 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1685709
馬來西亞貨運與物流:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Malaysia Freight And Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
價格
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
簡介目錄
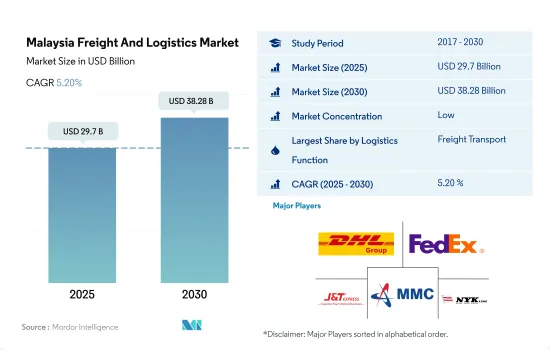
馬來西亞貨運代理和物流市場規模預計在 2025 年為 297 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 382.8 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 5.20%。
經濟穩定和不斷成長的投資機會推動了該國的貨運需求
- 2024年6月,馬來西亞將開通東協快線,這是一條連接馬來西亞與泰國、寮國和中國的國際貨運列車,加強與東南亞和中國的貿易聯繫。該服務將連接多個內陸港口,包括雪蘭莪州的貨櫃國家內陸港、玻璃市內陸港、泰國的拉卡邦內陸港和寮國的塔納楞陸港。從雪蘭莪到重慶,走海路一般需要14至21天,而搭火車只需9天。
- 據韓國貿易和工業部稱,航運、造船和修船(SBSR)產業對美國的出口額最高,其次是印尼和阿拉伯聯合大公國。此外,2023 年 4 月,馬來西亞政府宣布計劃建造一個耗資 280 億馬幣(63.4 億美元)的港口,預計於 2060 年完工。該計劃旨在將巴生港的貨櫃和常規貨物處理能力從 2022 年的 1,320 萬標準箱提高到 2060 年的 3,600 萬標準箱。
馬來西亞貨運及物流市場趨勢
儘管外國直接投資虧損達 725 萬美元,但馬來西亞 2022 年運輸和倉儲業仍將與前一年同期比較增 33%
- 「一帶一路」計劃正在推動馬來西亞基礎設施發展。東海岸鐵路連接線(ECRL)旨在改善東海岸吉蘭丹、登嘉樓和彭亨與西海岸森美蘭州、雪蘭莪州和布城之間的連通性。這些地區目前缺乏完整的鐵路連通。預計東部鐵路將推動馬來西亞經濟成長高達 2.7%。而且,預計建成20年後,馬來西亞的經濟成長率將達到4.6%。 ECRL計劃預計於2026年12月完工,並於2027年1月開始營運。
- 捷運3號線是吉隆坡城市軌道運輸網的最後一條主要線路,全長50.8公里,貫穿吉隆坡郊區。預計建設將於 2023 年初開始,並於 2030 年全面竣工,第一階段的營運將於 2028 年開始。透過酵母鐵路連接 (ECRL),雙軌鐵路連通基礎設施計劃於 2017 年啟動,其中包括 20 個車站:14 個客運站、5 個客貨合一站和 1 個貨運站。
正在討論取消柴油補貼,使零售燃油價格與市場價格保持一致
- 馬來西亞計劃自 2024 年 6 月起取消柴油補貼,並將零售價格與市場價格保持一致,為每公升 3.35 馬來西亞林吉特(0.75 美元),比 2.15 馬來西亞林吉特(0.48 美元)上漲 55%。儘管可能產生政治影響,但預計這項變化對通膨的影響較小。 2023 年的柴油補貼預計將達到 145 億馬來西亞林吉特(32.8 億美元),政府預計補貼合理化每年可節省約 40 億馬來西亞林吉特(9 億美元)。該國的柴油補貼高達每月 10 億馬來西亞林吉特(2.2 億美元),而每天因洩漏造成的損失高達 450 萬馬來西亞林吉特(102 萬美元)。
- 作為馬來西亞總理安瓦爾·易卜拉欣長期努力改革國家燃油補貼制度的一部分,2024 年 6 月馬來西亞的柴油價格上漲了 50% 以上。改革旨在透過取消普遍能源補貼、將援助重點放在最需要的人身上來減輕公共財政壓力。此舉也旨在解決補貼柴油被走私到鄰國並以高價交易的問題。
馬來西亞貨運及物流業概況
馬來西亞的貨運代理和物流市場較為分散,主要五大參與者分別是 DHL 集團、聯邦快遞、J&T Express、MMC Corporation Berhad 和日本郵船(按字母順序排列)。
其他福利
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章執行摘要和主要發現
第2章 報告要約
第 3 章 簡介
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 研究範圍
- 調查方法
第4章 產業主要趨勢
- 人口統計
- 按經濟活動分類的 GDP 分佈
- 經濟活動帶來的 GDP 成長
- 通貨膨脹率
- 經濟表現及概況
- 電子商務產業趨勢
- 製造業趨勢
- 交通運輸倉儲業生產毛額
- 出口趨勢
- 進口趨勢
- 燃油價格
- 卡車運輸成本
- 卡車持有量(依類型)
- 物流績效
- 主要卡車供應商
- 模態共享
- 海運能力
- 班輪連結性
- 停靠港和演出
- 貨運趨勢
- 貨物噸位趨勢
- 基礎設施
- 法律規範(公路和鐵路)
- 馬來西亞
- 法律規範(海運和空運)
- 馬來西亞
- 價值鏈與通路分析
第5章 市場區隔
- 最終用戶產業
- 農業、漁業和林業
- 建設業
- 製造業
- 石油和天然氣、採礦和採石
- 批發和零售
- 其他
- 物流功能
- 快遞、快遞和包裹 (CEP)
- 目的地
- 國內的
- 國際的
- 貨物
- 按運輸方式
- 航空
- 海上和內陸水道
- 其他
- 貨物
- 交通方式
- 航空
- 管道
- 鐵路
- 路
- 海上和內陸水道
- 倉庫存放
- 透過溫度控制
- 無溫度控制
- 溫度管理
