 |
市場調查報告書
商品編碼
1687105
印尼貨運與物流:市場佔有率分析、產業趨勢與統計、成長預測(2025-2030 年)Indonesia Freight and Logistics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030) |
||||||
※ 本網頁內容可能與最新版本有所差異。詳細情況請與我們聯繫。
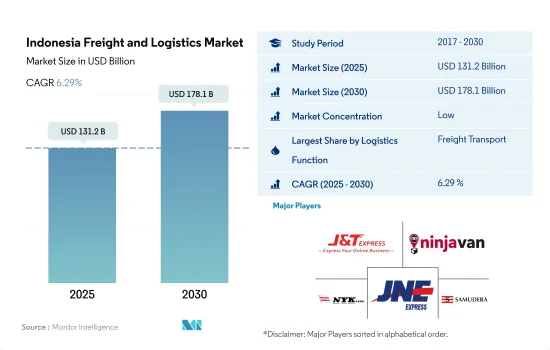
印尼貨運代理和物流市場規模預計在 2025 年為 1,312 億美元,預計到 2030 年將達到 1,781 億美元,預測期內(2025-2030 年)的複合年成長率為 6.29%。
政府對印尼基礎設施的投資正在推動市場成長
- 2024 年 10 月,聯邦快遞在印尼峇里島登巴薩開設了一個新的門戶設施。該設施旨在簡化運輸流程,減少運輸時間並提供滿足登巴薩出口商需求的服務。聯邦快遞強調,由於能夠從登巴薩直接出口到新加坡,繞過經雅加達的傳統出口路線,客戶可以享受更快、更可靠的運輸服務。此外,該設施還為第 9 類危險物品(包括固態乾冰和麻醉物品)提供全面的物流服務。
- 對於 2025 會計年度,公共工程和住宅部(PUPR)公路總局分配的預算上限為 21 億美元。同時,2025 年國家預算草案 (RAPBN)提案為 PUPR 部分配總計 49.1 億美元的預算。在這項撥款中,公路總局已撥款 6.6 億美元用於道路基礎設施,3.4 億美元用於橋樑基礎設施,5.8 億美元用於國家公路和橋樑的保護和維護。
印尼貨運及物流市場趨勢
受基礎設施計劃增加的推動,運輸和倉儲行業預計將增加其對 GDP 的貢獻
- 2024年5月,日本政府為印尼雅加達高鐵建設提供了約1,407億日圓(9億美元)的貸款。東西鐵路計劃全長84.1公里,將於2026年至2031年分兩階段實施。該鐵路的列車和號誌系統將採用日本先進的技術。這些舉措將有助於提高運輸和倉儲產業對GDP的貢獻。
- 交通運輸是國家基礎建設工作的重中之重。在該領域,正在進行和計劃中的舉措總數的 29% 用於公路計劃,22% 用於鐵路計劃,23% 用於港口基礎設施。這些計劃對於加強連結性和促進經濟成長至關重要。印尼的一個重點項目是全長135公里的洛修馬威-朗薩收費公路。這個雄心勃勃的計劃計劃於 2024 年初開始,並於 2027 年底完成,目標是緩解交通堵塞並縮短旅行時間。收費公路將有助於最佳化物流,提高運輸和倉儲產業對GDP的貢獻。
2022年,印尼在油價上漲和補貼壓力下面臨財政挑戰,但稅率將維持不變,直至2024年。
- 2024年11月,印尼改革了燃料補貼制度。新總統的目標是削減補貼,2023 年補貼約佔政府支出的 16%。雖然液化石油氣補貼將保持不變,但政府正在決定調整燃料和電力補貼。印尼的能源補貼有助於抑制通貨膨脹,但也使其面臨全球油價波動的影響。政府計劃以對貧困家庭的現金轉移支付來取代這些補貼,旨在透過更有針對性的援助節省約 129.9 億美元。
- 截至 2024 年 6 月,印尼能源和礦產資源部 (ESDM) 正在起草法規,為綠氫開發者提供獎勵和稅收減免,以鼓勵綠色氫產業的發展。 ESDM 的目標是到 2060 年每年生產 990 萬噸氫氣,以滿足工業(390 萬噸/年)、運輸(110 萬噸/年)、電力(460 萬噸/年)和國內天然氣網路(28 萬噸/年)的需求。這些產業也可能成為出口產品。
印尼貨運及物流業概況
印尼的貨運和物流市場較為分散,主要五家參與者分別是 J&T Express、Ninja Van(包括 Ninja Express)、NYK Line、PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir(JNE Express)和 PT Samudera Indonesia Tangguh(按主要企業順序排列)。
其他福利:
- Excel 格式的市場預測 (ME) 表
- 3 個月的分析師支持
目錄
第 1 章執行摘要和主要發現
第2章 報告要約
第 3 章 簡介
- 研究假設和市場定義
- 研究範圍
- 調查方法
第4章 產業主要趨勢
- 人口統計
- 按經濟活動分類的 GDP 分佈
- 經濟活動帶來的 GDP 成長
- 通貨膨脹率
- 經濟表現及概況
- 電子商務產業趨勢
- 製造業趨勢
- 交通運輸倉儲業生產毛額
- 出口趨勢
- 進口趨勢
- 燃油價格
- 卡車運輸成本
- 卡車持有量(依類型)
- 物流績效
- 主要卡車供應商
- 模態共享
- 海運能力
- 班輪連結性
- 停靠港和演出
- 貨運趨勢
- 貨物噸位趨勢
- 基礎設施
- 法律規範(公路和鐵路)
- 印尼
- 法律規範(海運和空運)
- 印尼
- 價值鏈與通路分析
第5章 市場區隔
- 最終用戶產業
- 農業、漁業和林業
- 建設業
- 製造業
- 石油和天然氣、採礦和採石
- 批發和零售
- 其他
- 物流功能
- 快遞、快遞和包裹 (CEP)
- 目的地
- 國內的
- 國際的
- 貨物
- 按運輸方式
- 航空
- 海上和內陸水道
- 其他
- 貨物
- 按運輸方式
