 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1690717
中國 CEP(快遞包裹):市場佔有率分析、行業趨勢和統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)China Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
價格
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
簡介目錄
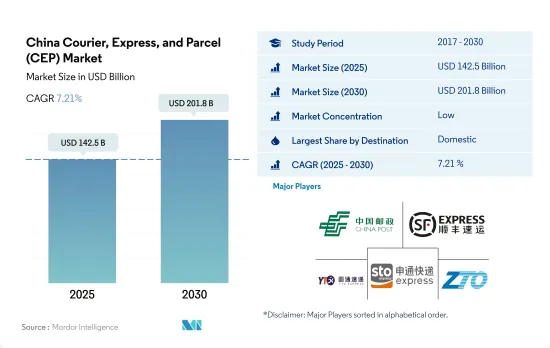
預計 2025 年中國快遞包裹 (CEP) 市場規模為 1,425 億美元,到 2030 年將達到 2,018 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 7.21%。
跨境電子商務推動國際宅配服務成長
- 2023年,全國約有29,522家宅配企業。過去十年,中國的快遞行業呈指數級成長,這主要得益於網上零售的快速成長。為了增加 CEP 數量,許多公司正在採用各種策略。例如,從 2023 年 9 月開始,Shein 將從中國向其美國倉庫發送更多低成本服裝和家居用品,加快消費者的送貨時間。
- 國內和國際宅配、快遞和小包裹遞送領域的金額和數量將主要受電子商務推動,2023 年 27.6% 的零售額將透過線上管道實現。預計到 2027 年,電子商務用戶數量將達到 13.3 億,電子商務市場的價值預計將進一步增加。
中國CEP(快遞包裹)市場趨勢
「十四五」規劃將更重視清潔能源基礎建設和交通運輸部門的投資,以推動經濟成長
- 2023年,中國清潔能源產業為國家經濟擴張做出了重大貢獻。根據能源與清潔空氣中心(CREA)統計,中國對可再生能源基礎設施的投資達8,900億美元,幾乎相當於當年全球對石化燃料供應的投資。清潔能源,包括再生能源來源、核能、電網、能源儲存、電動車和鐵路,將佔中國GDP的9.0%,與前一年同期比較7.2%。 2023年電動車產量與前一年同期比較增加36%。
- 中國在「十四五」規劃(2021-2025年)中公佈了擴大交通網路的目標。到2025年,高鐵里程由2020年的3.8萬公里增加到5萬公里,線路長度達到250公里,覆蓋95%的50萬人口以上城市。至2025年,全國鐵路營業里程將達到16.5萬公里,民用機場270個以上,都市區地鐵1萬公里,高速公路19萬公里,內河高等級航道1.85萬公里。 2025年實現全面發展是首要目標,重點在於轉變交通運輸體系並提高其對GDP的貢獻。
受俄烏戰爭影響,中國柴油、汽油零售價格飆升至歷史高點。
- 2023年,中國原油進口量預計將較2022年增加11%,至5.6399億噸,或1,128萬桶/日。隨著俄羅斯與烏克蘭戰爭導致全球油價上漲,中國燃料價格也創下歷史新高。 2024年1-2月原油進口量達8,831萬噸,年增5.1%。這一成長是由於之前以較低價格購買了原油。布倫特期貨在2023年9月達到高峰97.69美元,12月跌至72.29美元,2024年3月漲至84.05美元。 OPEC+集團在2024年3月決定將減產延長至6月底,進一步推高了油價。此舉引發了人們對全球石油需求的擔憂,因為該組織將減產近6%以滿足全球需求。此外,近期原油價格上漲可能從 2024 年下半年開始抑制中國的進口。
- 中國計劃根據近期國際原油價格波動調整汽油、柴油零售價格。價格上漲反映了全球供應緊張和需求前景改善。根據國發改委預測,2024年中國汽油和柴油價格將上漲28美元/噸。儘管預計燃料需求將下降,但到2035年,石油基燃料仍可能是主要選擇。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章執行摘要和主要發現
第2章 報告要約
第 3 章 簡介
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 研究範圍
- 調查方法
第4章 產業主要趨勢
- 人口統計
- 按經濟活動分類的 GDP 分佈
- 經濟活動帶來的 GDP 成長
- 通貨膨脹率
- 經濟表現及概況
- 電子商務產業趨勢
- 製造業趨勢
- 交通運輸倉儲業生產毛額
- 出口趨勢
- 進口趨勢
- 燃油價格
- 物流績效
- 基礎設施
- 法律規範
- 中國
- 價值鏈與通路分析
第5章 市場區隔
- 目的地
- 國內的
- 國際的
- 送貨速度
- 表達
- 非快遞
- 模型
- 企業對企業 (B2B)
- 企業對消費者 (B2C)
- 消費者對消費者(C2C)
- 運輸重量
- 重型貨物
- 輕型貨物
- 中等重量貨物
- 運輸方式
- 航空郵件
- 路
- 其他
- 最終用戶
- 電子商務
- 金融服務(BFSI)
- 衛生保健
- 製造業
- 一級產業
- 批發零售(線下)
- 其他
第6章 競爭格局
- 主要策略趨勢
- 市場佔有率分析
- 業務狀況
- 公司簡介
- China Post
- DHL Group
- FedEx
- Hongkong Post
- La Poste Group
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- Shanghai YTO Express(Logistics)Co., Ltd.