- 其他服務
- 快遞、快遞和包裹 (CEP)
第6章 競爭格局
- 主要策略趨勢
- 市場佔有率分析
- 業務狀況
- 公司簡介.
- City-Link Express
- CJ Logistics Corporation
- Deutsche Bahn AG(including DB Schenker)
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(De Sammensluttede Vognmaend af Air and Sea)
- FedEx
- FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- GDEX Group
- Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- J&T Express
- Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- Kuehne+Nagel
- MMC Corporation Berhad
- NYK(Nippon Yusen Kaisha)Line
- POS Malaysia Bhd
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- SkyNet Worldwide Express
- Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- TransOcean Holdings Bhd
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
- Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd
第7章:執行長的關鍵策略問題
第 8 章 附錄
- 世界概況
- 概述
- 五力分析框架
- 全球價值鏈分析
- 市場動態(市場促進因素、限制因素、機會)
- 技術進步
- 資訊來源和進一步閱讀
- 圖表清單
- 關鍵見解
- 資料包
- 詞彙表
- 外匯
簡介目錄
Product Code: 46576
The Malaysia Freight And Logistics Market size is estimated at 29.7 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 38.28 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.20% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Growing economic stability along with investment opportunities leading to freight demand in the country
- In June 2024, Malaysia enhanced its trade connectivity with South-East Asia and China by launching the Asean Express, an international freight train linking Malaysia to Thailand, Laos, and China. This service connects several inland ports, including the Kontena Nasional Inland Clearance Depot in Selangor, Perlis Inland Port, Latkrabang Inland Port in Thailand, and Thanaleng Dry Port in Laos. The train significantly reduces transit times, taking just nine days from Selangor to Chongqing, compared to the usual 14 to 21 days by sea.
- According to the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI), the maritime and shipbuilding and ship repairing (SBSR) industries had the highest value of exports to the United States, followed by Indonesia and the United Arab Emirates. Moreover, in April 2023, the Malaysian government announced its plan to construct a port for RM 28 billion (USD 6.34 billion), scheduled to be completed by 2060. This initiative aims to enhance the handling capacity for both container and conventional cargo at Port Klang to 36 million TEUs in 2060 from 13.2 million TEUs in 2022.