- 航空
- 管道
- 鐵路
- 路
- 海上和內陸水道
- 倉庫存放
- 透過溫度控制
- 無溫度控制
- 溫度管理
- 其他服務
- 快遞、快遞和包裹 (CEP)
第6章 競爭格局
- 主要策略趨勢
- 市場佔有率分析
- 業務狀況
- 公司簡介.
- Deutsche Bahn AG(including DB Schenker)
- DHL Group
- DSV A/S(De Sammensluttede Vognmaend af Air and Sea)
- Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- FedEx
- J&T Express
- Kuehne+Nagel
- Linfox Pty Ltd.
- LOGWIN
- Ninja Van(including Ninja Express)
- NYK(Nippon Yusen Kaisha)Line
- Pancaran Group
- PT ABM Investama TBK(including CKB Logistics)
- PT Bina Sinar Amity(BSA Logistics Indonesia)
- PT Cardig International
- PT Citrabati Logistik International
- PT Dunia Express Transindo
- PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir(JNE Express)
- PT Kamadjaja Logistics
- PT Lautan Luas TBK
- PT Pandu Siwi Group(Pandu Logistics)
- PT Perusahaan Perdagangan Indonesia(including BGR Indonesia)
- PT Pos Indonesia(Persero)
- PT Repex Wahana(RPX)
- PT Samudera Indonesia Tangguh
- PT Satria Antaran Prima TBK(SAPX Express)
- PT Siba Surya
- PT Soechi Lines Tbk
- Puninar Logistics
- SF Express(KEX-SF)
- SINOTRANS
- United Parcel Service of America, Inc.(UPS)
第7章:執行長的關鍵策略問題
第 8 章 附錄
- 世界概況
- 概述
- 五力分析框架
- 全球價值鏈分析
- 市場動態(市場促進因素、限制因素、機會)
- 技術進步
- 資訊來源和進一步閱讀
- 圖表清單
- 關鍵見解
- 資料包
- 詞彙表
- 外匯
The Indonesia Freight and Logistics Market size is estimated at 131.2 billion USD in 2025, and is expected to reach 178.1 billion USD by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 6.29% during the forecast period (2025-2030).

Government investments in Indonesia's infrastructure are set to drive the market's growth
- In October 2024, FedEx inaugurated a new gateway facility in Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia. This move aims to streamline shipping processes, enhance delivery times, and provide services tailored to the distinct needs of Denpasar's exporters. FedEx highlighted that customers can expect quicker and more dependable shipping services, with exports now being routed directly from Denpasar to Singapore, bypassing the previous route through Jakarta. Additionally, the facility provides comprehensive logistics services for Class 9 dangerous goods, including solid dry ice and items with anesthetic properties.