- STO Express Co., Ltd.(Shentong Express)
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
- Yunda Holding Co. Ltd.
- ZTO Express
第7章:執行長的關鍵策略問題
第 8 章 附錄
- 世界概況
- 概述
- 五力分析框架
- 全球價值鏈分析
- 市場動態(DRO)
- 技術進步
- 資訊來源和進一步閱讀
- 圖表清單
- 關鍵見解
- 資料包
- 詞彙表
簡介目錄
Product Code: 71121
The China Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market size is estimated at 142.5 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 201.8 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 7.21% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Increase in international parcel delivery services owing to cross-border e-commerce
- There were around 29,522 courier businesses operating in the country in 2023. China's express delivery industry has grown exponentially over the past decade, largely driven by the rapid growth of online retail. Many companies are adopting different strategies to increase CEP volumes. For instance, since September 2023, Shein has been sending more low-priced apparel and home goods to U.S. warehouses from China to speed up shipping times for shoppers.
- The value and volume of the domestic and international courier, express, and parcel delivery segments are largely driven by e-commerce, wherein 27.6% of retail sales were made online in 2023. The value of the CEP market is further expected to rise as e-commerce users are expected to reach 1.33 billion by 2027.
China Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market Trends
Rising focus on developing clean energy infrastructure and transport sector investment under 14th Five-Year Plan driving growth
- In 2023, China's clean energy sector significantly contributed to the country's economic expansion. According to Energy and Clean Air (CREA), China's investment in renewable energy infrastructure amounted to USD 890 billion, almost matching global investments in fossil fuel supply for the same year. Clean energy, including renewable energy sources, nuclear power, electricity grids, energy storage, electric vehicles (EVs), and railways, constituted 9.0% of China's GDP in 2023, up from 7.2% YoY. EV production grew by 36% YoY in 2023.
- In the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025), China revealed goals for expanding its transportation network. By 2025, high-speed railways will extend to 50,000 kms, up from 38,000 kms in 2020, with 95% of cities with populations above 500,000 covered by 250-km lines. The country aims to increase its railway length to 165,000 kms, civil airports to over 270, subway lines in cities to 10,000 kms, expressways to 190,000 kms, and high-level inland waterways to 18,500 kms by 2025. The primary objective is to achieve integrated development by 2025, emphasizing advancements in the transformation of the transportation system and its contribution to GDP.
China's retail diesel and gasoline prices were soared to historically high levels amid the Russia-Ukraine War
- In 2023, China imported 11% more crude oil than in 2022, totaling 563.99 mn metric tons (MMT), or 11.28 mn barrels per day. This surge was due to increased global crude oil prices amid the Russia-Ukraine War, causing fuel prices in China to reach historic highs. In Jan-Feb 2024, crude oil imports rose by 5.1% YoY, reaching 88.31 MMT. This increase was driven by purchasing crude oil at lower prices earlier. Brent futures peaked at USD 97.69 in September 2023, fell to USD 72.29 in December, and rose to USD 84.05 by March 2024. The decision made by the OPEC+ group in March 2024 to extend output cuts until the end of June has further boosted crude prices. This move has raised concerns about global oil demand, as the group is reducing production by nearly 6% of world demand. The recent increase in crude prices may also dampen China's imports starting from H2 2024.
- China plans to adjust retail prices for gasoline and diesel to align with recent shifts in global crude oil prices. The price hike reflects a tightening of global supply and a positive forecast for demand. According to NDRC, gasoline and diesel prices in China will increase by USD 28 per ton in 2024. Although there's expectation of declining demand for fuels, oil-based fuels will remain the primary choice until 2035.
China Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Industry Overview
The China Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP) Market is fragmented, with the major five players in this market being China Post, SF Express (KEX-SF), Shanghai YTO Express (Logistics) Co., Ltd., STO Express Co., Ltd. (Shentong Express) and ZTO Express (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Logistics Performance
- 4.11 Infrastructure
- 4.12 Regulatory Framework
- 4.12.1 China
- 4.13 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes Market Value in USD, Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 Destination
- 5.1.1 Domestic
- 5.1.2 International
- 5.2 Speed Of Delivery
- 5.2.1 Express
- 5.2.2 Non-Express
- 5.3 Model
- 5.3.1 Business-to-Business (B2B)
- 5.3.2 Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
- 5.3.3 Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
- 5.4 Shipment Weight
- 5.4.1 Heavy Weight Shipments
- 5.4.2 Light Weight Shipments
- 5.4.3 Medium Weight Shipments
- 5.5 Mode Of Transport
- 5.5.1 Air
- 5.5.2 Road
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 End User Industry
- 5.6.1 E-Commerce
- 5.6.2 Financial Services (BFSI)
- 5.6.3 Healthcare
- 5.6.4 Manufacturing
- 5.6.5 Primary Industry
- 5.6.6 Wholesale and Retail Trade (Offline)
- 5.6.7 Others
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 China Post
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 FedEx
- 6.4.4 Hongkong Post
- 6.4.5 La Poste Group
- 6.4.6 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.7 Shanghai YTO Express (Logistics) Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 STO Express Co., Ltd. (Shentong Express)
- 6.4.9 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.10 Yunda Holding Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.11 ZTO Express
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR CEP CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (DROs)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219