Malaysia Freight And Logistics Market Trends
Malaysia's transportation and storage sector experienced 33% YoY growth in 2022, despite USD 7.25 million FDI deficit
- The Belt and Road Initiative is driving Malaysia's infrastructure growth. The East Coast Rail Link (ECRL) seeks to improve connectivity between Kelantan, Terengganu, and Pahang in the East Coast with Negeri Sembilan, Selangor, and Putrajaya in the West Coast. These areas currently lack complete railway connections. The ECRL is forecasted to boost Malaysia's economic growth by up to 2.7%. Furthermore, two decades after its construction, Malaysia's economic growth is expected to reach 4.6%. The ECRL project is set to finish by December 2026 and is expected to start operating in January 2027.
- The MRT3 is the last critical route to complete the Kuala Lumpur urban rail network; the line is 50.8 km long and runs around Kuala Lumpur's outskirts. Its construction began in early 2023 and is slated for full completion by 2030, while operations for the first phase are anticipated to commence in 2028. Through East Coast Rail Link (ECRL), a double-track railway linking infrastructure project, which includes 20 stations, began in 2017, with 14 passenger stations, five combined passenger and freight stations, and one freight station.
Elimination of Diesel subsidies under discussions, in order to align retail fuel prices to align with market rates
- Starting in June 2024, Malaysia plans to eliminate diesel subsidies, allowing retail prices to align with the market rate of MYR 3.35 (USD 0.75) per litre, marking a 55% increase from MYR 2.15 (USD 0.48). Despite potential political consequences, this change is projected to have minimal impact on the country's inflation rate. In 2023, diesel subsidies amounted to MYR 14.5 billion (USD 3.28 billion), and the government anticipates saving approximately MYR 4 billion (USD 0.90 billion) annually through this Subsidy Rationalization. Diesel subsidies in the country amount to MYR 1 billion (USD 0.22 billion) monthly, with daily losses from leaks totaling MYR 4.5 million (USD 1.02 million).
- Diesel prices in Malaysia surged by over 50% in June 2024 as part of Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim's efforts to reform the country's long-standing fuel subsidy system. The restructuring aimed to alleviate pressure on national finances by eliminating universal energy subsidies and focusing assistance on those most in need. This move also aims to address issues like the smuggling of subsidized diesel to neighboring countries, where it fetches higher prices.
Malaysia Freight And Logistics Industry Overview
The Malaysia Freight And Logistics Market is fragmented, with the major five players in this market being DHL Group, FedEx, J&T Express, MMC Corporation Berhad and NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.11 Trucking Fleet Size By Type
- 4.12 Logistics Performance
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Modal Share
- 4.15 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.16 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.17 Port Calls And Performance
- 4.18 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.19 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.20 Infrastructure
- 4.21 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.21.1 Malaysia
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.22.1 Malaysia
- 4.23 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes 1. Market value in USD for all segments 2. Market volume for select segments viz. freight transport, CEP (courier, express, and parcel) and warehousing & storage 3. Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode Of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode Of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 City-Link Express
- 6.4.2 CJ Logistics Corporation
- 6.4.3 Deutsche Bahn AG (including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.4 DHL Group
- 6.4.5 DSV A/S (De Sammensluttede Vognmaend af Air and Sea)
- 6.4.6 FedEx
- 6.4.7 FM Global Logistics Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.8 GDEX Group
- 6.4.9 Hellmann Worldwide Logistics
- 6.4.10 Hextar Technologies Solutions Bhd
- 6.4.11 J&T Express
- 6.4.12 Keretapi Tanah Melayu Bhd
- 6.4.13 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.14 MMC Corporation Berhad
- 6.4.15 NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- 6.4.16 POS Malaysia Bhd
- 6.4.17 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.18 SkyNet Worldwide Express
- 6.4.19 Taipanco Sdn Bhd
- 6.4.20 Tiong Nam Logistics Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.21 TransOcean Holdings Bhd
- 6.4.22 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
- 6.4.23 Xin Hwa Holdings Bhd
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR FREIGHT AND LOGISTICS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (Market Drivers, Restraints & Opportunities)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
- 8.7 Currency Exchange Rate
02-2729-4219
+886-2-2729-4219