- For Fiscal Year (FY) 2025, the Highways Directorate General of the Public Works and Housing (PUPR) Ministry allocated a budget ceiling of USD 2.10 billion. Meanwhile, the 2025 Draft State Budget (RAPBN) proposes a total budget ceiling of USD 4.91 billion for the PUPR Ministry. Within this allocation, the Highways Directorate General designates USD 0.66 billion for road infrastructure, USD 0.34 billion for bridge infrastructure, and USD 0.58 billion for the preservation and maintenance of national roads and bridges
Indonesia Freight and Logistics Market Trends
The transportation and storage sector expected to witness boost in GDP contributions, fueled by rising infrastructure projects
- In May 2024, the Japanese government extended a loan of approximately JPY140.7 billion (USD 900 million) for the construction of a high-speed rail line in Jakarta, Indonesia. Spanning 84.1 km, the East-West rail project will be executed in two phases, commencing in 2026 and concluding by 2031. The rail line will incorporate advanced Japanese technology for both trains and signaling systems. These initiatives are poised to enhance the GDP contribution from the transport and storage sector.
- Transportation is at the forefront of the nation's infrastructure expansion efforts. In this domain, ongoing and upcoming initiatives allocate 29% of their overall value to road projects, 22% to rail, and 23% to port infrastructure. These projects are crucial for enhancing connectivity and boosting economic growth. A significant undertaking in Indonesia is the Lhokseumawe to Langsa Toll Road, spanning 135 km. Commencing in early 2024, this ambitious project is slated for completion by late 2027, with the goal of alleviating traffic congestion and shortening travel times. This toll road will be instrumental in optimizing logistics and boosting the transport and storage sector's contribution to GDP.
Indonesia faced fiscal challenges amid surging crude oil prices and subsidy pressures in 2022, however the rates remained unchanged till 2024
- In November 2024, Indonesia reformed its fuel subsidy system. The new president is targeting a reduction in subsidies, which constituted roughly 16% of government spending in 2023. While the subsidy for LPG will stay the same, the government is still determining adjustments for fuel and electricity subsidies. Indonesia's energy subsidies help keep inflation low but expose the nation to global oil price swings. The government plans to replace these subsidies with cash transfers for needy families, aiming to save about USD 12.99 billion through more targeted support.
- As of June 2024, the Indonesian Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (ESDM) was drafting regulations to provide incentives and tax relief for green hydrogen developers to boost the industry's growth. ESDM aimed to produce 9.9 million tons of hydrogen per year by 2060 to meet the needs of industry (3.9 Mtpa), transportation (1.1 Mtpa), electricity (4.6 Mtpa), and household gas networks (0.28 Mtpa). These sectors could also become export commodities.
Indonesia Freight and Logistics Industry Overview
The Indonesia Freight and Logistics Market is fragmented, with the major five players in this market being J&T Express, Ninja Van (including Ninja Express), NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line, PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir (JNE Express) and PT Samudera Indonesia Tangguh (sorted alphabetically).
