesia
- 5.4.5 Malaysia
- 5.4.6 Philippines
- 5.4.7 Rest of ASEAN
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration Overview
- 6.2 Company Profiles
- 6.2.1 Nippon Express
- 6.2.2 United Parcel Service of America
- 6.2.3 Deutsche Post DHL
- 6.2.4 Yamato Transport Co. Ltd
- 6.2.5 DSV Agility Logistics
- 6.2.6 NYK (Yusen Logitics & TASCO)
- 6.2.7 Tiong Nam Logistics
- 6.2.8 Sinchai Cold Storage
- 6.2.9 Jentec Storage Inc.
- 6.2.10 JWD Logistics
- 6.2.11 KOSPA
- 6.2.12 PT. Pluit Cold Storage
- 6.2.13 PT. Wahana Cold Storage
- 6.2.14 Havi Logistics
- 6.2.15 Royal Cargo
- 6.2.16 Thai Max Co. Ltd
- 6.2.17 MGM Bosco*
7 FUTURE OF THE MARKET
8 KEY VENDORS AND SUPPLIERS
- 8.1 STORAGE EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURERS
- 8.2 CARRIER MANUFACTURERS
- 8.3 TECHNOLOGY PROVIDERS
9 APPENDIX
- 9.1 Annual Statistics on Refrigerated Storage Facilities
- 9.2 Import and Export Trade Data of Frozen Food Products
- 9.3 Insights into Regulatory Framework on Food Transportation and Storage in Key Countries
- 9.4 Insights into the Food and Beverage Sector in Southeast Asia