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY & KEY FINDINGS
2 REPORT OFFERS
3 INTRODUCTION
- 3.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 3.2 Scope of the Study
- 3.3 Research Methodology
4 KEY INDUSTRY TRENDS
- 4.1 Demographics
- 4.2 GDP Distribution By Economic Activity
- 4.3 GDP Growth By Economic Activity
- 4.4 Inflation
- 4.5 Economic Performance And Profile
- 4.5.1 Trends in E-Commerce Industry
- 4.5.2 Trends in Manufacturing Industry
- 4.6 Transport And Storage Sector GDP
- 4.7 Export Trends
- 4.8 Import Trends
- 4.9 Fuel Price
- 4.10 Trucking Operational Costs
- 4.11 Trucking Fleet Size By Type
- 4.12 Logistics Performance
- 4.13 Major Truck Suppliers
- 4.14 Modal Share
- 4.15 Maritime Fleet Load Carrying Capacity
- 4.16 Liner Shipping Connectivity
- 4.17 Port Calls And Performance
- 4.18 Freight Pricing Trends
- 4.19 Freight Tonnage Trends
- 4.20 Infrastructure
- 4.21 Regulatory Framework (Road and Rail)
- 4.21.1 Indonesia
- 4.22 Regulatory Framework (Sea and Air)
- 4.22.1 Indonesia
- 4.23 Value Chain & Distribution Channel Analysis
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION (includes 1. Market value in USD for all segments 2. Market volume for select segments viz. freight transport, CEP (courier, express, and parcel) and warehousing & storage 3. Forecasts up to 2030 and analysis of growth prospects)
- 5.1 End User Industry
- 5.1.1 Agriculture, Fishing, and Forestry
- 5.1.2 Construction
- 5.1.3 Manufacturing
- 5.1.4 Oil and Gas, Mining and Quarrying
- 5.1.5 Wholesale and Retail Trade
- 5.1.6 Others
- 5.2 Logistics Function
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
- 5.2.1.1 By Destination Type
- 5.2.1.1.1 Domestic
- 5.2.1.1.2 International
- 5.2.2 Freight Forwarding
- 5.2.2.1 By Mode Of Transport
- 5.2.2.1.1 Air
- 5.2.2.1.2 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.2.1.3 Others
- 5.2.3 Freight Transport
- 5.2.3.1 By Mode Of Transport
- 5.2.3.1.1 Air
- 5.2.3.1.2 Pipelines
- 5.2.3.1.3 Rail
- 5.2.3.1.4 Road
- 5.2.3.1.5 Sea and Inland Waterways
- 5.2.4 Warehousing and Storage
- 5.2.4.1 By Temperature Control
- 5.2.4.1.1 Non-Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.4.1.2 Temperature Controlled
- 5.2.5 Other Services
- 5.2.1 Courier, Express, and Parcel (CEP)
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Key Strategic Moves
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Landscape
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and Analysis of Recent Developments).
- 6.4.1 Deutsche Bahn AG (including DB Schenker)
- 6.4.2 DHL Group
- 6.4.3 DSV A/S (De Sammensluttede Vognmaend af Air and Sea)
- 6.4.4 Expeditors International of Washington, Inc.
- 6.4.5 FedEx
- 6.4.6 J&T Express
- 6.4.7 Kuehne+Nagel
- 6.4.8 Linfox Pty Ltd.
- 6.4.9 LOGWIN
- 6.4.10 Ninja Van (including Ninja Express)
- 6.4.11 NYK (Nippon Yusen Kaisha) Line
- 6.4.12 Pancaran Group
- 6.4.13 PT ABM Investama TBK (including CKB Logistics)
- 6.4.14 PT Bina Sinar Amity (BSA Logistics Indonesia)
- 6.4.15 PT Cardig International
- 6.4.16 PT Citrabati Logistik International
- 6.4.17 PT Dunia Express Transindo
- 6.4.18 PT Jalur Nugraha Ekakurir (JNE Express)
- 6.4.19 PT Kamadjaja Logistics
- 6.4.20 PT Lautan Luas TBK
- 6.4.21 PT Pandu Siwi Group (Pandu Logistics)
- 6.4.22 PT Perusahaan Perdagangan Indonesia (including BGR Indonesia)
- 6.4.23 PT Pos Indonesia (Persero)
- 6.4.24 PT Repex Wahana (RPX)
- 6.4.25 PT Samudera Indonesia Tangguh
- 6.4.26 PT Satria Antaran Prima TBK (SAPX Express)
- 6.4.27 PT Siba Surya
- 6.4.28 PT Soechi Lines Tbk
- 6.4.29 Puninar Logistics
- 6.4.30 SF Express (KEX-SF)
- 6.4.31 SINOTRANS
- 6.4.32 United Parcel Service of America, Inc. (UPS)
7 KEY STRATEGIC QUESTIONS FOR FREIGHT AND LOGISTICS CEOS
8 APPENDIX
- 8.1 Global Overview
- 8.1.1 Overview
- 8.1.2 Porter's Five Forces Framework
- 8.1.3 Global Value Chain Analysis
- 8.1.4 Market Dynamics (Market Drivers, Restraints & Opportunities)
- 8.1.5 Technological Advancements
- 8.2 Sources & References
- 8.3 List of Tables & Figures
- 8.4 Primary Insights
- 8.5 Data Pack
- 8.6 Glossary of Terms
- 8.7 Currency Exchange Rate




